The Electoral Process and Functions of Governments in Other Parts of The World (Great Britain)30/12/2021 BRITAIN
Britain comprises England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland. The country has evolved a parliamentary system of government over the years.
The Saxon Kings who invaded Britain in the 5th Century AD had absolute powers- ruling without consulting the citizens, and their positions were hereditary. However, in the 12th century AD, they introduced the parliamentary system. They agreed that the kings/queens could only rule according to the laws of the land that should be made by the representatives of the people. This was what came to known as a constitutional monarchy. The electoral process in Britain
The British government is based on the party system. Elections for party leaders are held separately before the general elections. The three main parties are the Conservative Party, Liberal Party and Labor Party.
Unlike USA and other major democratic states outside commonwealth, there is no fixed date for British parliamentary elections. The date of a general election is decided upon by the prime Minister.
The Choice of a date of elections is influenced by the following factors;
There are two types of elections for the House of Commons.
In Britain, there are also euro-elections, first introduced in 1979, in which representatives to the European Union parliament are chosen.81 MPs were elected in 1979. Voter Registration.
It is the local authorities that hold the responsibility of registering voters. Since 1948, a postal vote is possible for citizens who are away from their constituencies during the voting period, either on business or other reasons.
The following categories of people qualify to vote in Britain;
The following are ineligible to vote in Britain.
A candidate who wishes to contest for a parliamentary seat in Britain must fulfil the following conditions;
The following are disqualified from vying for a parliamentary seat in Britain.
Candidates vie for 650 parliamentary seats. The candidates are either nominated by respective parties or stand as independent candidates and need not reside in the constituencies as long as they register as voters in that constituency.
Once nomination of candidates has taken place, campaigns are allowed for two weeks before voting; Each candidate appoints an election agent to manage the finances and protect the interests of the candidate during the campaign. The agent also explains the candidate’s party policies and identifies party supporters within the constituency. He/she familiarizes the candidate’s name to prospective voters.
Election officials work hand in hand with party agents during Election Day.
Each candidate must deposit 500 sterling pounds with the registrar, which is returned in the event that the candidate garners over 5% of the total vote in the constituency. Elections in Britain are by plurality. Candidates who get the highest of votes win the elections. The party that secures most parliamentary seats is declared winner and is asked to form the next government. Emphasis is on number of seats not votes cast. The House of Lords members are drawn from people with high offices. E.g. bishops, distinguished scientists and artists, great sportsmen, retired judges etc. Functions of Government in Britain.
The British government operates around four basic institutions;
The Monarchy.
In Britain, the Monarchy is represented by the queen. The Monarch assents to all legislations. The Monarch appoints the PM and approves the cabinet
Other Functions of the Monarchy.
Importance of the monarchy to the British people.
The Legislature/parliament.
It is made up of the monarchy, House of Lords and House of commons.
The following are ways through which one can gain membership to parliament in Britain;
How parliamentary supremacy is demonstrated in Britain.
The House of Lords.
Membership to The House of Lords is based on nomination by the monarch or by hereditary principle.
Some membership is through holding senior positions within the Church of England Consists of 1200 members 800 of whom are heredity peers, 26 are Bishops and 21 are Lords of Appeal. One can become a member of the House of Lords in the following ways;
Role played by the House of Lords in the British parliamentary system.
House of Commons.
It is the major legislative arm of the government. It comprises 650 elected members representing constituencies. The leader of the House is the P.M. The chief officer is the speaker who is elected at the start of a new parliamentary session.
Functions of the House of Commons.
Factors which influence the activities of Parliament in Britain.
The executive.
The executive is made up of the Prime Minister, the cabinet and the civil service.
The Prime Minister.
Appointed by the monarch, being the leader of the political party that controls an absolute majority, He/she is the Chief executive of the country.
He performs the following functions;
The Cabinet.
The cabinet is made of the ministers appointed by the P.M with the approval of the monarch and nominated from the party with the majority of seats.
The cabinet performs the following functions;
The following conventions provide guidance on the operation of the cabinet;
The Civil Service
The British law stipulates the civil servants are servants of the crown. A civil servant is expected to nonpartisan and to serve the government of the day without favour. Civil service staff does not change with change of government. Recruitment In the civil service is based on merit.
Functions of the civil Service in Britain.
Principles that characterize the British civil service.
The Judiciary.
The judiciary in Britain is based on the supremacy of the law. To safeguard the rule of law, the British Judiciary has an independent court system.
How judicial independence is ensured in Britain.
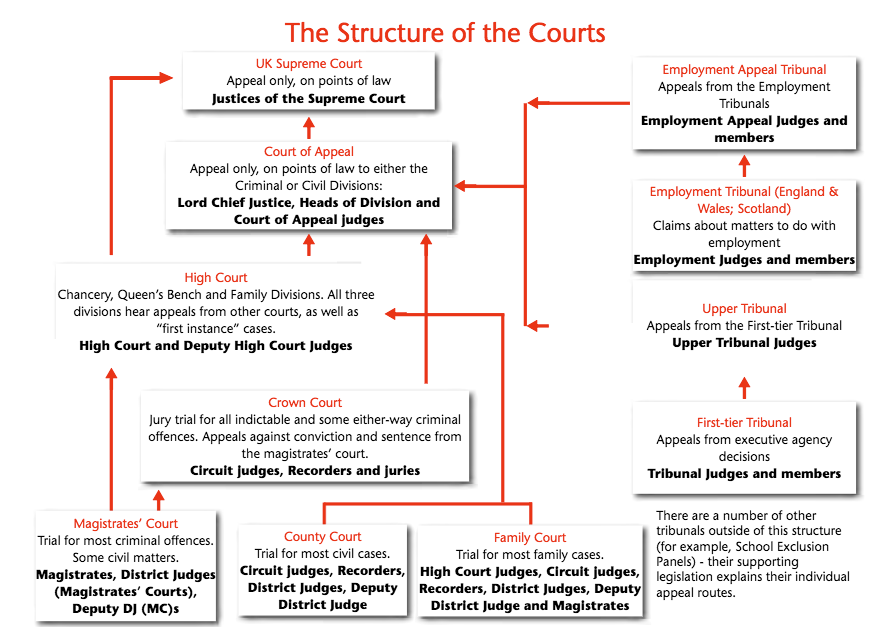
The structure of the British Court System.
England and Wales share a unified court system, based on common law principles, which originated in medieval England. Scotland and Northern Ireland each have their own judicial systems.
The court system in Northern Ireland closely resembles that of England and Wales, while the Scottish court system is a hybrid model that combines elements of both common and law and civil law systems. This research guide focuses on the unified court system of England and Wales. For information about the Scottish judicial system, consult the Scottish Courts and Tribunals website. For information about the judicial system in Northern Ireland, consult the NIDirect website.
In England and Wales, most civil cases are heard in the County Court. Many specialist tribunals have been created to resolve particular types of civil disputes, such as those involving taxation and employment, as well as immigration and asylum cases. All criminal cases originate in the Magistrates' Court, but more serious offenses are referred to the Crown Court.
The High Court functions as both a court of first instance for high value civil claims and as an appellate court for civil and criminal cases. It consists of three divisions: the Queen's Bench, the Chancery Division, and the Family Division. The Court of Appeal functions solely as an appellate chamber. The Civil Division hears appeals form the High Court and the County Court, and the Criminal Division hears appeals from the Crown Court. Components of the British constitution.
0 Comments
|
Archives
April 2024
Categories
All
|


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed