A Journey into the Origins and Evolution of Early ManEarly man refers to the earliest known human beings who lived on Earth thousands of years ago. They were the ancestors of modern humans and played a crucial role in shaping human history. Here are some key points about early man:
0 Comments
Work to Do
Suggested Activities
Cultural and Economic Practices of Early Man
Cultural practices depict the totality of man's way of life. Economic practices are the methods that man uses to exploit the environment for his well-being.
The evolution of man and his way of life can well be understood through the study of the Stone Age period. Through this study, we can understand events that have shaped and influenced man's life, these are:
The Old Stone Age (Lower-Palaeolithic)
This period, also referred to as Early Stone Age, lasted approximately from 3,000,000 - 200,000 years ago, and saw important advances in the pre-historic culture of early man. These advances included:
Weapons and Tools
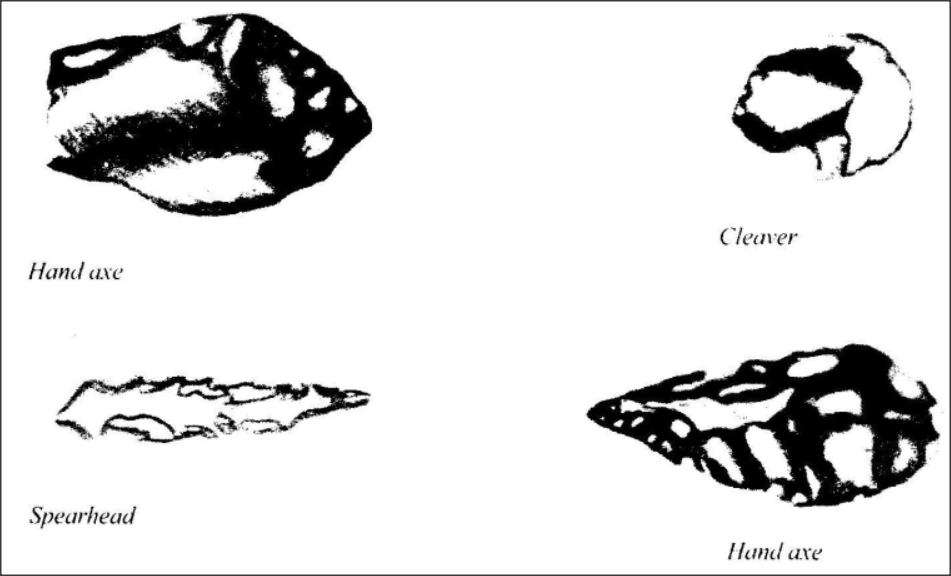
The stone tools made by early man in the first phase of the Old Stone Age have been referred to as Oldowan or pebble tools. Some of these tools are shown in Figure below.
They were named Oldowan after Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania where they were first discovered. They were also called pebble tools because they were made from pebbles i.e., fairly large round stones.
Oldowan tools have been found widespread in South, Central and North Africa, suggesting that they were made and used only in Africa. The makers of Oldowan tools are believed to have been Homo habilis.
In the second phase of the Old Stone Age period, the stone tools man made have been called acheulian. These were named after Saint Acheul Valley in North France where they were first discovered. They first appeared in East Africa about 1.5 million years ago. They seem to have existed in some areas until 200.000 - 50.000 years ago.
At Koobi Fora near Lake Turkana in Kenya and at Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania, stone tools dating back to about 1.5 million years old have been discovered.
In Ethiopia, interesting tools and weapons which are more than one million years old have also been found at Hadar and Gona. and are among the earliest stone tools found in the world. These include scrapers and choppers or hand axe heads.
They were used for digging up roots. skinning animals. and cutting and scrapping animal skins. Acheulian tools were made by a more improved tool-making technique whereby a core stone was flaked on both sides to produce a sharp pointed end and longer cutting edges on both sides. Acheulian tools Hand axe Clothing
The Old Stone Age period must have been much colder than it is now. Therefore, as a result, man must have had a much more hairy body than he has now. He also walked naked because he had not learned how to make clothes.
Shelter
The Old Stone Age people had not learnt to build houses. But research carried out in the Olduvai Gorge by Louis and Mary Leakey shows that on site DK 1, a semi-circular group of natural stones suggests a hiding place. The Old Stone Age people.slept in forests and on trees to avoid attacks by wild animals. They also used stone caves and rocks as shelter.
Food
The Old Stone Age people ate raw meat for they had not discovered the art of making fire. Typha roots at one of Bed I sites at Olduvai Gorge, the presence of fig leaves at East Turkana show that early man brought back to his home base the plant foods he ate. In addition to this, he ate birds, eggs and insects which he gathered and collected.
Hunting
In addition to gathering and collecting, the Old Stone Age man also hunted wild animals. ~ Hunting was a group activity. Man hunted by chasing the wild animals. He also trapped and caught wild animals around the watering points.
After successfully catching his prey, man then skinned the carcass and ate the meat raw. There was a bit of specialisation during this period whereby men hunted while women spent most of the day collecting wild fruits and berries. This life required strong people.
Communication
Man still used a crude form of communication, based on gestures, growling and whistling.
The Middle Stone Age (Middle Palaeolithic)
This period lasted between 200,00-50,000 years ago. Man changed his life by improving his weapons, building better shelter and inventing fire. Life became easier than during the Old Stone Age period.
Tools and Weapons
The Middle Stone Age period is associated with Homo erectus. Throughout Africa and the world where this hominid is thought to have lived, there was a general attempt to try and improve the tools using the Levallois method or technique.
This entailed the use of cores of smaller stones to hit bigger ones in a special way in order to remove the relatively thin sharp pieces called flakes and blade forms. Man then trimmed the flakes and ades into a variety of daggers, scrappers, pear points, choppers, etc.
In many areas of East and CentralAfrica, there is evidence of improved weapons and the attempts to make them smaller, thinner, lighter, sharper and therefore more convenient.
In East Africa in particular, there was an attempt to make tools from more than one material. Wood and stone for instance could be used together.
The Invention and use of Fire
One of the most important developments in the Middle Stone Age period was that man had learned to make and use fire. Clear traces of fire have been discovered in places where man lived. In South Africa, there are pre-historic sites where hearths of ash and charcoal have been found. Early man must have lighted this fire by rubbing two sticks against one another or striking one stone on another as shown in figure below.
The invention of fire changed man's life in the following ways:
Shelter (Housing)
During the Middle Stone Age period, man had started to have particular places where he took his game after hunting and where his family could retire and rest after the day's activities. This was an artificial shelter. An example of such home has been found at Orangia in Southern Africa.
The open site has at least six semi-circular stone structures two to three metres across and all open to the west. The ground inside each shelter had been scooped out to form a hollow perhaps for sleeping. A similar dwelling place was found at Olorgesailie pre-historic site near Magadi in Kenya.
Later on, man started to live in caves and rock shelters. At night they kept fires burning at the entrance to scare away wild animals. Examples of such caves are Matupi cave in the Democratic Republic of Congo, Gamble's cave near Lake Nakuru in Kenya and Dar es Soltan in Southern Africa.
Food
During the Middle Stone Age period, man continued hunting wild animals for meat which was his main food. His methods of hunting had now improved because he had better, lighter, sharper and highly specialised weapons like knives, spears and choppers.
It is likely that in the equatorial areas, very large animals like elephants and hippopotamuses were preferred for meat while in the grasslands the grazing antelopes were the main sources of meat. With the invention of fire. man could now cook the meat.
This did not only soften it but also added flavour. Cooking also neutralised the poison in some raw vegetables that man ate. In addition to meat, man ate fruits, birds eggs, insects and fish.
Clothing
By this time man had learnt to wear animal skins. He scraped the skins clean to make cloaks out of them. He also made shells and necklaces and painted his body with red ochre and oil.
Communication
Man improved on gestures and growling and began to use clicks and grunts.
The New Stone Age (Neolithic)
This period, also referred to as Late Stone Age, is associated with Homo sapiens and is thought to have lasted roughly between 5,000 to 2,500 years ago. In this period there was a big change in many aspects of man's way of life.
Socially, politically and economically, man made great advances. He changed and improved the way he lived with his fellow men. Technologically he improved and invented new tools.
Tools and Weapons
In the Old Stone Age period, man merely chipped pieces of stone into the required shape. But in the Late Stone Age further improvement of Stone Age technology was noted. This period is marked by a type of tools called microliths. Microliths were very small tools, sometimes less than a centimetre in length. It was found that by pressing one stone against another, a tool maker could flake off small pieces of microliths.
Microliths were not used as tools alone. They were fitted or glued into wood and bone handles and used together as tools. In the Late Stone Age, emphasis was on "composite tools". These tools were made by fixing several microliths together in wooden or bone shafts. Examples of such tools include fishing harpoons, saw blades, arrow heads, sickles, bone needles for sewing skin cloths, bows and arrows.
Examples of these microlith tools made by New Stone Age Neolithic) man are found in places such as the Qadan site in the Nile Valley.
Settlements
The tremendous technological advances enabled man to settle in villages, perhaps of about 1,000 members. As man began leading a settled life, several cultural practices developed. Man began to appreciate the need for bodily decorations. Man prepared red ochre in stone bowls and used it as body make-up.
In addition, he decorated himself with beads made of seeds, bone and ostrich egg shells. The use of rock shelters became more widespread during this time. Man decorated them with paintings of animals, hunting scenes and other designs.
Art and Crafts
The New Stone Age Neolithic man also made efforts to invent and develop simple arts and crafts. Man learned how to make rough baskets, how to spin and weave flax and other natural fibre, and how to make pots by shaping clay and baking it hard using fire.
Rock Art
He also painted pictures of the animals he hunted like elephants and reindeer on walls of caves. The best examples of this in Africa are found in Kondoa and Singida in North Central Tanzania and in Southern Africa at Apollo II cave.
It is likely that these pre-historic men thought that painting pictures of the animals they hunted would give their hunts greater success. By drawing pictures of wild animals, man believed that he could magically have a controlling power over his prey. Occasionally, he drew arrows piercing the animals he hoped to kill. Cave paintings also showed a keen observation of animal life.
Communication
The New Stone Age man developed a rudimentary form of spoken language with sign language being predominant.
Religion and Government
Another important cultural development was the beginning of religion and government. The first aspect of religion was the performance of rites and ceremonies by man probably with a belief that these rites and ceremonies could influence natural forces such as rain, drought and even death which were the main threats to man's life.
Examples of the development of religious practices are found at Njoro River cave and Hyrax Hill in Kenya. Here cremated remains of human beings buried with some of their tools and possessions have been found. This shows that the Late Stone Age man was religious and believed in life after death.
The New Stone Age paved way for the Iron Age. In some regions, some form of the two co-existed as iron-ore was not universally available. Gradually iron- working revolutionised agriculture and industry.
In conclusion, the cultural development of the Stone Age man from the period of Australopithecus was rough and long. He had started with crude and rough stone tools and improved and perfected them into lighter, and sharper tools and then invented fire.
During the New Stone Age period and after, man had developed smaller and sharper microlith tools and started moving towards a settled agricultural life; planting crops and domesticating animals. This organised systems led to the emergency of government and laws.
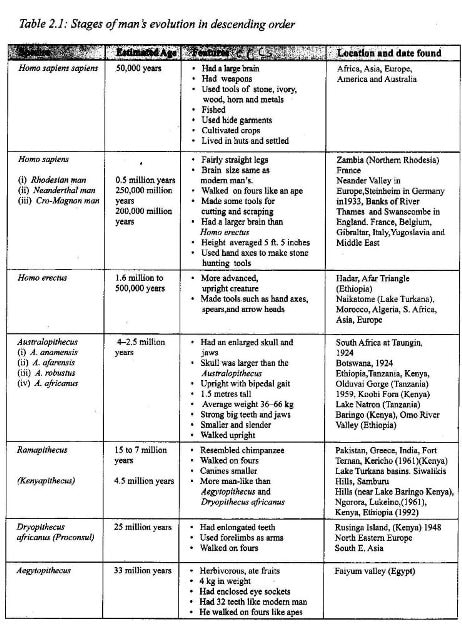
Stages through which Man Evolved
Archaeological studies show that man evolved through various stages. At each stage man developed certain physical and cultural features. The following are the stages of the evolution of man.
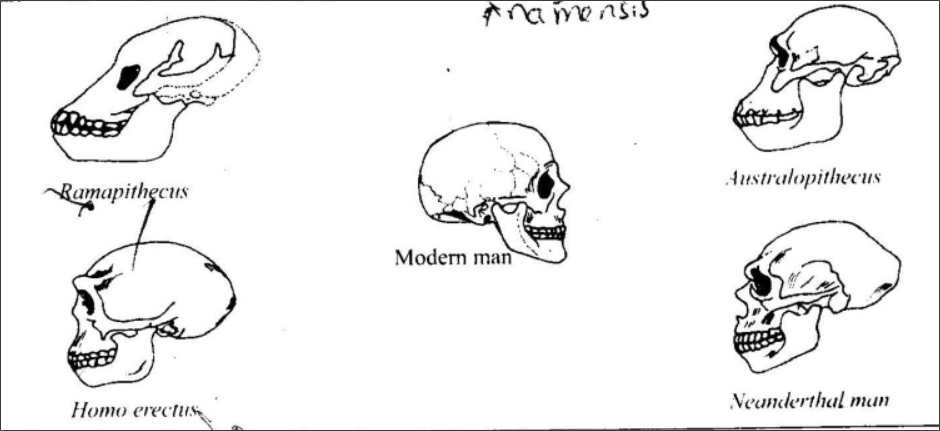
Aegyptopithecus
The probable earliest ancestor of man was an ape-like creature whose skull was discovered in the Faiyum Valley in Egypt. This creature was herbivorous. It lived about 33 million years ago.
Features:
Dryopithecus Africanus (Proconsul)
The skull was discovered on Rusinga Island in Lake Victoria in 1948. It resembled a chimpanzee. It lived about 25 million years ago.
Features
Kenyapithecus (Ramapithecus)
Also known as the grassland ape, Kenyapithecus lived between 15 million and 7 million years ago. Its remains were first discovered at Fort Ternan, near Kericho in 1961. It was more man-like than other earlier ape. Other discoveries have been made at Samburu Hills, Lake Baringo and Lake Turkana basins.
Features
Australopithecines
Between four and two and a half million years ago, two varieties of small ape-like men came into existence in Southern and Eastern Africa.
These creatures are also referred to as Southern ape-men because their remains were first discovered in Southern Africa at Taung near Kimberley in 1924.
Similar fossils of a hominid belonging to the Australopithecus genius have been found scattered throughout Eastern Africa at such pre-historic sites as Olduvai Gorge and Lake Natron in Tanzania.
Australopithecus used the stone tools he made for defence and to get food. They used sticks and pebble tools to kill small animals for food. They lived in small hunting camps near water bodies and led a nomadic life often migrating following the game they hunted. Hunting was the chief process which set man on the evolutionary path that was to lead to his dominance over all other animals.
Species of Australopithecines
Features of the Australopithecines
Homo Habilis
At Olduvai Gorge where Mrs Mary Leakey found the Zinjanthropus skull, another of her sons, Jonathan Leakey, found the skull fragments of a very young hominid. The pieces were stuck together to form the back part of the head. Later a lower jaw and the bones of a hand were found.
Dr Leakey, convinced that this was a true ancestor of man, called the creature Homo habilis, meaning handy man', 'man with ability' or simply practical man'. Homo habilis thus became the first species of the genus Homo or man. Homo habilis had a bigger brain capacity (775 cc) compared to Australopithecus and was the first true man to make and use tools.
It is believed that both Homo habilis and Australopithecus lived in Africa about one and three quarter million years ago. But Australopithecus then disappeared giving way to new people who had bigger brains. Homo habilis represents a stage of human evolution at which the brain and the hands were beginning to work in closer conjunction.
Features of Homo Habilis
Homo Erectus
The other hominid which lived in Africa about one million years ago is called Homo erectus, also referred to as the "upright man". As the name implies. Homo erectus. resembled the modern man especially the upright walking posture. Some fossils have been found of Homo erectus in Hadar in the Afar Triangle of Ethiopia, about 500 km north-east of Addis Ababa.
Homo erectus is thought to have been more intelligent than Australopithecus and Homo habilis. He had a much higher brain capacity of between 750 and 1000 cc. He could spend a long time chipping away at pieces of stone and bone to make the weapons and tools he needed.
Evidence shows that Homo erectus lived in Africa, Europe and Asia and learnt to make many different and more refined tools like hand axes and later crude spears and arrow heads all from stone. It is believed that Homo erectus' knew how to use fire and had a primitive form of speech compared to any of his predecessors.
Features of Homo Erectus
Homo Sapiens
Homo sapiens was divided into three species.
Rhodesian Man
The Rhodesian man was given this name because his skull was found in Zambia, then called Northern Rhodesia.
Rhodesian man was closer to the modern man than Homo erectus was.
Neanderthal Man
Even closer to the modern man was a hominid called "Neanderthal Man", whose fossils were first found in Neander Valley in Europe. Traces of Neanderthal have been found scattered throughout Europe and the Near East.
The oldest remains of the Neanderthal is dated about 250,000 years old. They consist of one nearly complete skull found in 1933 at Steinheim, Germany and three skull bones found in ancient gravels on the bank of River Thames and Swanscombe in England. More than 100 bones of this hominid have been excavated in South West France, Belgium, Gibraltar, Italy, Germany, former Yugoslavia, the middle East and North Africa.
They skillfully chipped stone tools and with them hunted a wide range of game. The arrangements of their bones found in excavations indicate ceremonial burials which show that they had developed religious practices.
Cro-magnon
Cro-magnon lived in Western Europe about 20,000 years ago.
Features of Homo Sapiens
Homo Sapiens Sapiens
Homo sapiens sapiens brings to the end the long struggle for early man to better himself and become civilised. This is when he made weapons and tools of flint stone, ivory, wood and horn. These tools were more refined than the earlier ones.
He caught fish with bone harpoons, cleaned animal hides with scrapers and made garments out of them with bone needles. Since he was intelligent and was thinking, he made fire and pots. The hunters captured and tamed animals. He began to grow crops, build huts and started leading a settled life.
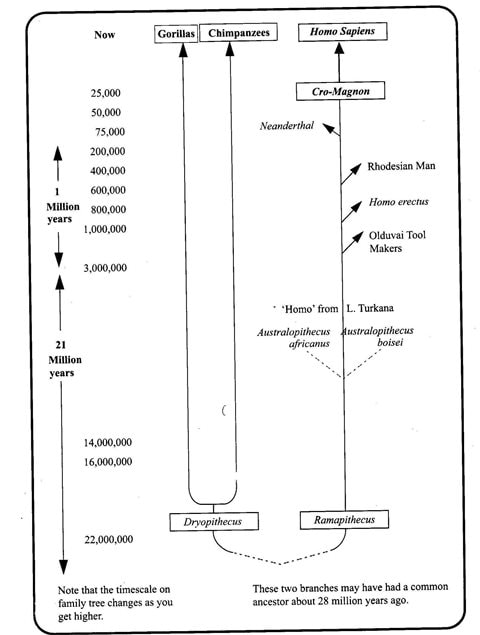
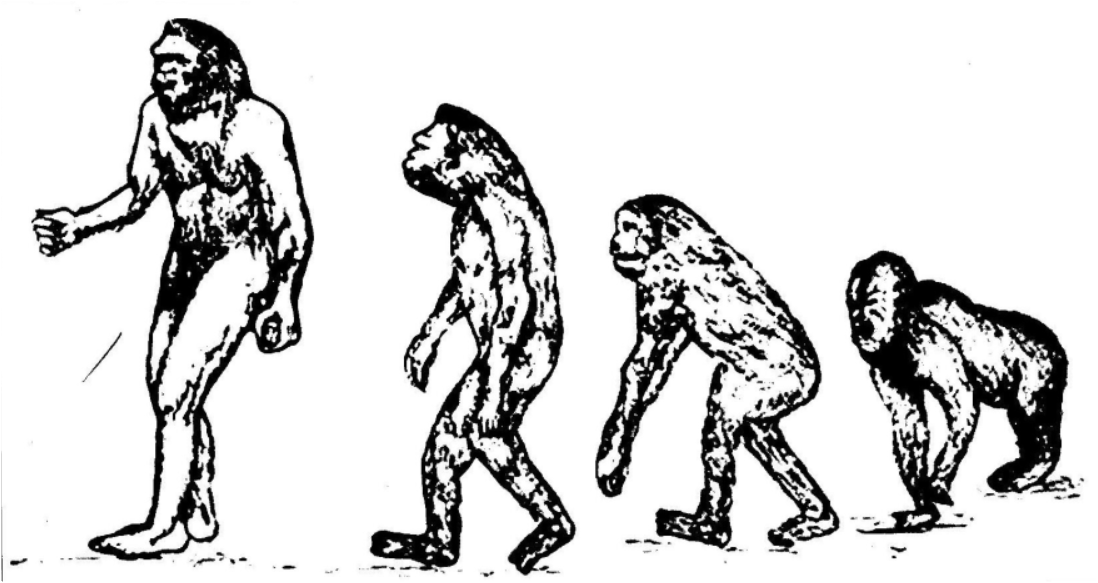
Figure below depicts the evolution stages man is thought to have gone through.
Features of Homo Sapiens Sapiens
Why Africa is considered the cradle of man?Africa is considered the cradle of man because of the following factors:
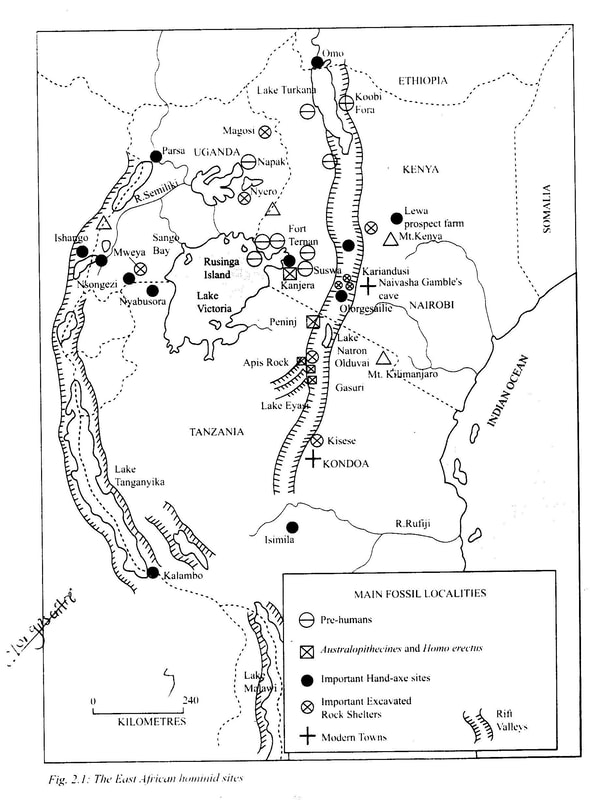
Archaeological Sites in East Africa
Among the most important pre-historic sites in Kenya are:
In Tanzania there are:
Some of the important sites outside East Africa are Omo Valley and Hadar in Ethiopia, and the South Africa limestone cave sites of Skerkfontein, Kromdraai, Swartkrans and Maka Pansgat. Origin of Man
Among all living creatures, man is unique because of his high level of thinking. This is one reason why the origin of man has been of great interest to scholars for ages. There are three theories which explain the origin of man. These are:
Oral Traditions
Throughout the ages, individuals, communities and peoples have tried to explain how they came into existence. This explanation is given through the oral traditions, for example, in myths and legends. The Agikuyu believe that Ngai (God) appeared and created their ancestors, Gikuyu and Mumbi at Mukurwe wa Gathanga. The Maasai believe that their ancestors were dropped by Enkai (God) from the sky.
The Creation Theory
This is explained in various Holy Books, e.g., the Bible and the Koran. In the book of Genesis, it is written that God created the universe and all the living creatures, including man, in six days. God created man and woman in his own image. He blessed them and told them to reproduce and fill the earth. He gave them authority to control the earth in all ways.
The Evolution Theory
The evolution theory was put forward by Charles Darwin in 1859. In his book, The Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, he argues that plants and animals evolved from simple life forms that transformed or changed slowly over millions of years through;
Mutation
Is an abrupt change in the form of a living thing as dictated by the climate or the genetic components of the living thing involved.
Natural selection
Is an instinct by which the stronger species out-compete the weaker ones for resources.
Environmental adaptation
Follows after the first two where the surviving species isolate themselves from others as they adapt to the new environment. According to the evolution theory, human beings and primates (monkeys, gorillas and chimpanzees) had a common ancestor.
Man then developed over millions of years through evolution. During this evolutionary period, certain creatures (hominids) who were more man-like than ape-like developed. The term hominids refers to man and his ape- like ancestors.
The increasing discoveries of fossil remains of the pre-historic man by archaeologists, especially his skull, bones and the tools he made and used. have made the theory of evolution more acceptable over the years.
Evolution of Man
Evolution can be defined as a process of slow or gradual change. Although our knowledge about the early stages of man's evolutionary process is limited, it is certain that through evolution, man experienced both physical and cultural changes over millions of years, transforming him from a primitive form to the state he is in today.
Several millions of years ago, man and apes shared a common ancestry as primates. Man's particular family group is called Hominidae while that of the apes is Pongidae. Through evolution and environmental adaptation, man soon separated from his ape-like ancestors and took his own line of development. The first stage in this series was marked by the appearance of creatures called hominids which were more man-like than ape-like and therefore the ancestors of the human family.
Most information about the early man is obtained from archaeologists. Archaeological studies have proved that Africa was the cradle of mankind; man first originated and lived in Africa before moving into Europe and Asia. Existing evidence shows that the earliest apes and hundreds of other different kinds of animals first lived probably around what is now lake Victoria and the Rift Valley before moving into Europe and Asia, less than two million years ago.
At this time, there were thick forests near the equator, especially in Central and West Africa. Around the Great Lakes of East Africa there was savanna or grassland with scattered trees and bushes. It is in this environment that man may have had his first home.
Studies carried out in Central and East Africa show that the Great Rift Valley was formed and was still taking shape long after hominids had started roaming about in East Africa. At that time, earthquakes tilted the ground and volcanoes brought up a great deal of ash which covered places where the hominids had left their weapons and tools. Some hominids' remains even their own bones and those of other animals were covered too. The location of those remains form major archaeological sites in East Africa.
|
Archives
April 2024
Categories
All
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed