|
Explain four methods of classifying computers.
0 Comments
Computers have evolved through a number of generations. List any three characteristics of the First generation of computers.
State three characteristics of mainframe computers.
Characteristics of mainframe
State three features of fifth generation computers.
Features of fifth generation computers
State the hardware technological differences between the second generation and the third generation computers. (2 marks)
State two advantages of using portable computers.
Advantages of portable computers
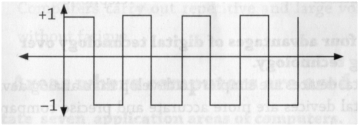
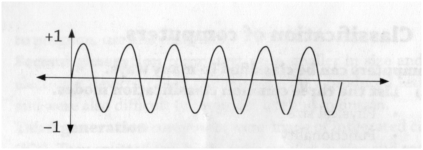
Differentiate between analogue data and digital data as used in computers. (2 marks)
State two reasons for the increased use of laptop computers in government offices. (2 marks)
Reasons for the preference for laptops.
Describe each of the following types of computers: hybrid; and embedded.
(a) (i) What is a computer keyboard? (1mk)
Input device with keys for keying in data in the form of characters
List four types of keys found on a computer keyboard. Give an example of each. (4mks)List three differences between a microcomputer and a super computer (3mks)Microcomputers
Supercomputers
Define authenticity as used in software selection
Explain why smart phones and personal digital assistants (PDAs) may be regarded as personal computers.
PDAs and smart phones are powered by microprocessors, which coordinate all of the functions according to programmed instructions just like all other personal computers.
State four reasons why a mobile phone is regarded as a computer.(a) List four devices which though traditionally analog, have evolved to digital systems.
(b) State four advantages of digital technology over analog technology.
Distinguish between general and special purpose computers
General purpose computers are designed to be able to perform variety of tasks when loaded with appropriate programs, while special purpose computers are designed to accomplish a single task.
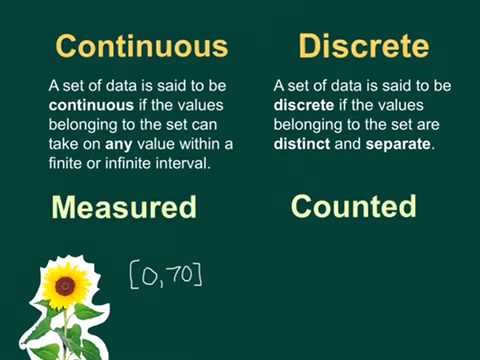
Differentiate between discrete and analog data
Computers can be classified in many ways.
|
|
#
|
ANALOGUE
|
DIGITAL
|
|
1
|
analogue data is continuous in nature (continuous data is quantitative data that can be measured. • it has an infinite number of possible values within. a selected range e.g. temperature range.)
|
digital data is discrete in nature (discrete data is quantitative data that can be counted, Discrete data is based on counts. Only a finite number of values is possible, and the values cannot be subdivided meaningfully.)
|
|
2
|
less accurate
|
more accurate
|
|
3
|
more affected by other factors
|
less affected by other factors
|
|
4
|
requires complex programs to run
|
requires simple programs to run
|
|
Famous examples of analog computers are the Planimeter, the nomogram, operational amplifiers, mechanical integrators, slide rules, tide predictors, electric integrators that solve partial differential equations, electronic machines that solve ordinary differential equations, machines to solve algebraic equations, the Norden bomb sight, and neural networks.
|
All modern computers, laptops, and calculators are all digital computers.
|
Categories
All
1998
1998 KCSE
1999
2020
Applications Areas Of ICT
Areas Where Computers Are Used
Career Opportunities In ICT
Classification Of Computers
COMPUTER SYSTEMS
Data
DATABASE
DATA PROCESSING
DATA SECURITY AND CONTROLS
Definition Of A Computer
Development Of Computers
DTP
ELEMENTARY PROGRAMMING PRINCIPLES
FIELD
FILE
FORM 1
FORM 2
FORM 3
FORM 4
IMPACT OF I.C.T ON SOCIETY
Information
INPUT DEVICES
INTRODUCTION TO NETWORKING AND DATA COMMUNICATION
Intro. To Computers
KCSE 2018
KCSE QUESTIONS 1998
KCSE QUESTIONS 2007
MID-TERM EXAMS
MIND BLOWING Q & A
MOCKS
Operating System
OPERATING SYSTEMS
OUTPUT DEVICES
Parts Of A Computer
PROCESSING DEVICES
PROCESSORS
PROGRAM DESIGN
RECORD
REGISTERS
REVISION KITS
SPREADSHEET
SPREADSHEETS
STORAGE DEVICES
SYSTEM DESIGN
TERM 1
THE COMPUTER LABORATORY
The CPU
WORD PROCESSORS
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MICRO-COMPUTERS AND MAINFRAME COMPUTERS
|
#
|
MAINFRAME COMPUTER
|
MICRO-COMPUTERS
|
|
1
|
large in size
|
small in size
|
|
2
|
not portable
|
portable
|
|
3
|
more powerful processing speeds
|
less powerful processing speeds
|
|
4
|
ability to multi-task, multi-process numerous tasks
|
can process limited tasks
|
|
5
|
uses a number of processors
|
uses only one processor
|
Categories
Join our Whatsapp Notifications and Newsletterstouch here COURTESY OF ATIKA SCHOOL
All
1998
1998 KCSE
1999
APPLICATIONS AREAS OF ICT
Career Opportunities In ICT
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS
COMPUTER SYSTEMS
DATABASE
DATA PROCESSING
DATA SECURITY AND CONTROLS
ELEMENTARY PROGRAMMING PRINCIPLES
FIELD
FILE
FORM 1
FORM 2
FORM 3
FORM 4
IMPACT OF I.C.T ON SOCIETY
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS
INTRODUCTION TO NETWORKING AND DATA COMMUNICATION
KCSE 2018
KCSE QUESTIONS 1998
KCSE QUESTIONS 2007
MIND BLOWING Q & A
MOCKS
Operating System
OPERATING SYSTEMS
OUTPUT DEVICES
PROGRAM DESIGN
RECORD
REGISTERS
REVISION KITS
SPREADSHEET
SPREADSHEETS
STORAGE DEVICES
SYSTEM DESIGN
THE COMPUTER LABORATORY
WORD PROCESSORS
Categories
All
1998
1999
2000
2001
2002
2003
2004
2005
2006
2007
2008
2009
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
2019
2020
2022
Analogue And Digital Systems
Applications Areas Of ICT
Areas Where Computers Are Used
Auxiliary Storage Devices
Basic Computer Set Up And Cabling
Binary Conversion
Booting
CABLES AND PORTS
Career Opportunities In ICT
Classification Of Computers
Coaxial Cables
Coding Schemes
COMPACT DISK
COMPLETE PAPERS
Computer Crimes
Computer Files
Computer Memory
Computer Software
Computer Systems
COMPUTER VIRUS
Dashboard
Database
Data Collection
Data Communication
Data Integrity
Data Processing
Data Representation In A Computer
Data Security And Controls
Definition And Development Of Algorithm
Desktop Publisher
Development-of-computers
DTP
DVD
Electronic Data Processing Modes
Elementary Programming Principles
Errors-in-data-processing
Evolution-of-computer-systems
Fibre Optic Cables
File Management Using An Operating System
File-organization-methods
Flowchart
Form 1 Level
Form 2 Level
Form 3 Level
Form 4 Level
Formatting Features
Hands On Skills
HARDCOPY OUTPUT DEVICES
Hard Disk
Hardware
Impact Of Ict On Society
IMPACT PRINTERS
Information
Input Devices
Internet And Email
Introduction To Computers
Introduction To Networking And Data Communication
ISP
Levels-of-programming-languages
Midterm-exams
Mind-blowing-q-a
Mocks
Network Topologies
Network-topology
NON-IMPACT PRINTERS
Ones And Twos Compliments
Operating Systems
Output Devices
Paper 1
Parts Of A Computer
Practical Hands On Skills
Printers
Processing-devices
Processors
Program-construction
Program-control-structures
Program-design
Program Development
Program-documentation
Protocols
Registers
Review Questions
Revision Kits
Secondary Storage Media
Section A
Section B
Security Threats And Control Measures
Software
Spreadsheets
Stages Of System Development
Storage Devices
Symbolic-representation
System-design
System Development
System-documentation
Term-1
TERM 2
The Computer Laboratory
The CPU
The Keyboard
Types Of Computer Files
Types-of-networks
User Interface
Uses-of-computers
Word Processors
Worksheet-formatting
Archives
December 2024
January 2024
December 2023
October 2023
September 2023
July 2023
June 2023
February 2023
November 2022
September 2022
April 2022
January 2022
December 2021
November 2021
July 2021
March 2021
February 2021
January 2021
December 2020
October 2020
April 2020
February 2020
October 2019
August 2019
July 2019
April 2019
March 2019
November 2018
August 2018
July 2018
December 2017
November 2017
October 2017
July 2017
August 2016
June 2016
January 2016
December 2015
November 2015
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |


















 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

