K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN019
(a) Figure 14 shows an E shaped steel block being magnetized by a current through two coils in series.
On the figure, indicate
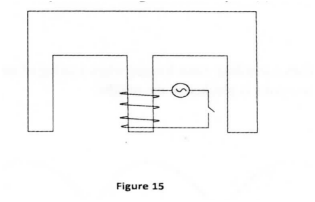
(i) the north and south poles of the resulting magnet (ii) the complete magnetic field pattern between the poles. (b) Figure 15 shows the permanent magnet made in part (a) above.
A coil wound loosely on the middle limb is connected in series with a low voltage a.c. and a switch. State and explain the observation made on the coil when the switch is closed.
(c) In a simple cell, the zinc plate gets negatively charged and the copper plate gets positively charged. (i) Name the electrolyte in the cell. (ii) Explain how: (I) Zinc gets negatively charged. (II) Copper gets positively charged (iii) State what constitutes the current when a wire is used to connect the zinc plate and the copper plate externally.
1 Comment
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN018
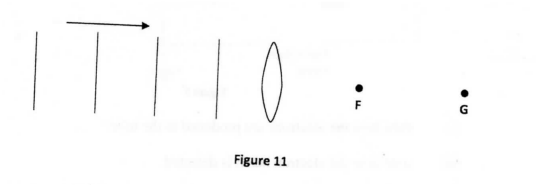
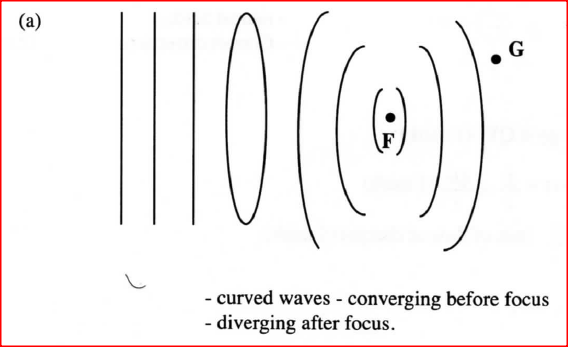
(a) Figure 11 shows plane light waves in air incident on a convex lens whose principal focus is F, the waves move past point G.
Complete the diagram to show the pattern of the emergent waves between the lens and point G.
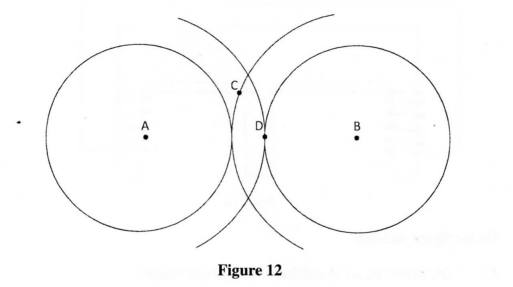
(b)Figure 12 shows crests of circular water waves spreading from two points A and B due to a vibrator. C and D are points on the surface of the water.
Given that the amplitude of each wave is 5 cm, state with a reason the amplitudes of the waves at point:
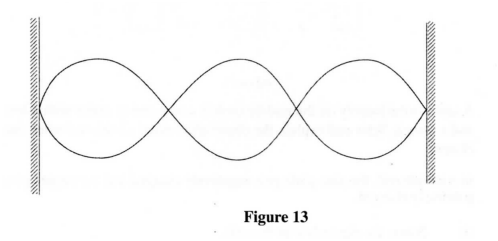
(i) C; (ii) D. (c) Figure 13 shows a standing wave formed when a string of length 1 .5 m stretched between two supports is plucked in the middle.
(î) Explain how the standing wave is formed.
(ii) Determine the wavelength of the standing wave. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN017
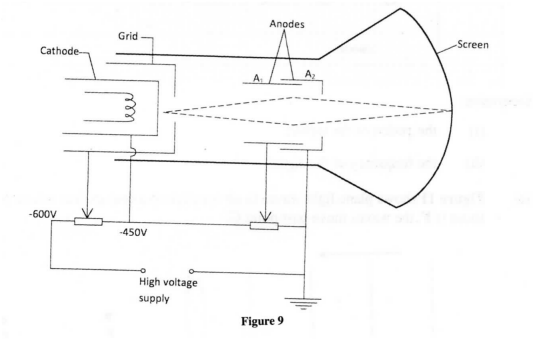
(a) Figure 9 shows a cathode ray tube in which a beam of electrons is cast on the screen.
(i) state how the electrons are produced in the tube.
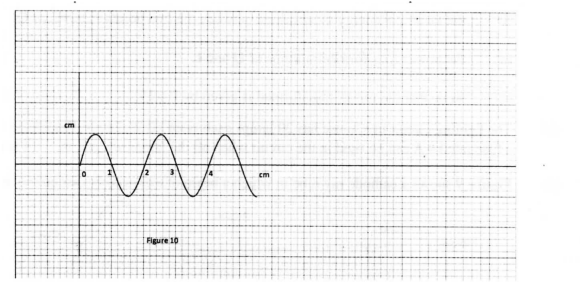
(ii) state how the electron beam is detected. (iii) State the reason for having a variable potential difference (p.d.) at the: (I) grid; (II) anodes. (b) Figure 10 shows the waveform of a signal applied at the y-plates of an oscilloscope whose time-base is switched to the scale of 2 milliseconds per centimeter.
Determine:
(i) the period of the signal; (ii) the frequency of the signal. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN16
(a) Two points A and B have a potential difference of V volts. Q coulombs of charge flow between A and B for t seconds. Determine:
(i) the electrical energy transformed between the two points in terms of Q. (ii) the power transformed in terms of Q and t. (iii) show that the power transformed is given by P = IV.
(b) The lighting circuit in a house has 20 lamps each rated 60 W, 240 V. Determine whether a fuse rated 4 A can be used in the circuit when all the lamps are put on.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN15
(a) Explain how a positively charged electroscope gets discharged when the cap is touched with a finger.
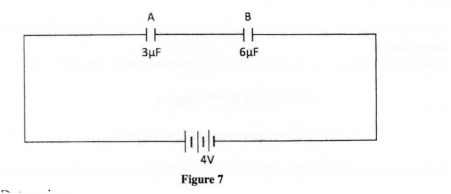
(b) Figure 7 shows capacitors A and B connected in series with a battery of e .m .f 4 V.
Determine:
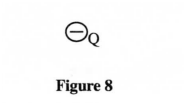
(ï) the effective capacitance of the circuit. (ii) the quantity of charge in capacitor A. (iii) the quantity of charge in capacitor B. (c) Figure 8 shows an isolated negative point charge Q.
On the figure. sketch the electric field pattern around the charge.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN14
Figure 6 shows two convex lenses A and B used to produce a magnified virtual image of an object.
(a) Determine the focal length of lens A. (Take unit to represent 10cm).
(b) State the function of: (i) lens A (ii) lens B (c) State how the functions in (b) are achieved by: (i) lens A (ii) lens B (d) Determine the magnification produced by: (i) lens A: (ii) the whole system. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN13
When a germanium crystal is doped with arsenic, it becomes an N-type semiconductor. Explain how this change occurs.
(Number of electrons in the outermost shell for germanium = 4. Arsenic = 5)
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN12
A photon of ultraviolet light having energy E falls on a photoemissive surface whose work function is T. Write an expression for the maximum kinetic energy of the resulting photoelectron in terms of E and T.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN11
Explain the fact that radiant heat from the sun penetrates a glass sheet while radiant heat from burning wood is cut off by the glass sheet.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN10
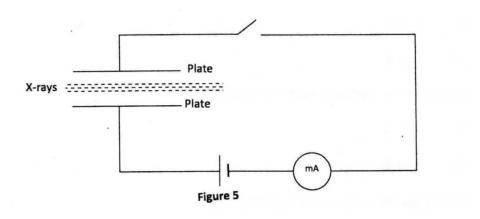
Figure 5 shows a narrow beam of x-rays passing between two metal plates in air. The plates are connected in series with a switch, a cell and a milliameter.
It is observed that when the switch is closed a current flows in the milliameter. Explain this observation.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN09
In domestic wiring systems lamps in the lighting circuit are required to be in parallel and not in series. State two reasons for this requirement.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN08
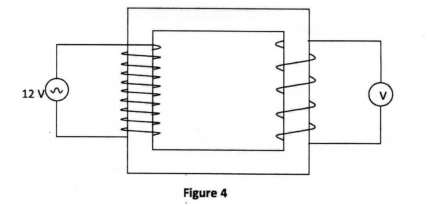
Figure 4 shows a simple transformer connected to a 12 V a.c. source and an a.c. voltmeter.
By counting the number of turns in each coil, determine the reading on the voltmeter.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN07
The equation below represents a nuclear reaction in which two deuterium nuclei fuse to form Helium and X.
(a) Determine the values of a and b.
(b) Identify X.
answers
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN06
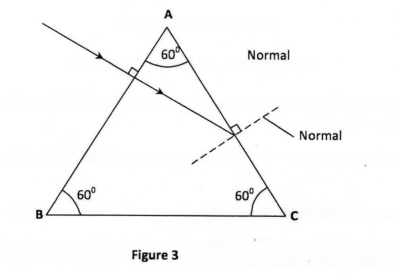
Figure 3 shows a ray of light passing into a glass prism ABC.
Sketch the path of the ray as it travels from face AC. (critical angle for glass is 42o)K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN05
Figure 2 shows the image of an object formed by reflection in a converging mirror. C is the centre of curvature of the mirror
Complete the diagram to show:
(a) how incident rays are reflected to form the image; (b) the object position. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN04
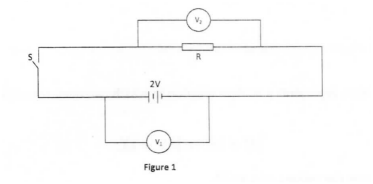
Figure 1 shows a cell of e.m.f. 2 V connected in series with a resistor R and a switch S. Voltmeters V1 and V2 are connected across the cell and the resistor respectively.
(a) State the reading of V1 with S open.
(b) With S closed, V1 reads 1.6 V. State the reading of V2.
answer
(a) 2V
(b) 1.6V
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN03
State the reason why the magnetic field strength of a magnet is greatest at the poles.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN02
Explain why the image formed in a pin hole camera gets blurred when the hole is enlarged.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN01State the reason why when a ray of light strikes a mirror at 900, the reflected ray travels along the same path as the incident ray.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN18
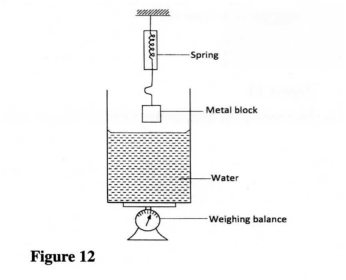
(a) Figure 12 shows a weighing balance on which a beaker containing some water is placed. The reading on the balance is 2.80 N. A metal block weighing 2.7 N is suspended from a spring balance
(i) State what is observed on the spring balance and the weighing balance, as the metal block is gradually lowered into the water.
(I) Observation on spring balance. (II) Observation on weighing balance. (ii) Explain the observation made on the spring balance in (I). (iii) When the metal block is fully immersed in the water, the reading on the spring balance is found to be 2.46 N. Determine the: (I) reading on the weighing balance. (II) density of the metal. (c) Figure 13 shows a hydrometer with a thin stem floating in water in a beaker.
State with a reason what is observed on the hydrometer when the temperature of the water is raised.
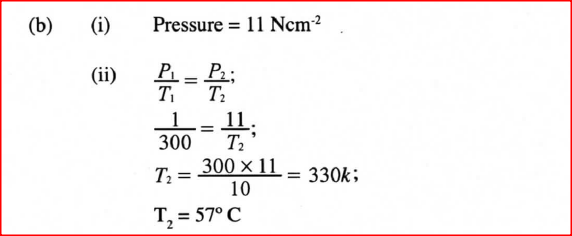
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN17Figure 11 shows an insulated cylinder fitted with a pressure gauge, a heating coil and a frictionless piston of cross-sectional area 100 cm2.(a) While the piston is at position O, the pressure of the enclosed gas is 10 Ncm-2 at a temperature of 27°C. When a 10 kg mass is placed on the piston, it comes to rest at position A without change in the temperature of the gas.
|
CATEGORIES
Categories
All
Topics
FORM I - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM II - PHYSICS SYLLABUSTOPICS
FORM III - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM IV - PHYSICS SYLLABUSARCHIVES
RSS FEEDS
AUTHOR
M.A NyamotiMy passion is to see students pass using right methods and locally available resources. My emphasis is STEM courses
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|


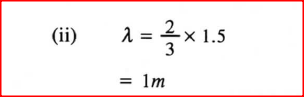
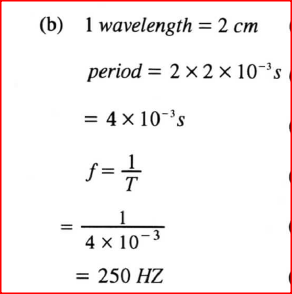


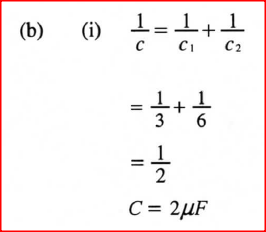




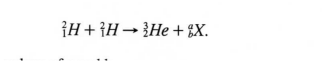














 RSS Feed
RSS Feed