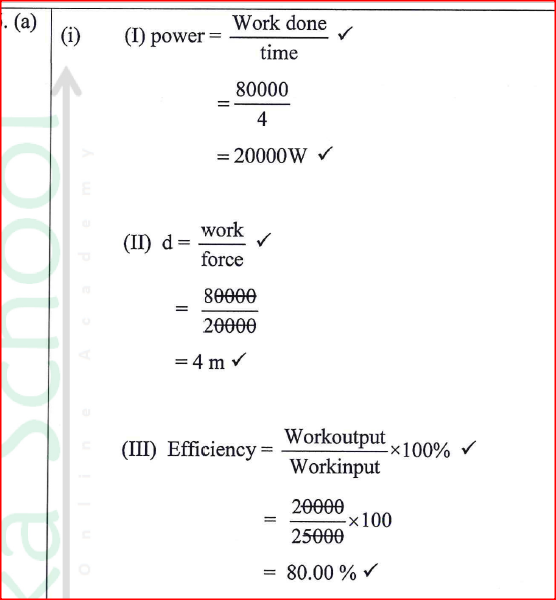
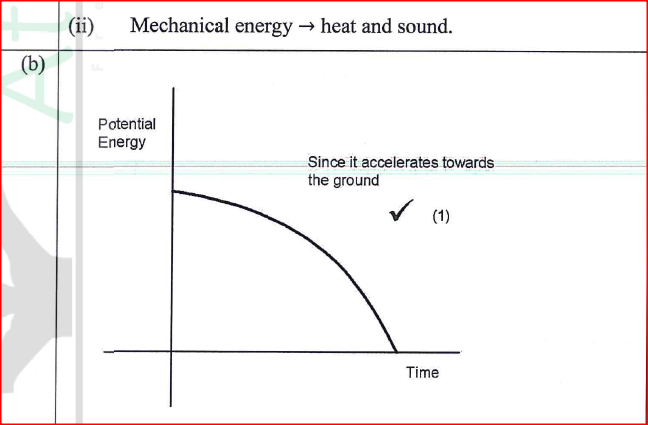
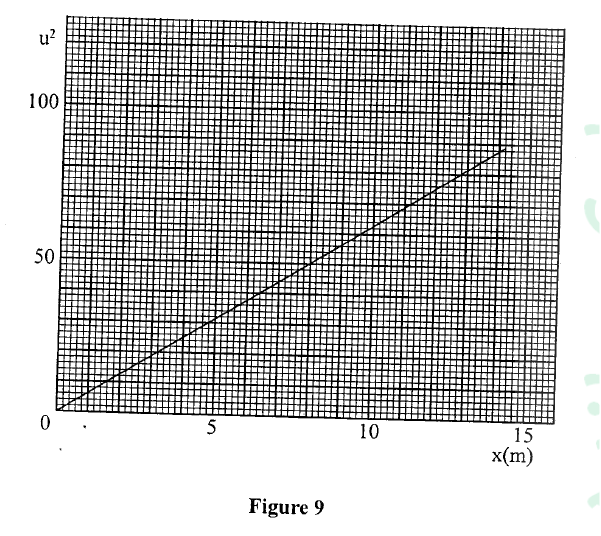
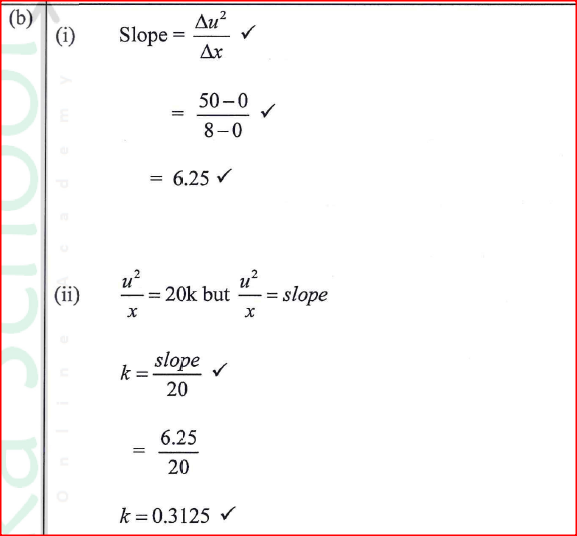
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP2QN19
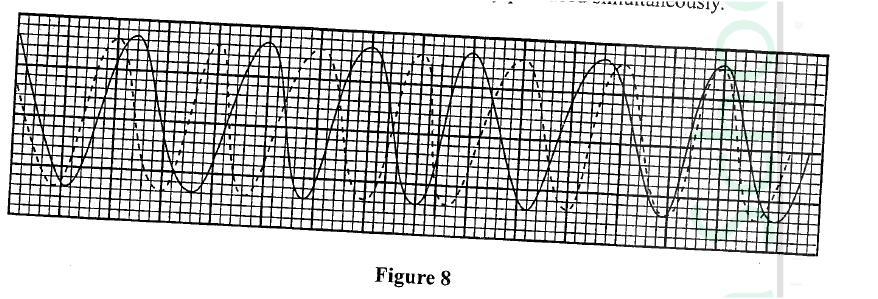
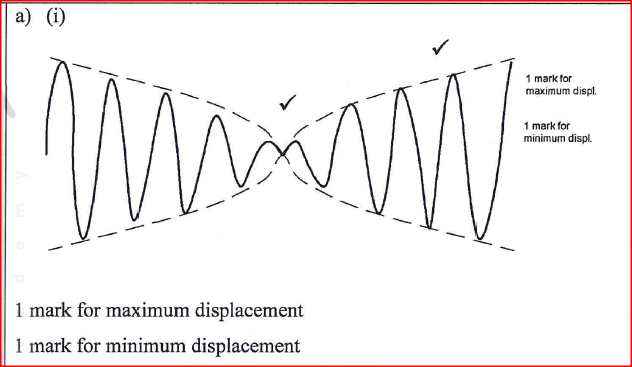
Figure 8 shows two waves of nearly equal frequency produced simultaneously.
On the space provided, sketch the resultant of the two waves (beats).
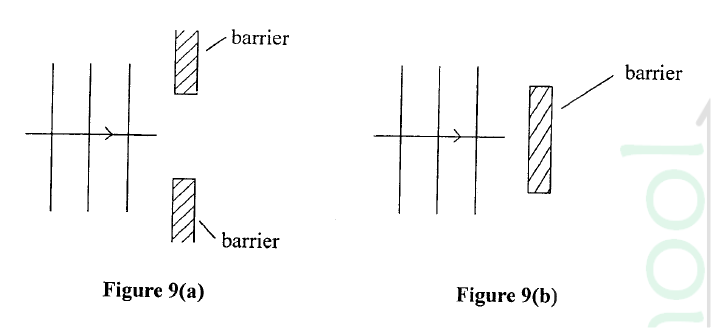
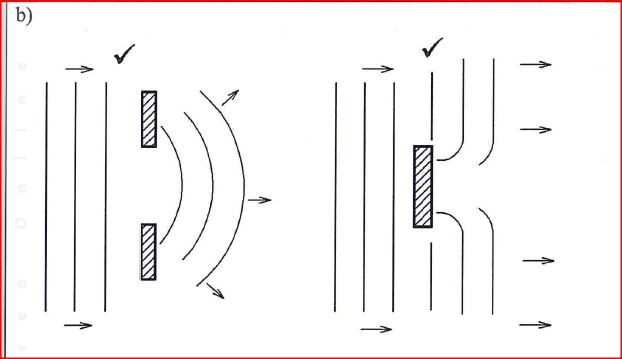
(b) Figure 9(a) and 9(b) show barriers placed in the path of plane waves.
On each figure, sketch the pattern of waves after they pass the barrier.
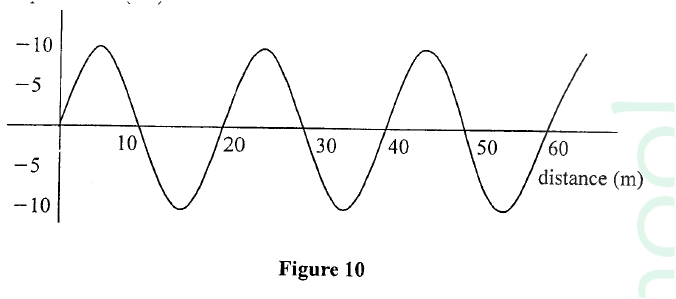
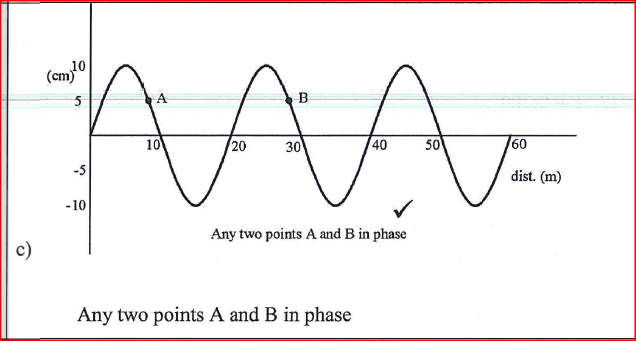
(c) Figure 10 shows a displacement—distance graph for a certain wave motion.
(i) Indicate on the figure with letters A and B any two points that are in phase.
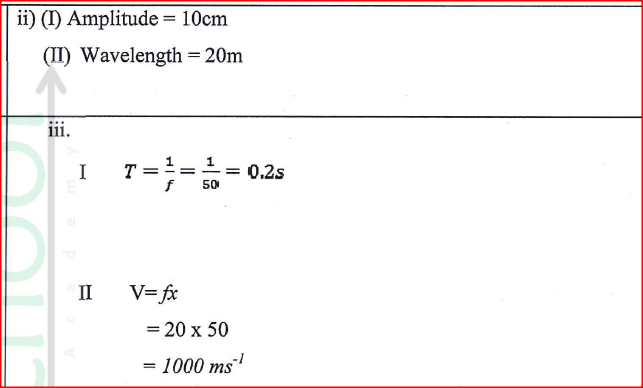
(ii) Determine the: (I) amplitude of the wave (II) wavelength of the wave (iii) Given that the frequency of the waves is 50 Hz, determine the: (I) period (II) speed of the wave
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP2QN18
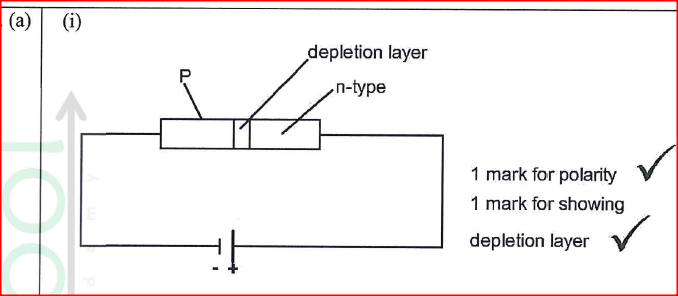
(a) (i) Draw a circuit diagram showing the depletion layer of a p—n junction diode connected in the reverse bias mode.
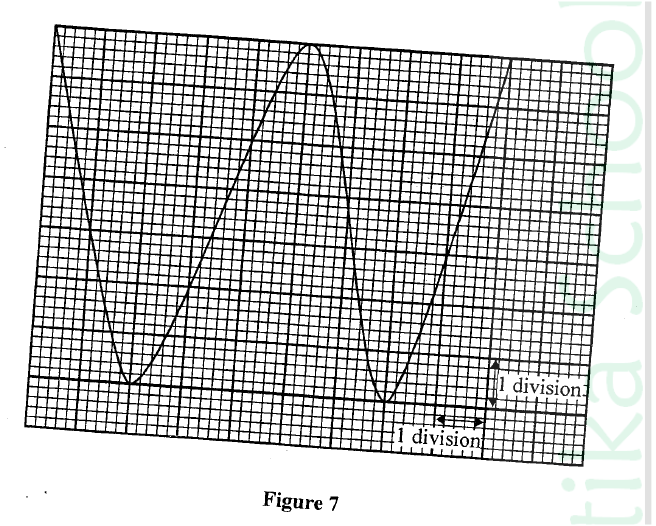
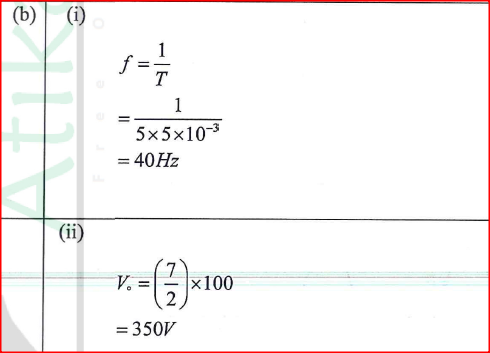
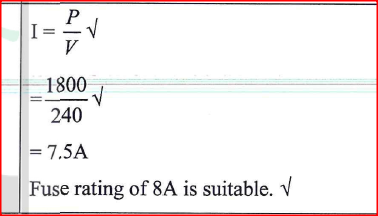
(ii) State the reason why increasing the external voltage in (i) makes the depletion layer wider. (iii) State the meaning of breakdown voltage of a junction diode. (iv) State one application of diodes. (b) Figure 7 shows the output on a screen of a CR0 when an a.c. signal is connected to the Y-plates with the time base on.
(i) Given that the time control is 5 ms per division and the y-gain is 100 V per division determine the:
(I) frequency of the ac. signal (II) peak voltage of the input signal (ii) State the adjustment that may be made in order to halve the frequency of the a.c. signal.
answers
(ii) The holes and the electrons in their respective regions are attracted away from the junction by the external voltage.
(iii) The voltage at which the diode begins to conduct in the reverse bias mode. (iv) In rectification circuits for changing a.c. to d. c. In control of voltages of Zener diode.
(iii) Double the time control to 10ms per division.
Adjust the frequency of the source to half the value K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP2QN17
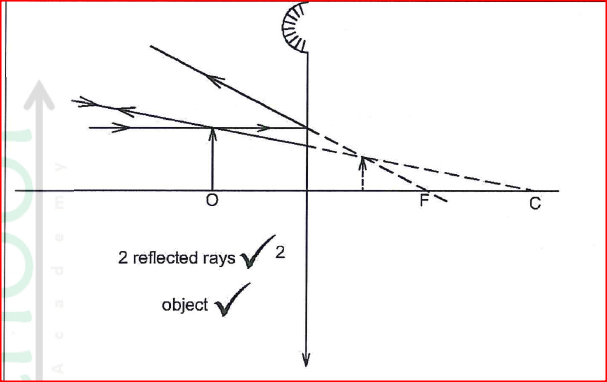
(a) Water waves from a certain Source move from the shallow end to the deep end. State the change that occurs at the deep end on the following:
(i) Frequency (ii) Wavelength (iii) Velocity
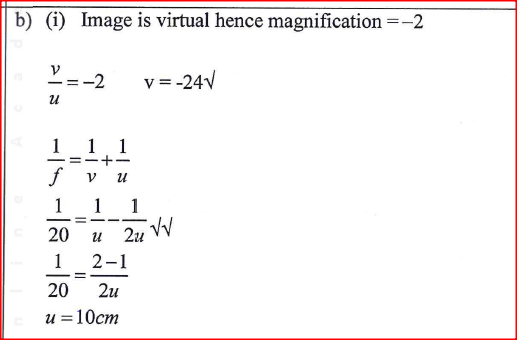
(b) (i) A biconvex lens forms an upright image twice the size of the object. If the focal length of the lens is 20cm, determine the object distance.
(ii) State two optical instruments which produce a magnified real image using a Convex lens. (c) State one difference between the working of the human eye and the lens of a camera. (d) A lens of focal length 2Ocm forms a virtual image when an object is placed 60cm from the lens. State with a reason the type of lens used.
answers
(a)(i) No change in frequency
(ii) Wavelength increases (iii) Velocity increases
(ii) a film projector
A compound microscope (c) In a camera focusing is done by changing the distance between the lens and the film. While in the eye focusing is done by changing the curvature of the lens. d) Diverging lens Forms a virtual image when the object distance is greater than the focal length. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP2QN16
(a) State the meaning of the following terms:
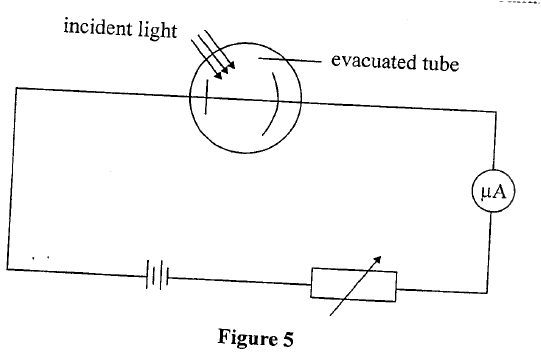
(i) Photoelectric effect (ii) Threshold frequency (b) Figure 5 shows some light incident on the cathode of a photocell. The photocell is connected in series with a battery, a variable resistor and a microammete
(î) Explain how the microammeter reading is affected when the intensity of the incident light is increased.
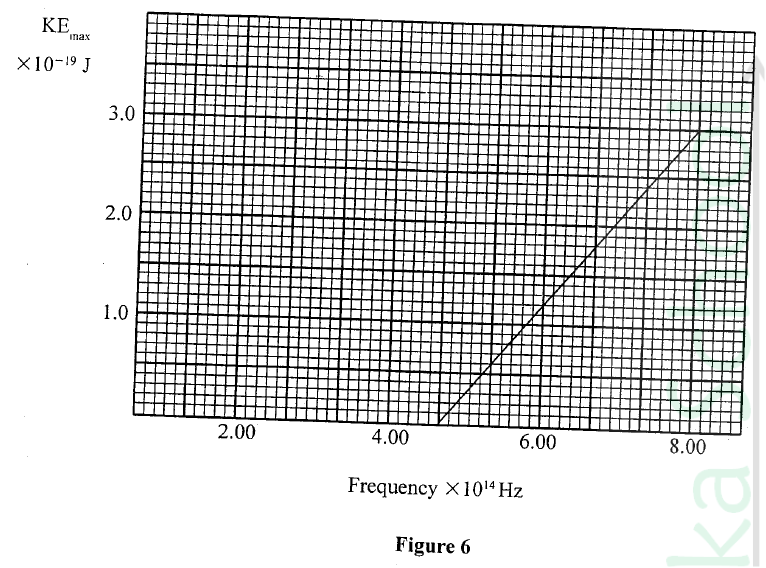
(ii) State the reason why the tube is evacuated (c) Figure 6 shows a graph of maximum kinetic energy (KE max) of photoelectrons against the frequency of the incident radiation. From the graph, determine:
|
CATEGORIES
Categories
All
Topics
FORM I - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM II - PHYSICS SYLLABUSTOPICS
FORM III - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM IV - PHYSICS SYLLABUSARCHIVES
RSS FEEDS
AUTHOR
M.A NyamotiMy passion is to see students pass using right methods and locally available resources. My emphasis is STEM courses
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|

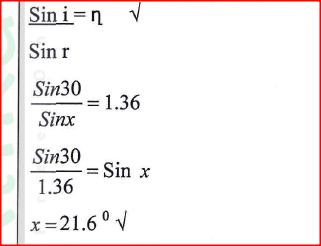





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed