The bob in the figure above is deflected then released to oscillate. State and explain one factor that will determine whether the string breaks or not (2mks)
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN06
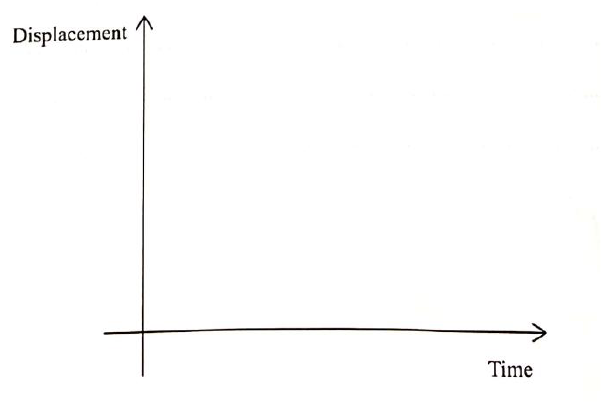
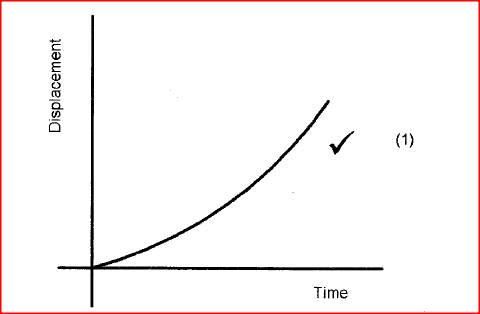
On the axes provided, sketch a displacement — time graph for a trolley moving down a frictionless inclined plane till it reaches the end of the incline.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN14
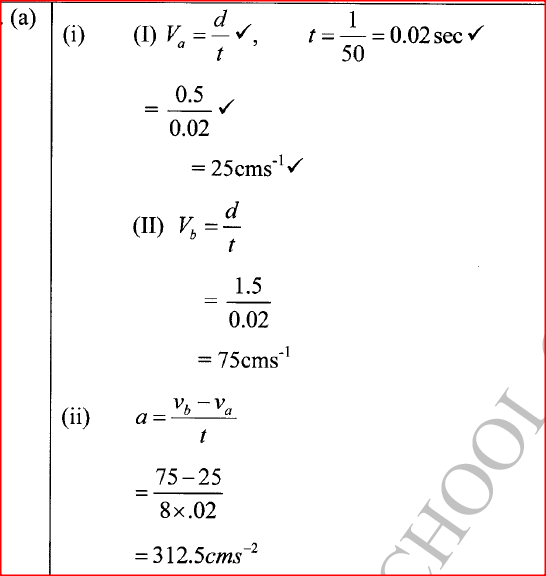
(a) A tape attached to an accelerating trolley passes through a ticker timer that makes dots on it at a frequency of 50Hz. The ticker timer makes 10 dots on a 10cm long tape such
that; the distance a between the first two dots is 0.5 cm and the distance b between the last two dots is 1.5cm.
(i) Determine the velocity of the trolley at:
(I) distance a, (II) distance b. (ii) Determine the acceleration of the trolley. (b) State with a reason what would be observed on the spacing between the dots on the tape when the trolley is made to move on a horizontal surface.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN07
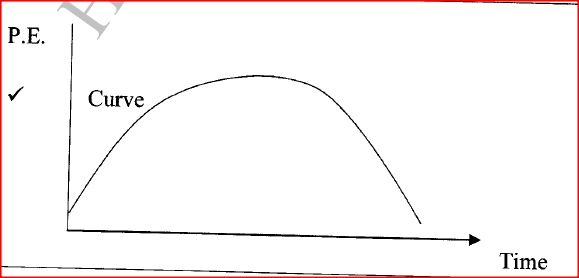
A stone is thrown vertically upwards. Sketch a graph of potential energy (y axis) against time as the stone moves until it hits the ground.K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN14
(a) Figure 7 (drawn to scale) shows a section of tape after passing through a ticker timer operated at a frequency of 50 Hz. The tape is attached to a trolley moving in the direction shown
(i) Determine the velocity between:
(I) P and Q: (II) X and Y. (ii) Determine the acceleration of the trolley. (b) Two bodies of masses 5 kg and 8 kg moving in the same direction with velocities 20 ms-1 and 15 ms-1 respectively collide inelastically. Determine the velocity of the bodies after the collision.K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN15
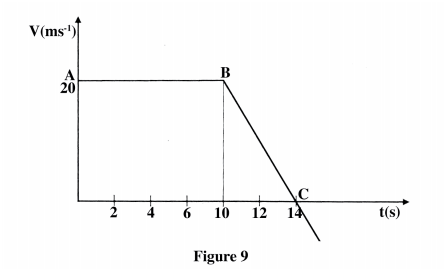
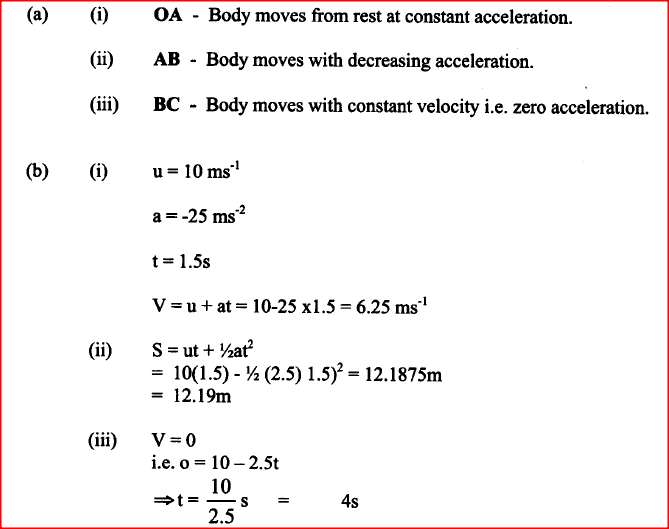
Figure 9 shows a velocity-time graph for the motion of a body of mass 2 kg
(a) Use the graph to determine the:
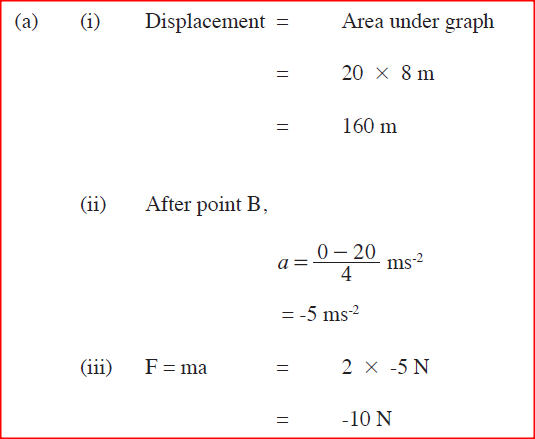
(i) displacement of the body after 8 seconds. (ii) acceleration after point B; (iii) force acting on the body in part (a) (ii). (b) Sketch a displacement-time graph for the motion from point A to C K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN04
Figure 2 shows a section of a curved surface ABCD. Point A is higher than point B while BCD is horizontal. Part ABC is smooth while CD is rough. A mass m is released from rest at A and moves towards D.
State the changes ¡n the velocity of m between:
(a)B and C; (b) C and D.
answer
(a) BC = Constant
(b) CD - decreasing K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN14
(a) State two ways in which the centripetal force on a body of mass m can be increased
(b) Figure 7 shows an object at the end of a light spring balance connected to a peg using a string. The object is moving in a circular path on a smooth horizontal table with a constant speed.
(i) State what provides the centripetal force.
(ii) Indicate with an arrow on the figure the direction of the centripetal force. (iii) State a reason why the object is accelerating while its speed remains constant. (iv) Given that the mass of the object is 0.5 kg and it is moving at a speed of 8 m/s at a radius of 2 m, determine the reading on the spring balance. (c) A stone thrown vertically upwards reaches a height of 100 m. Determine the: (i) initial velocity of the stone. (Neglect air resistance and take g =10m/s2) (ii) total time the stone is in air. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN14
(a) An aeroplane is moving horizontally through still air at a uniform speed. It is observed that when the speed of the plane is increased, its height above the ground increases.
State the reason for this observation. (b) Figure 5 shows parts A, B and C of a glass tube.
State with a reason the part of the tube in which the pressure will be lowest when air is blown through the tube from A towards C.
answers
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN11
Figure 3 shows a graph of velocity against time for a moving body.
Describe the motion of the body during the 10 seconds.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN02
A student pulls a block of wood along a horizontal surface by applying a constant force. State the reason why the block moves at a constant velocity.
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN16
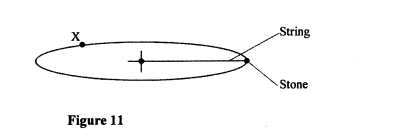
Figure 11 shows a stone attached to the end of a string moving in a horizontal circle with a uniform speed of 2m/s. When the stone reaches point X on the circle, the string breaks.
(i) indicate on the diagram with an arrow, the direction of the motion of the stone when the string breaks.
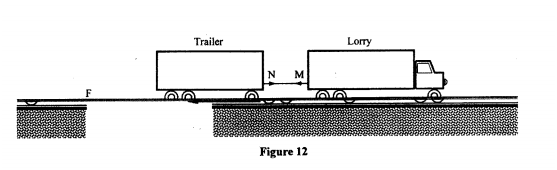
(ii) State the magnitude of the velocity after the string breaks. (iii) Give a reason for your answers in (i) and (ii). (b) Figure 12 shows a lorry towing a trailer using a rope.
The lorry exerts a force N on the trailer and the trailer exerts an equal but opposite force M on the lorry. The frictional force between the trailer and the road is F.
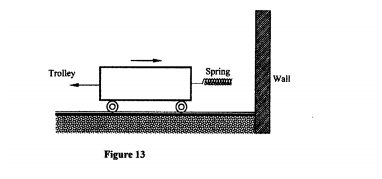
Explain how the forces N, M and F enable the trailer to move. (c) Figure 13 shows a frictionless trolley of mass 2kg moving with uniform velocity towards a wall. At the front of the trolley is a spring whose spring constant is 25N/m. The trolley comes to rest momentarily after compressing the spring by 3cm and then rebounds from the wall.
(I) Determine
(I) the force exerted on the wall by the spring. (II) the maximum acceleration of the trolley as it rebounds from the wall. (ii) State the reason why the trolley acquires a constant velocity after it rebounds. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN15
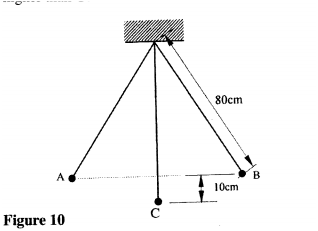
Figure 10 shows a simple pendulum of length 80cm. The pendulum bob whose mass is 50g oscillates between points A and B, through its rest position C. A and B are both 10cm higher than C
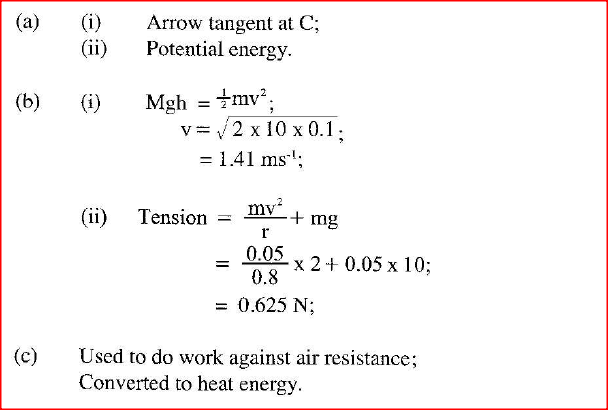
(a) (i) Indicate with an arrow, on the path ACB, the direction of the greatest velocity of the bob as it moves from A to B.
(ii) State the form of energy possessed by the pendulum bob at point A. (b) Determine: (i) the velocity of the bob at point C, (ii) the tension in the string as the bob passes point C.(take acceleration due to gravity g = 10 m/s2) (c) After some time, the pendulum comes to rest at point C. State what happens to the energy it initially possessed. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN13
A particle starts from rest and accelerates uniformly in a straight line. After 3 seconds it is 9m from the starting point. Determine the acceleration of the particle.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN06
Figure 5 is a graph of net force on a body against it’s velocity as it falls through a liquid.
Determine the terminal velocity of the body.
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2010PP1QN19
(a) Figure 9 shows a velocity-time graph for the motion of a certain bod
Describe the motion of the body in the region:
(i) OA; (ii) AB; (iii) BC. (b) A car moving initially at 10 ms-1 decelerates at 2.5 m/s2. (I) Determine: (I) its velocity after 1 .5s; (II) the distance travelled in 1.5s; (III) the time taken for the car to stop. (ii) Sketch the velocity-time graph for the motion of the car up to the time the car stopped. (iii) From the graph, determine the distance the car travelled before stopping. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2010PP1QN08
A cart of mass 30kg is pushed along a horizontal path by a horizontal force of 8N and moves with a constant velocity. The force is then increased to 14N.
Determine:
(a) the resistance to the motion of the cart;
(b) the acceleration of the cart. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2010PP1QN02
A stopwatch started O.50s after the start button was pressed. The time recorded using the stopwatch for a bail bearing falling through a liquid was 2.53s. Determine the time of fall.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2009PP1QN12
Figure 7 (a) shows the acceleration – time graph for a certain motion
On the axes provided in figure 7 (b), sketch the displacement – time graph for the same motion
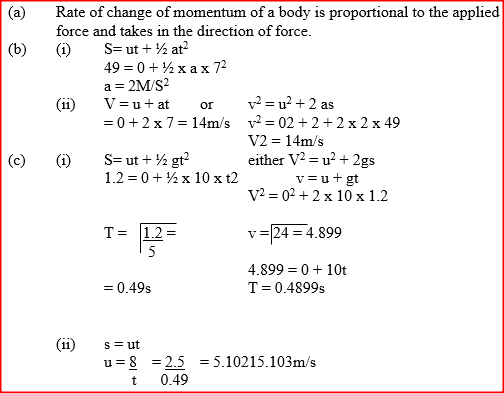
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2008PP1QN15
a) State Newton's second law of motion.
b) A matatu starts from rest and accelerates to cover a distance of 49m in 7 seconds. Determine (i) Its acceleration; (ii) Its velocity, after 7 seconds
c) A trolley moving on a horizontal bench of height 1.2m, strikes a barrier at the edge of the bench. The brass mass on the top of the trolley flies off on impact and lands on the ground 2.5m from the edge of the bench.
Determine: (i) The time taken by the brass mass to reach the ground; (ii) The speed at which the trolley struck the barrier. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2007PP1QN09&10
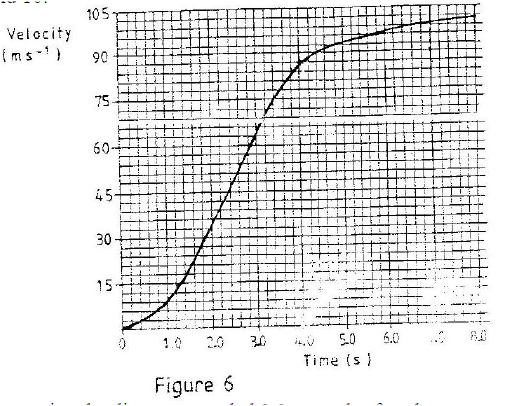
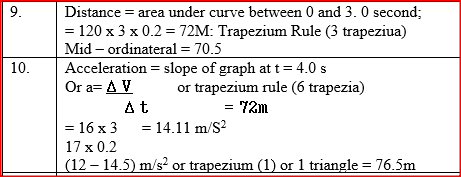
The graph in figure 6 shows the velocity of a car in the first 8 seconds as it accelerates from rest along a straight line. Use the graph to answer questions 9 and 10.
Determine the distance traveled 3.0 seconds after the start
Determine the acceleration of the car at 4.0 seconds K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN13
A footballer kicks a ball of mass 0.6 kg initially at rest using a force of 720N. If the foot was in contact with the ball for 0.1 seconds, what was the take off speed of the ball?
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN10
Figure 6 shows the path taken by a matatu traveling on a horizontal ground ( a winding road)
The speed of the matatu is constant. Identify with reason the point along the path which a load placed loosely on the rack (carrier) of the matatu is most likely to roll off.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN06
A car starting from rest accelerates uniformly for 5 minutes to reach 30m/s. It continues at this speed for the next 20 minutes and then decelerates uniformly to come to stop in 10 minutes.
On the axes provided, sketch the graph of velocity against time for the motion of the car. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN25
Fig 14 shows the velocity- time graph for a small metal sphere falling through a viscous fluid.
On the axes provided sketch the graph of momentum against time for the same mass.
|
CATEGORIES
Categories
All
Topics
FORM I - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM II - PHYSICS SYLLABUSTOPICS
FORM III - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM IV - PHYSICS SYLLABUSARCHIVES
RSS FEEDS
AUTHOR
M.A NyamotiMy passion is to see students pass using right methods and locally available resources. My emphasis is STEM courses
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|














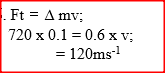





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed