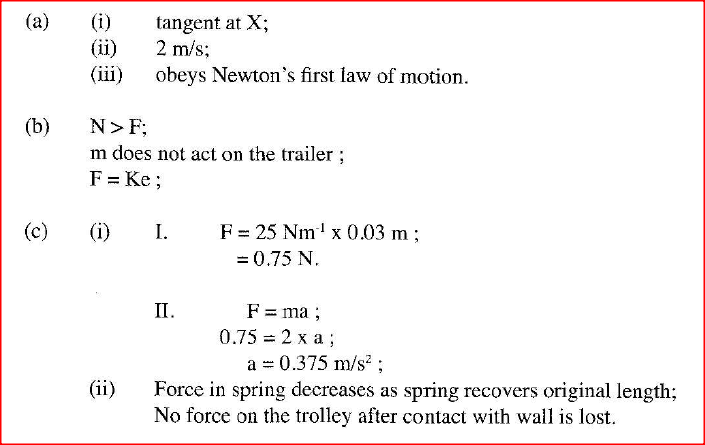
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN19
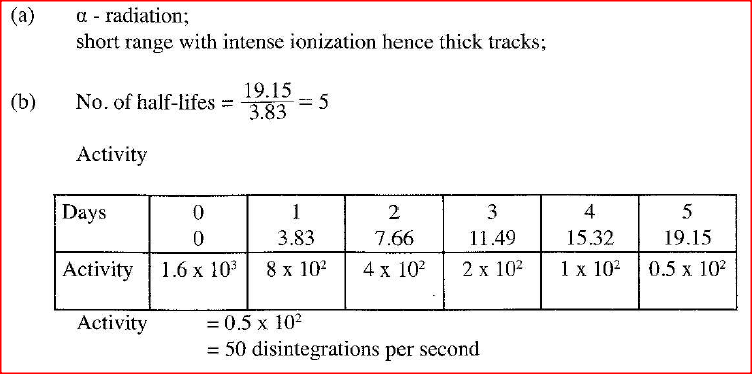
(a) When a radiation was released into a diffusion cloud chamber, short thick tracks were observed. State with a reason, the type of radiation that was detected.
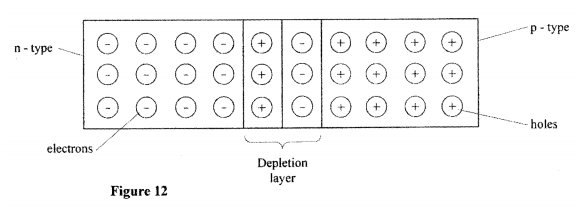
(b) The half-life of an element X is 3.83 days. A sample of this element is found to have an activity rate of 1.6 x 103 disintegrations per second at a particular time. Determine its activity rate after 19.15 days. (c) State what is meant by an extrinsic semiconductor. (d) Figure 12, shows a depletion layer in an unbiased p-n junction.
State how a battery can be used to make the depletion layer narrower.
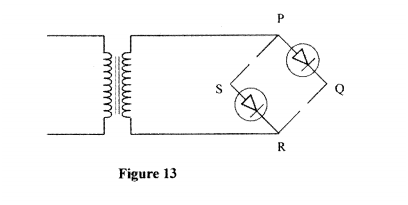
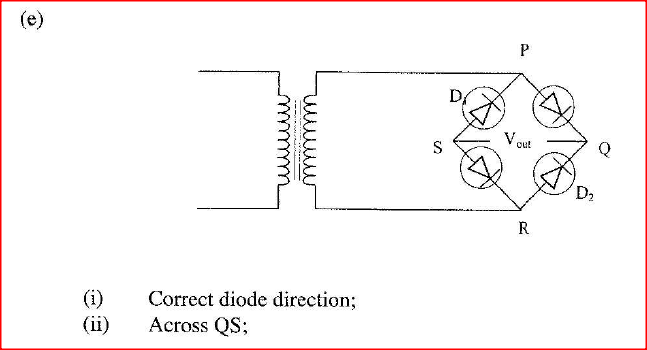
(e) Figure 13, shows an incomplete circuit of a full wave rectifier
(I) Draw in the figure two more diodes to complete the circuit.
(ii) Show on the figure the points across which the output of the rectifier should obtained.
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN18
(a) State two differences between cathode rays and electromagnetic radiations.
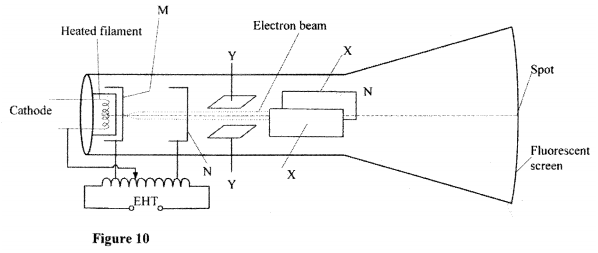
(b) Figure 10, shows the main features of a cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO)
(i) Name the parts labelled M and N.
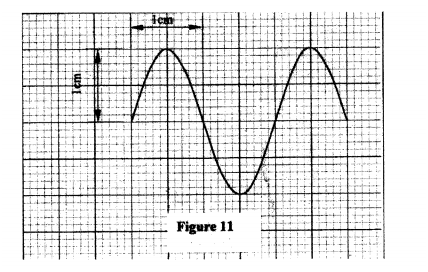
M N (ii) Explain how electrons are produced in the tube. (iii) When using the CRO to display waveforms of voltages, state where the following should be connected: (I) the voltage to be displayed on the screen; (II) the time base voltage. (iv) state why the tube is highly evacuated. (c) Figure 11, shows the waveform of a voltage displayed on the screen of a CRO. The Y-gain calibration was 5V per cm.
(i) Determine the peak-to-peak voltage of the Y-input.
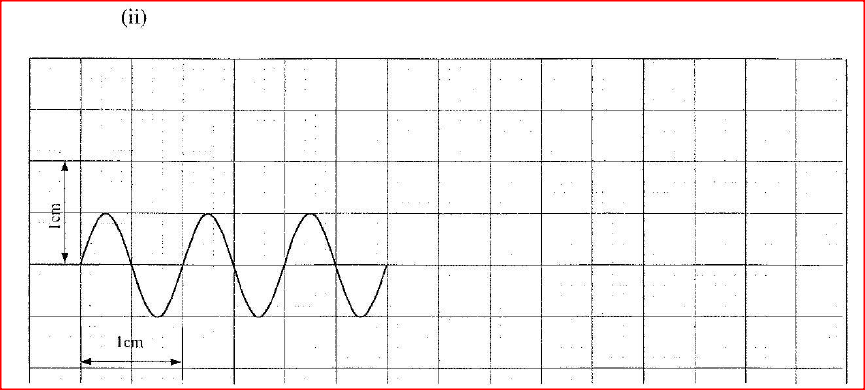
(ii) Sketch on the same figure the appearance of the waveform after the voltage of the input signal is halved and it’s frequency is doubled.
answers
(a) -Cathode rays have charge but e.m radiations don’t have charge;
-Cathode rays are particles and have a mass but e.m radiations are waves; -Cathode rays travel at a speed depending on the accelerating voltage but e.m radiations travel at the speed of light in vacuum; - Different in the mode of production. (b) (i) M - grid; N - accelerating anode/anode/vacuum; (ii) Cathode is heated by filament; electrons are released from cathode; by thermionic emission (iii) (I) across Y-Y plates. (Il) across X-X plates. (2 m (iv) to reduce collisions, (hence ionization) with air molecules in the tube. (c) (i) peak-to-peak voltage = 5 x 2 =10v K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN17
(a) State what is meant by the term “electromagnetic induction”.
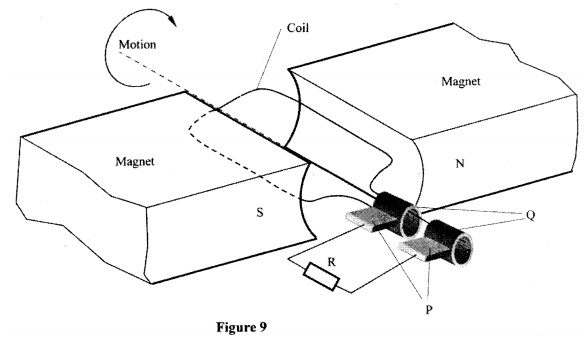
(b) Figure 9, shows a simple electric generator
(i) Name the parts labelled P and Q.
P . Q (ii) Sketch on the axes provided, a graph to show how the magnitude of the potential difference across R, changes with the time t.
(iii) State two ways in which the potential difference produced by such a generator can be increased.
(c) In a transformer, the ratio of primary turns to the secondary turns is 1:10. A current of 500mA flows through a 200 ohms resistor in the secondary circuit. Assuming that the transformer is 100% efficient, determine: (i) the secondary voltage; (ii) the primary voltage; (iii) the primary current. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN16
(a) State the meaning of the term “principal focus” as applied in lenses.
(b) You are provided with the following apparatus to determine the focal length of a lens: - a biconvex lens and lens holder. - alit candle. - a white screen. - a metre rule
(i) Draw a diagram to show how you would arrange the above apparatus to determine the focal length of the lens
(ii) Describe the procedure you would follow. (iii) State two measurements that you would take. (iv) Explain how the measurements in (iii) would be used to determine the focal length. (c) An object is placed 30cm in front of a concave lens of focal length 20cm. Determine the magnification of the image produced.
answers
(a) The point at which rays close to and parallel to the principal axis converge or seem to diverge from after striking the lens;
(ii) Candle is placed at a certain distance from the lens. The distance between the screen and the lens is adjusted until a sharp image is focused on screen.
(iii) The distance of candle from lens (U) is measured; The distance of screen from lens (V) is also measured; K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN15
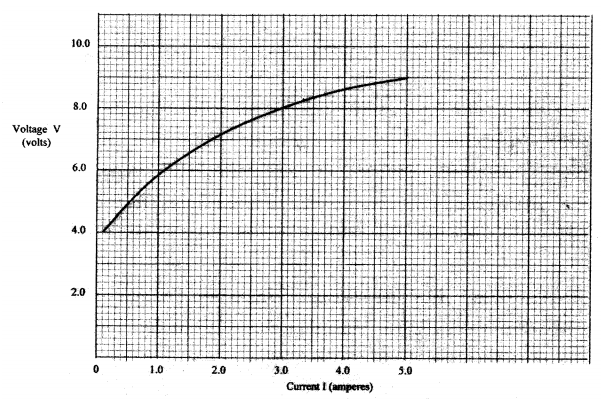
(a) Figure 8, shows a graph of potential difference V (volts) against a current I (amperes) for a certain device.
From the graph:
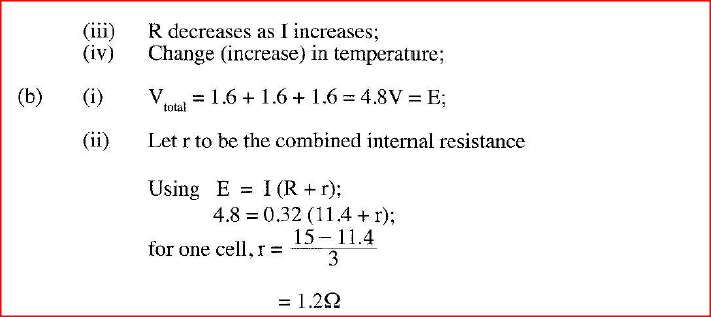
(i) state with a reason whether or not the device obeys ohms law. (ii) determine the resistance of the device at: (1) 1 =l.5A (II) I =3.5A (iii) From the results obtained in (ii) state how the resistance of the device varies as the current increases. (iv) State the cause of this variation in resistance. (b) Three identical dry cells each of e.m.f. 1 .6V are connected in series to a resistor of 11.4 ohms. A current of 0.32A flows in the circuit. Determine: (i) the total e.m.f. of the cells; (ii) the internal resistance of each cell;
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN14
State the meaning of the term “threshold frequency” as used in photoelectric emission.
answer
State the reason why electrical power is transmitted over long distances at very high voltages.20/7/2020
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN13
State the reason why electrical power is transmitted over long distances at very high voltages.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN12
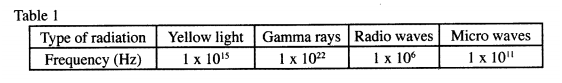
Table I shows radiations and their respective frequencies.
Arrange the radiations in the order of increasing energy.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN11
A 4 ohms resistor is connected in series to a battery of e.m.f 6V and negligible internal resistance. Determine the power dissipated by the resistor.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN10
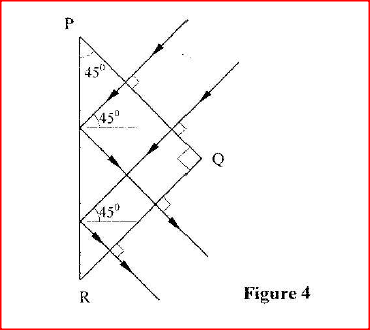
Figure 7, shows two rays of light incident normally on face PQ of a glass prism, whose critical angle is 42°.
Complete the diagram to show the paths of the two rays as they pass through the prism.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN09
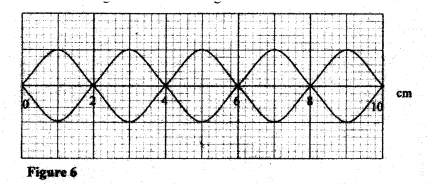
Figure 6, shows standing waves on a string. It is drawn to a scale of 1:5
(a) Indicate on the diagram the wavelength of the standing wave.
(b) Determine the wavelength of the wave. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN07&8
Figure 5, shows a motor connected to a magnetic switch called a relay operated by an ordinary switch S1 Use the information in the figure to answer questions 7 and 8.
Explain how the relay switches on the motor when S1 is closed.
State with a reason the effect on the motor, the iron core is replaced with a steel core and switch S1 is put on and then off.
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN06
One method of producing a weak magnet is to hold a steel rod in the North South direction and then hammer it continuously for some time. Using the domain theory of magnetism explain how this method works.
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN04&5
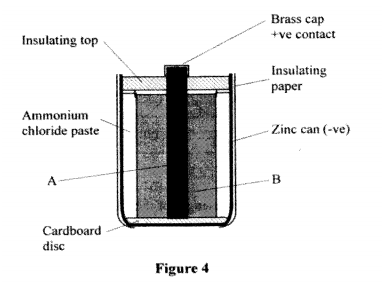
Figure 4. shows the cross-section of a dry cell. Use the information on the figure to answer questions 4 and 5.
Name the parts labelled A and B.
State the use of the manganese (IV) oxide in the cell.
answers
4. A = Carbon rod(+);
B = Manganese (VI) oxide 5. Manganese (IV) oxide is a depolarizer/oxidizing agent; K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN03
Figure 3, shows a voltmeter connected across two charged parallel plates.
When a thin sheet of mica is inserted between the plates, the voltmeter reading is observed to reduce. Explain this observation.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN02
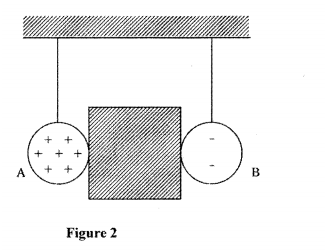
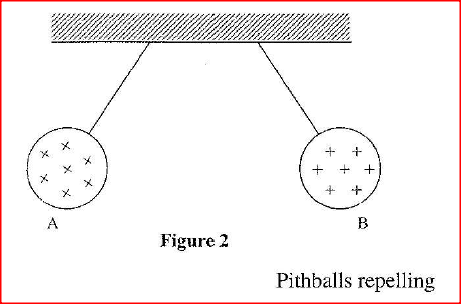
Figure 2, shows two identical pithballs A and B suspended with insulated threads. They are
separated by an insulator X. A is positively charged while B is negatively charged. The quantity of charge on A is three times the quantity of charge on B.
Sketch on the space besides the figure, the final position of the pithballs after the insulation removed.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN01
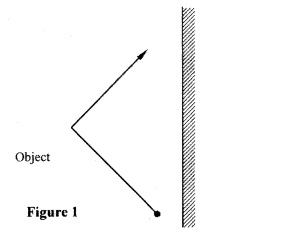
Figure 1, shows an object placed in front of a plane mirror.
Sketch the image of the object as seen in the mirror.
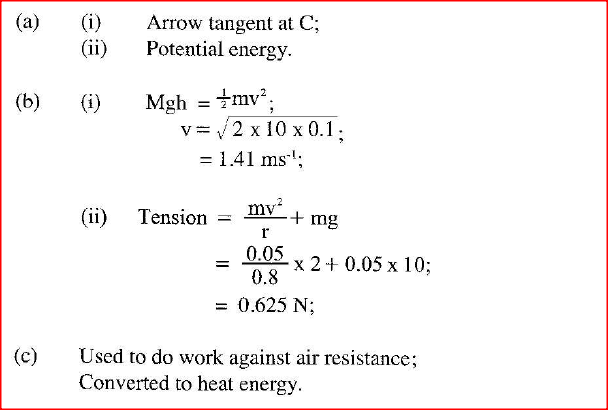
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN019
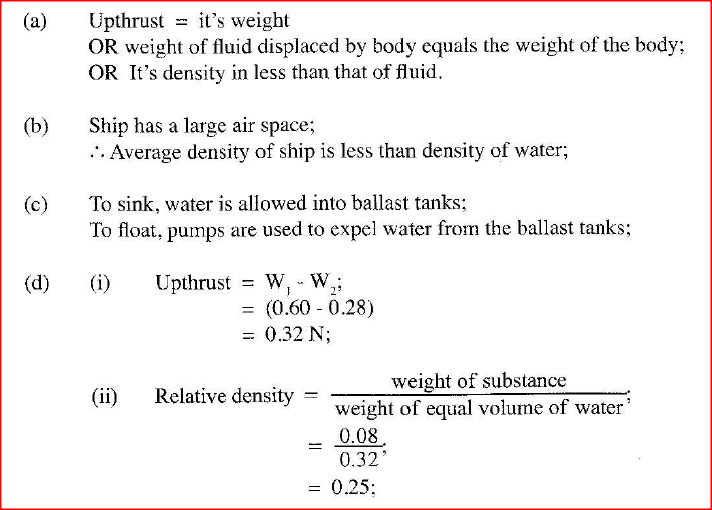
(a) State the condition necessary for a body to float in a fluid.
(b) A ship made of steel is observed to float on water yet the density of steel is approximately eight times that of water. Explain this observation. (c) Figure 17 shows three stages of an experiment to determine relative density of cork which normally floats on water. To make it sink, a sinker is hung below the cork.
In (1) a spring balance is used to measure the weight W of the cork in air.
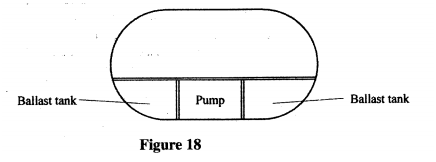
In (II) the spring balance is used to measure the apparent weight W1, when only the sinker is submerged in water. In (Ill) the spring balance is used to measure the apparent weight W2 when both the cork and the sinker are submerged. The following observations were made. W = 0.08N W = 0.60N W2 = 0.28N Use this information to determine the: (i) Upthrust on cork. (ii) relative density of cork. (d) Figure 18 shows parts of a simple submarine, a ship that can travel both on water and under water. To do this water is pumped in or out of the ballast tanks.
Explain how the tanks are used to change the depth of the submarine.
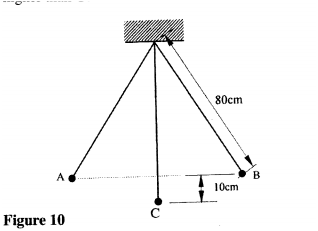
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN18
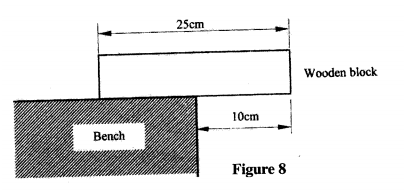
(a) Figure 15 shows a metal bolt which is threaded.
Explain how a metre rule can be used to measure the pitch (distance between adjacent peaks) of the threading.
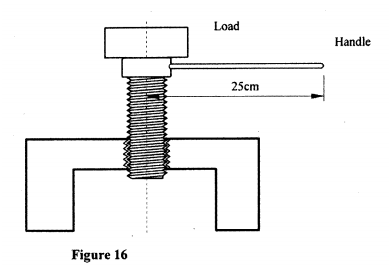
(b) Figure 16 shows a screw jack whose screw has a pitch of 1mm, and has a handle of 25 cm long.
Determine the velocity ratio of the jack.
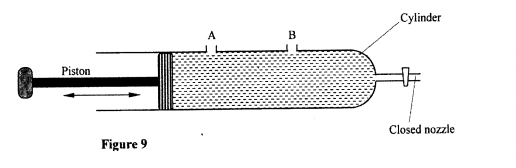
(c) A bullet of mass 60g travelling at 800m/s hits a tree and penetrates a depth of 15 cm before coming to rest. (i) Explain how the energy of the bullet changes as it penetrates the tree. (ii) determine the average retarding force on the bullet. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN17
(a) When the temperature of water reaches the boiling point, bubbles rise to the surface.
(î) State what is contained in the bubbles. (ii) State the reason why bubbles rise to the surface only at the boiling point. (b) Figure 14 shows a graph of vapour pressure against the temperature of water vapour, in a laboratory where a mercury barometer indicates a height of 61.8 cm. (b) (i) Determine the atmospheric pressure in the laboratory in Nm-2.
|
CATEGORIES
Categories
All
Topics
FORM I - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM II - PHYSICS SYLLABUSTOPICS
FORM III - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM IV - PHYSICS SYLLABUSARCHIVES
RSS FEEDS
AUTHOR
M.A NyamotiMy passion is to see students pass using right methods and locally available resources. My emphasis is STEM courses
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|
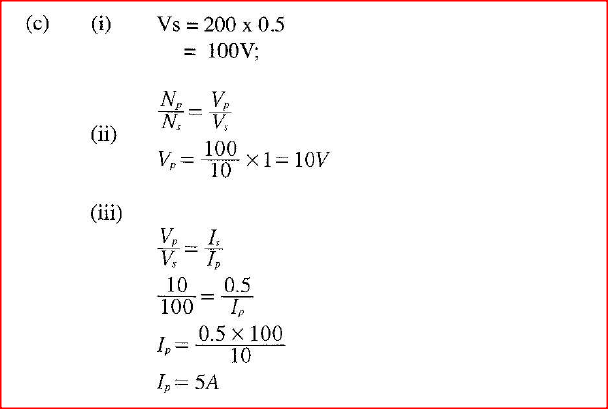



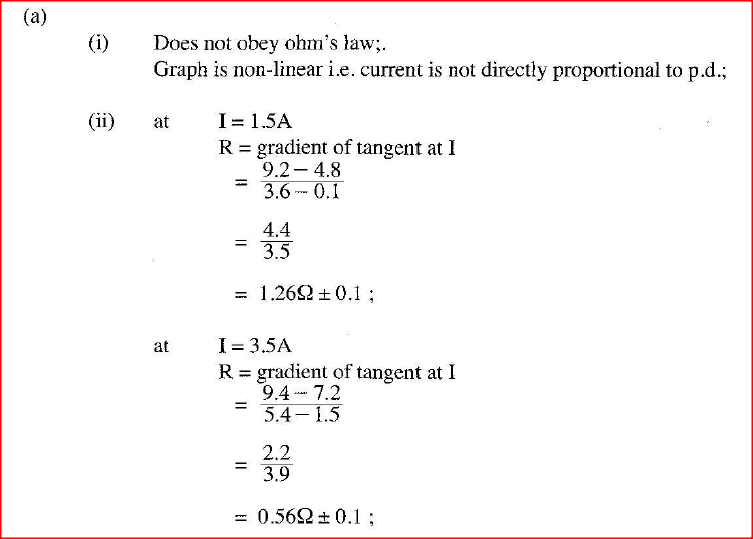
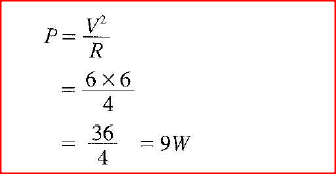












 RSS Feed
RSS Feed