State two uses of optical fibres whose working relies on total internal reflection (2mks)
0 Comments
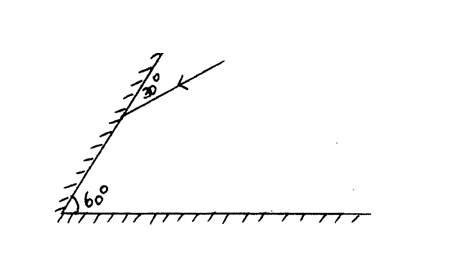
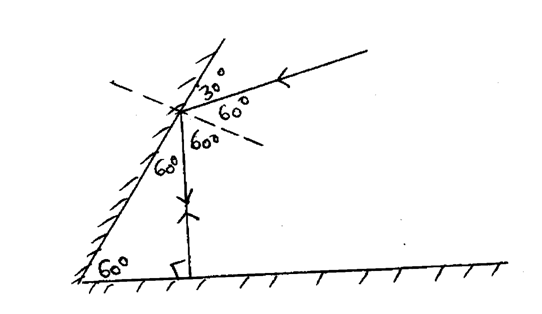
Two mirrors are inclined at 60o to each as shown:
Complete the ray diagram to show how it travels after striking the two mirrors and find the angle of reflection on each surface (2mks)SolutionTwo objects made of the same material and having the same mass are heated to a temperature of 35 degrees Centigrade above that of the atmosphere and then allowed to cool in still air for 30 minutes. State one factor that will determine their final temperature (1mk)Surface area to volume ratio
A turning effect of force depends on the magnitude of the force. State two other factors that determines the moment of a force (2mks)
A crystal of potassium permanganate was carefully introduced at the bottom of water column held in a gas jar. After sometime, the whole volume of water was coloured. Explain this observation (2mks)
The continuously moving water molecules hit the crystal from all directions causing it to split into the tiny particles of which it consist. The same movement caused the particles to diffuse to all parts of the liquid, this rendering the whole volume colored.
Define crystal cleavage (1mk)This is the phenomenon in which crystals break/fracture along specific planes to yield fresh smooth surface when hit or subjected to mechanical shock
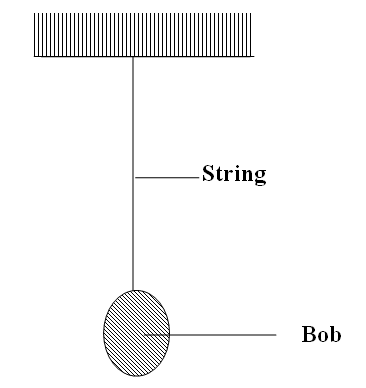
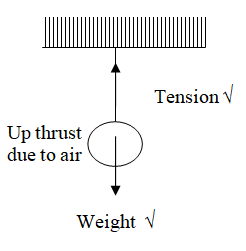
Mark on the diagram and name one other force acting on the bob.State one factor that a bimetallic strip relies on for its workingDifference in expansion rates of materials
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN09
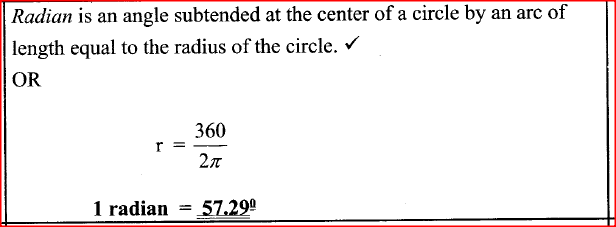
State the meaning of the term “radian” as a Unit of measurement.K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2019PP2QN02
State the reason why an increase in leaf divergence is the only sure way of determining whether an object is negatively charged using a negatively charged electroscope.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP2QN12
State the purpose of manganese(IV) oxide in a dry cell
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP2QN10
The sharp point of a pin is brought near the cap of a negatively charged electroscope .State and explain the observation made on the leaf of the electroscope
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN17
(a) State Pascal’s principle of transmission of pressure in liquids.
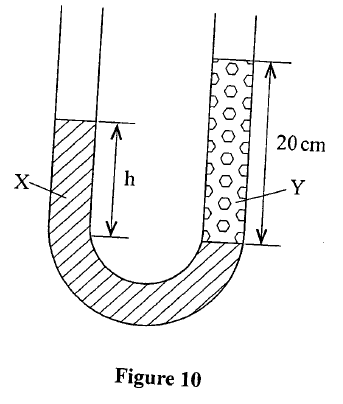
(b) Figure 10 shows heights of two immiscible liquids X and Y in a U-tube (drawn to scale).
(i) State with a reason which of the two liquids X and Y has a higher density.
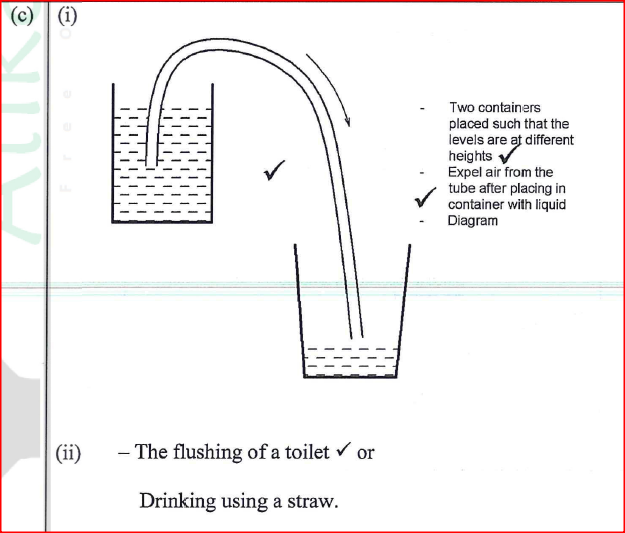
(ii) Determine the value of h. (iii) Given that the density of liquid Y is p, write down an expression for the density d of liquid X ¡n terms of p. (c) (i) With the aid of a diagram, describe how a liquid may be siphoned from one container to another using a flexible tube. (ii) State one application of the siphon.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN13
State two ways in which a mercury based thermometer can be modified to read very small temperature changes.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN07A wooden cube of side 0.5 m floats in water fully submerged. Determine the weight of the cube. (density of water = 1 gcm-3).K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN04
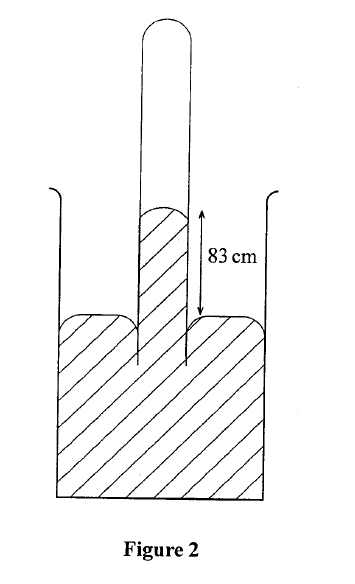
Figure 2 shows an instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure.
State with a reason the modification that would be required in a similar set up if mercury were to be replaced with water.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN02
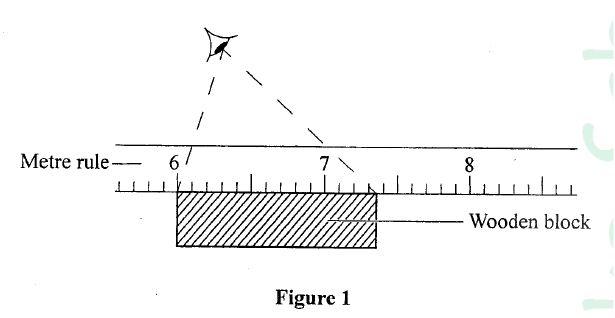
Figure 1 shows the position of a students eye while measuring the length of a wooden block using a metre rule.
Determine the length of the block as viewed by the student.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN01
State the reason why an object on earth has a higher weight than on the moon.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN11
Explain what is observed when an uncharged sphere is brought close to a positively charged electroscope.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN04
State what is meant by polarisation in simple cells.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN18
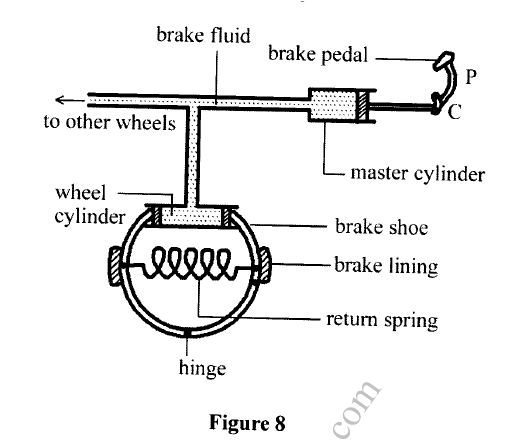
(a) Figure 8 shows part of a hydraulic brake system.
Describe how the systems works.
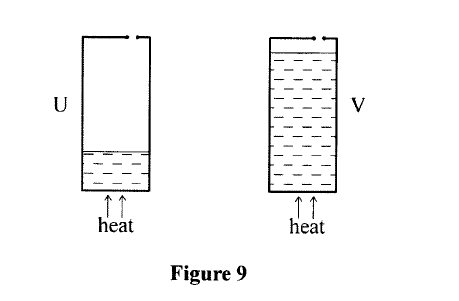
(b) State three conditions necessary for a driver to negotiate a bend on a flat level road at a relatively high speed. (c) Figure 9 shows two identical cans U and V each with a small opening at the top. Different amounts of water were put into the cans and heated until the water started to boil.
Explain what will be observed when both cans are then suddenly dipped into a cold water bath.
answers
(a) (i) The driver applies a force on the pedal.
This force transmits pressure the master cylinder fluid. Equal pressure is transmitted to the wheel cylinder causing the pistons of the wheel cylinder to push brake shoe hence Pressing the brake pads that in turn press the wheel reducing its rotation. When the applied force is removed, the return spring pulls back the shoe and pistons to the original position. (b) Higher friction (wider tyres, rougher road) Lower radius Higher mass (c) U is observed to crush. It has more steam which when cooled creates a greater vacuum hence pressure causes collapsing. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN03It is observed that when 20 cm3 of alcohol is mixed with 20 cm3 of water. the volume of the mixture is 39cm3. State a reason why the volume of the mixture is not 40 cm3.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN02
In an experiment to determine the density of Liquid R, a student obtained the followed data:
— Mass of an empty density bottle 550 g — Mass of the density bottle + water = 80.0 g — Mass of the density bottle + Liquid R = 70.0 g
Determine the density of Liquid R. (density of water is 1000 kgm^3)
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN07
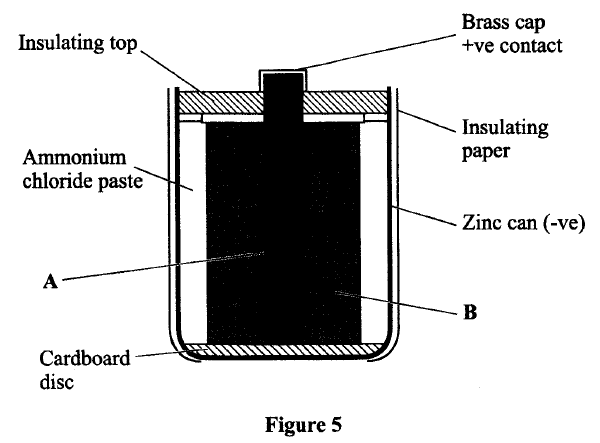
Figure 5 shows the cross-section of a dry cell. Use the information on the figure to answer questions below
(a) Name the parts labeled A and B.
(b) State the use of manganese (IV) oxide in the cell.
answers
(a) A – Carbon rod or graphite rod
B – Mixture of Manganese (IV) oxide with carbon powder (b) Manganese (IV) oxide is a depolarizer or oxidizing agent. It is used to oxidize hydrogen to water K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN10Figure 8 shows two cylinders of different cross-sectional areas connected with a tube. The cylinders contain an incompressible fluid and are fitted with pistons of cross-sectional areas 4 cm2 and 24 cm2.Opposing forces P and Q are applied to the pistons such that the pistons do not move. If the pressure on the smaller piston is 5 N cm2, Determine force Q. |
CATEGORIES
Categories
All
Topics
FORM I - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM II - PHYSICS SYLLABUSTOPICS
FORM III - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM IV - PHYSICS SYLLABUSARCHIVES
RSS FEEDS
AUTHOR
M.A NyamotiMy passion is to see students pass using right methods and locally available resources. My emphasis is STEM courses
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed