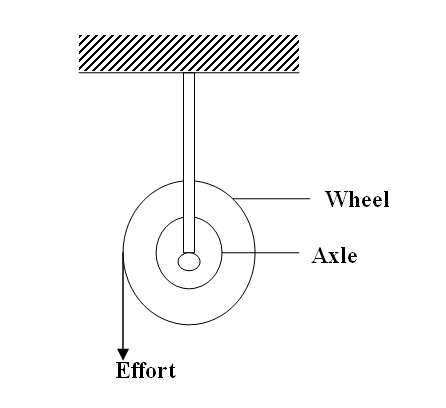
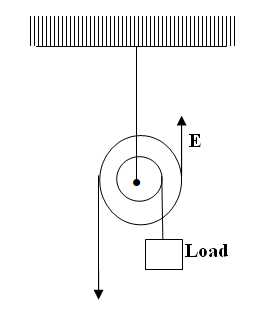
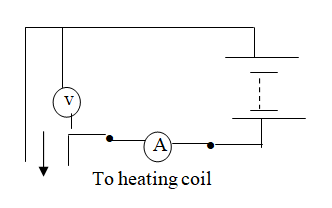
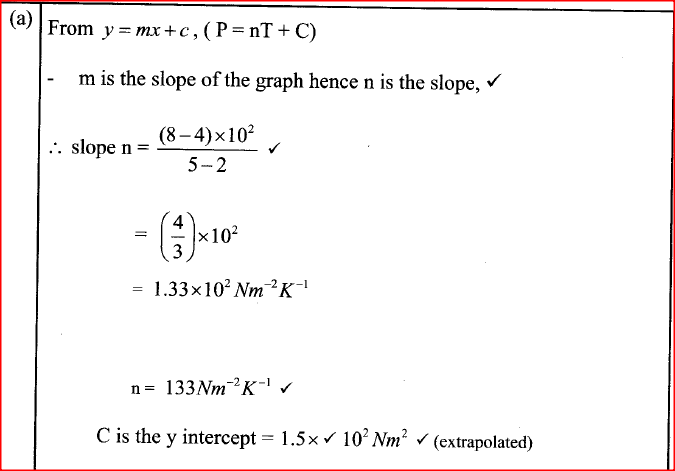
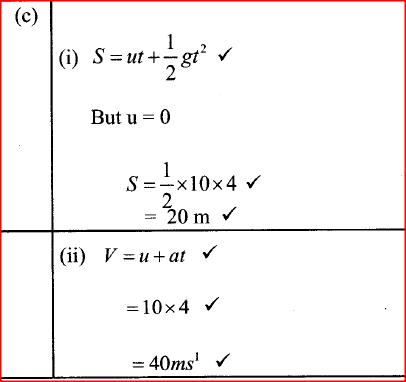
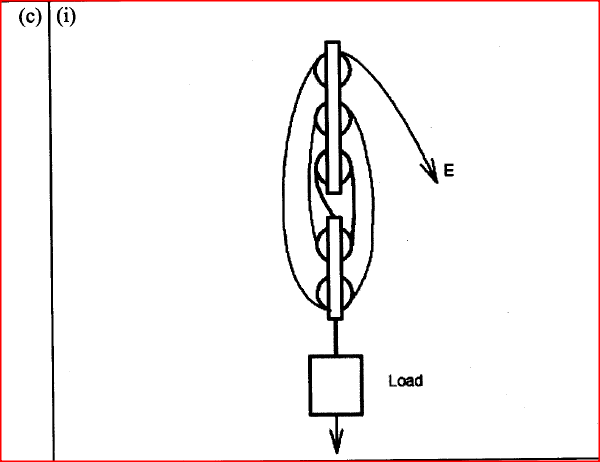
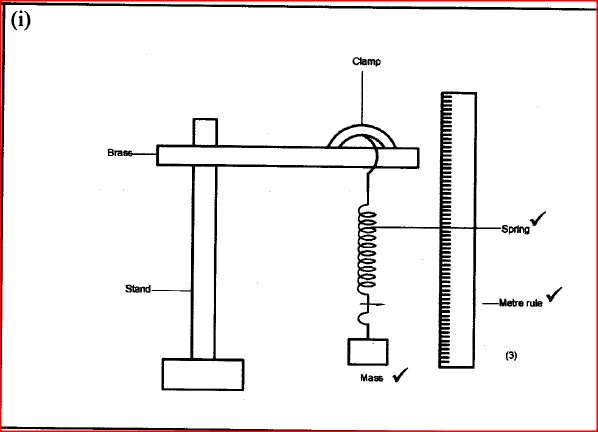
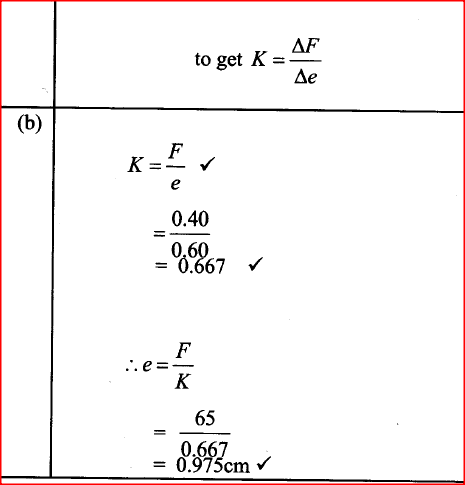
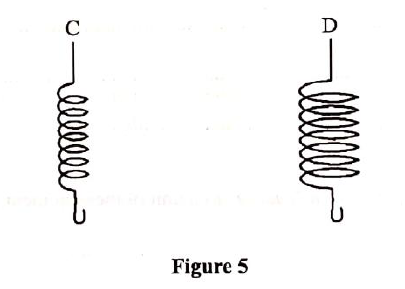
(a) The diagram in the figure below represents a wheel and axle used as a machine, whose efficiency is 80% to raise 400N of building materials. The wheel and axles have diameters of 75cm and 15cm respectively.
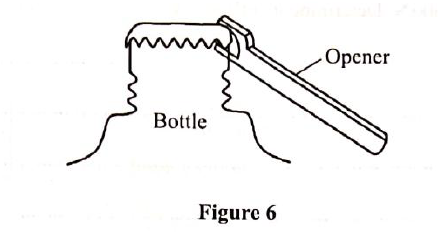
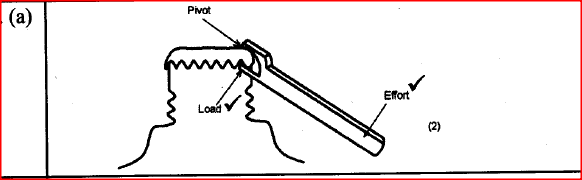
(i) Mark on the diagram the correct position and direction of the load to be lifted (1mk)(ii) Name the principle on which this machine works (1mk)
The principle of moments
(iii) Calculate the effort needed to raise the load (3mks)
(iv) The machine is operated manually and raises the load to a height of 5m in 20 seconds. Calculate the power developed by the operator (2mks)(b)
|
CATEGORIES
Categories
All
Topics
FORM I - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM II - PHYSICS SYLLABUSTOPICS
FORM III - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM IV - PHYSICS SYLLABUSARCHIVES
RSS FEEDS
AUTHOR
M.A NyamotiMy passion is to see students pass using right methods and locally available resources. My emphasis is STEM courses
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|
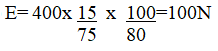
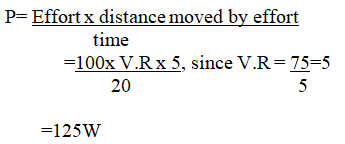

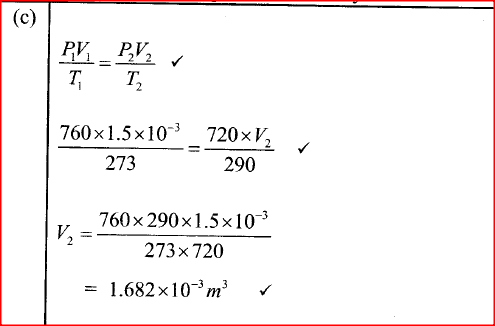

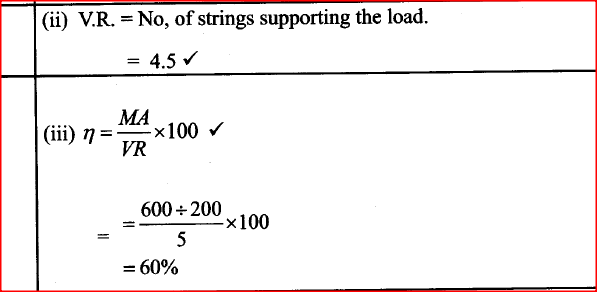






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed