(a) Define Radio-activity (2mks)
Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of a nucleus releasing
alpha, beta and gamma radiations accompanied by the release of energy (b) When carrying out experiments with radioactive substances the source should never be held with bare hands but with forceps. Explain? (1mk)
Radioactive substances are harmful to body cells when ingested
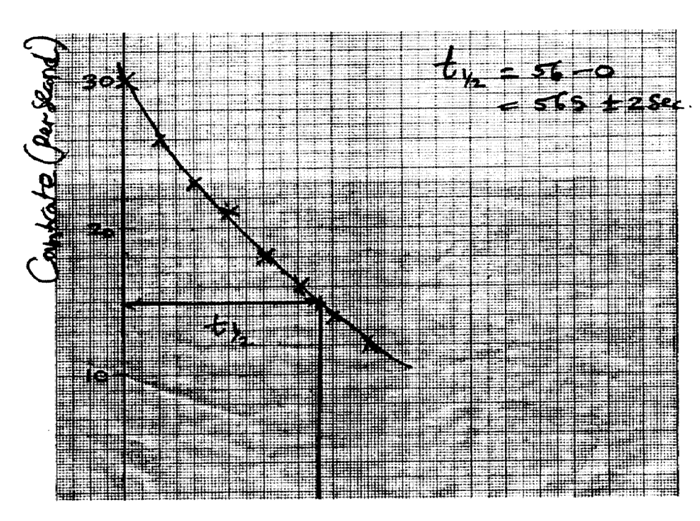
(i) Plot on the graph paper provided the graph of the count rate (y-axis) against time(ii) From the graph, determine the half-life of Radon-220 (1mk)
Half-life of radon 220=54 sec + 2 (showing on graph a must)
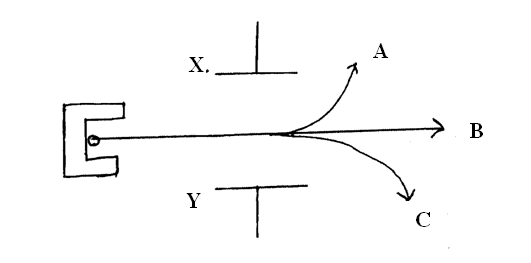
(e) The diagram in the figure below shows paths taken by three radiations A,B and C from a radioactive isotope through an electric field.(i) State the charge on plate Y (1mk)
(ii) Identify the radiations A and C (2mks)
(iii) Give a reason why C deviates more than A (1mk)
C more massive than A
0 Comments
Explain what you understand by each of the following terms:(i) Angular velocity (1mk)
The angle covered in radians per second by an object in circular motion
(ii) Centripetal force (1mk)
The force that keeps an object in circular motion
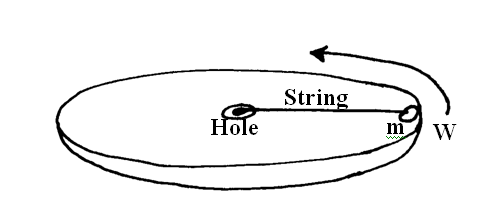
b) A bicycle wheel with radius 28cm moves with a linear velocity of 8m/s, determine(i) the angular velocity of the wheel (2mks)(ii) the centripetal acceleration of a point on the rim of the wheel (2mks)(c) To determine the relationship between angular velocity w and tension T, a student used a smooth disc with a hole at the centre, a string and cylindrical object of mass m, as shown belowDescribe how the student went about determining the relationship, specifying any other necessary material or instrument not shown in the diagram (3mks)
The cylindrical mass was attached to a known weight, T, hanging freely below the hole. The disc was rotated with an increasing angular velocity w, till the hanging weight was steady. The experiment was repeated to obtain other values of w and their corresponding hanging weights
Define crystal cleavage (1mk)This is the phenomenon in which crystals break/fracture along specific planes to yield fresh smooth surface when hit or subjected to mechanical shock
|
CATEGORIES
Categories
All
Topics
FORM I - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM II - PHYSICS SYLLABUSTOPICS
FORM III - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM IV - PHYSICS SYLLABUSARCHIVES
RSS FEEDS
AUTHOR
M.A NyamotiMy passion is to see students pass using right methods and locally available resources. My emphasis is STEM courses
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|
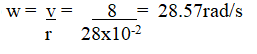
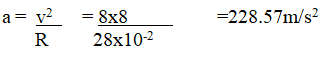
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed