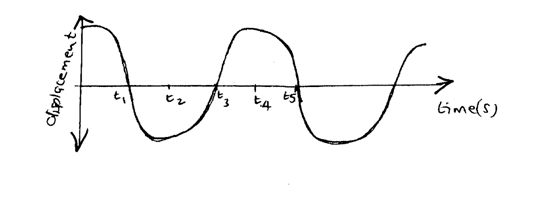
The figure bellows shows a wave profile for a wave whose frequency is 2HZDetermine the value of t3(s) (2mks)Solution
0 Comments
Give a reason why gases are poor transmitters of sound (1mk)
Molecules in gases are much further apart
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2019PP2QN16
(a) Define the following terms as used in waves:
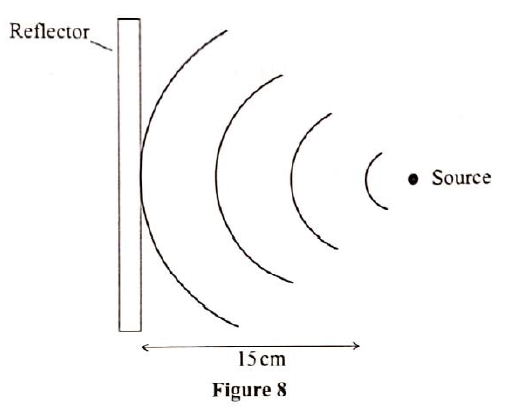
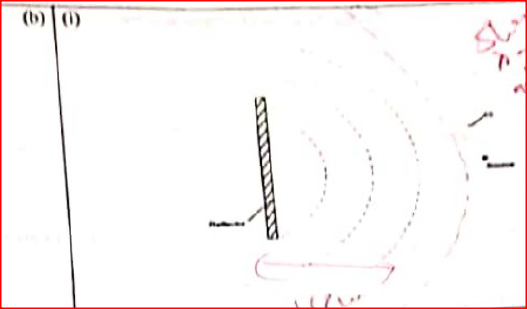
(I) Amplitude (ii) Wavelength (b) Figure 8 shows water waves approaching a straight reflector at a speed of 40 cm/s.
(I) Draw on the diagram the reflected waves.
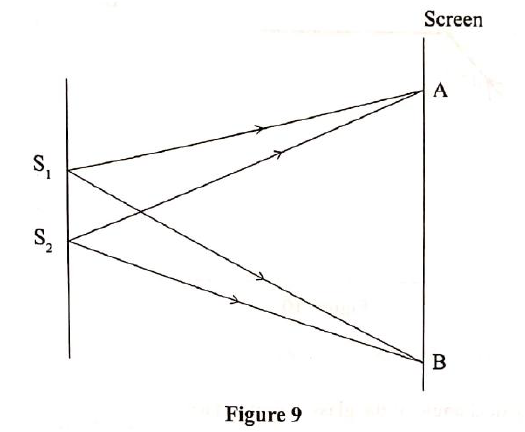
(ii) Given that the distance between the source and the reflector is 15 cm determine: I. the wavelength of the waves II. the frequency of the waves (c) Figure 9 Shows light rays from two coherent sources S1 and S2 falling on a screen. Dark and bright fringes are observed between A and B
(i) State how:
I. bright fringes are formed II. dark fringes are formed (ii) State what is observed when light of a higher frequency is used.
ANSWERS
(a)(i)Amplitude is the maximum displacement of a particle from the mean position
(ii)Wavelength is the distance between two successive points in a wave which are in phase OR Distance between two successive crests or troughs in a transverse Wave/between rarefaction or compressions in a longitudinal wave.
(c)(I) due to constructive interference
(II) due to destructive interference (ii) The fringes get closer OR When the frequency is higher the wavelength reduces hence the fringe separation decreases K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP2QN19
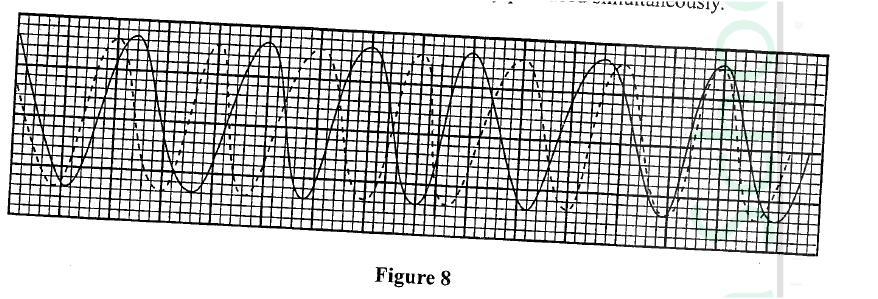
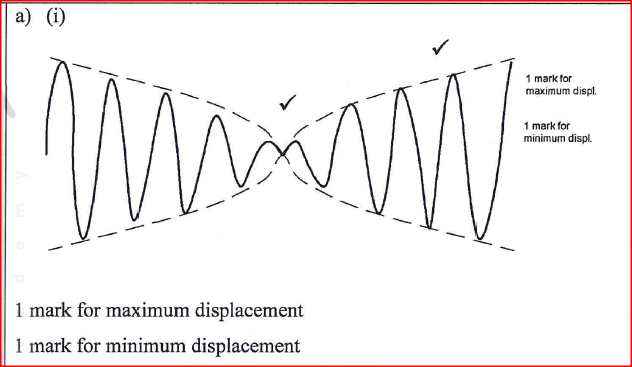
Figure 8 shows two waves of nearly equal frequency produced simultaneously.
On the space provided, sketch the resultant of the two waves (beats).
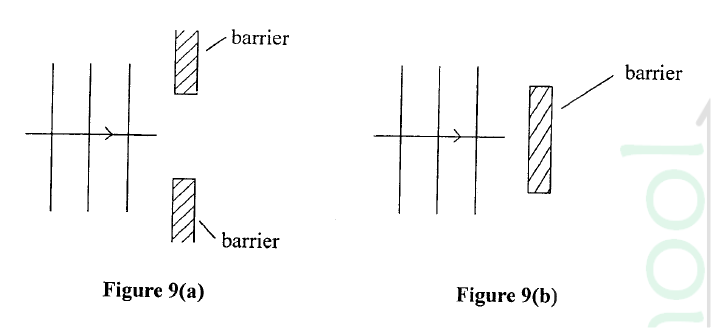
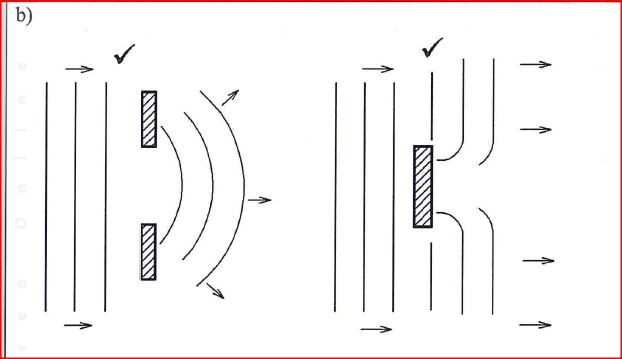
(b) Figure 9(a) and 9(b) show barriers placed in the path of plane waves.
On each figure, sketch the pattern of waves after they pass the barrier.
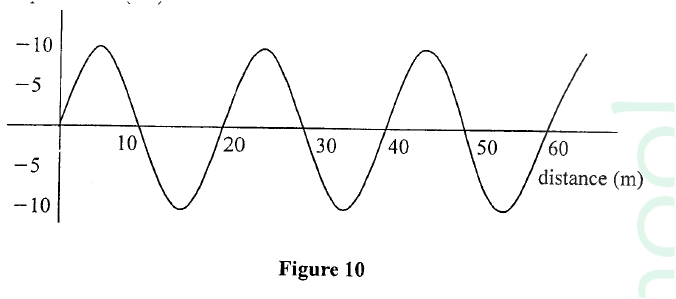
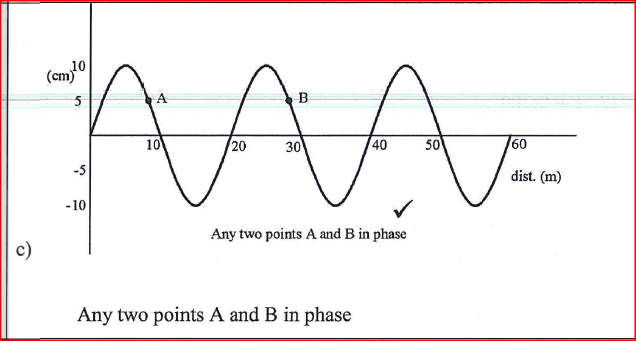
(c) Figure 10 shows a displacement—distance graph for a certain wave motion.
(i) Indicate on the figure with letters A and B any two points that are in phase.
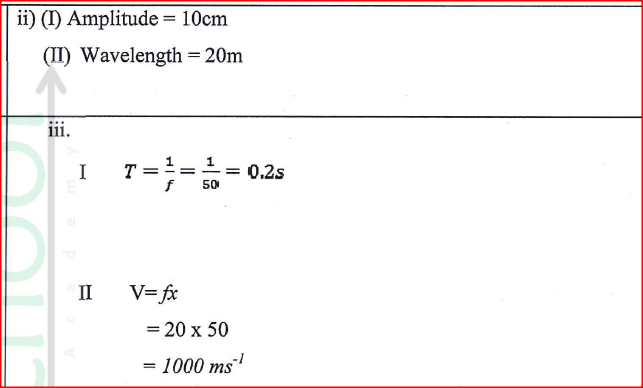
(ii) Determine the: (I) amplitude of the wave (II) wavelength of the wave (iii) Given that the frequency of the waves is 50 Hz, determine the: (I) period (II) speed of the wave K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP2QN17
(a) Water waves from a certain Source move from the shallow end to the deep end. State the change that occurs at the deep end on the following:
(i) Frequency (ii) Wavelength (iii) Velocity
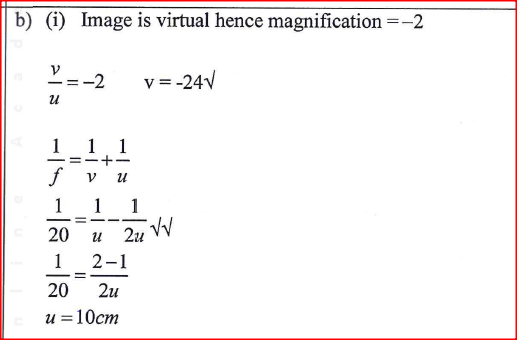
(b) (i) A biconvex lens forms an upright image twice the size of the object. If the focal length of the lens is 20cm, determine the object distance.
(ii) State two optical instruments which produce a magnified real image using a Convex lens. (c) State one difference between the working of the human eye and the lens of a camera. (d) A lens of focal length 2Ocm forms a virtual image when an object is placed 60cm from the lens. State with a reason the type of lens used.
answers
(a)(i) No change in frequency
(ii) Wavelength increases (iii) Velocity increases
(ii) a film projector
A compound microscope (c) In a camera focusing is done by changing the distance between the lens and the film. While in the eye focusing is done by changing the curvature of the lens. d) Diverging lens Forms a virtual image when the object distance is greater than the focal length. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN12
Figure 3 shows a transverse wave.
Determine the frequency of the wave.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN06
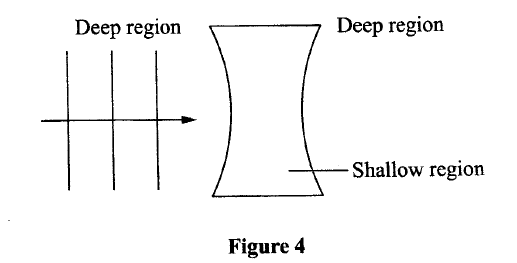
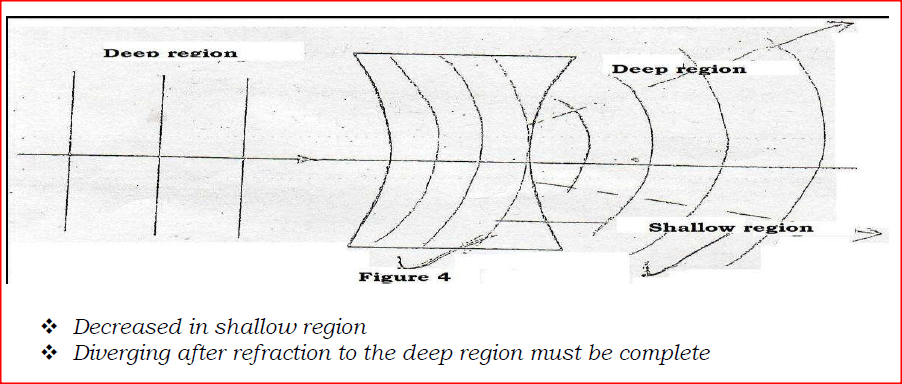
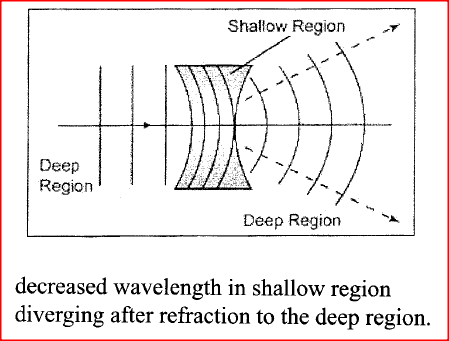
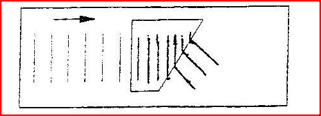
Figure 4 shows straight waves incident on a diverging lens placed in a ripple tank to reduce its depth
Complete the diagram to show the waves in both the shallow region and beyond the lens.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN04
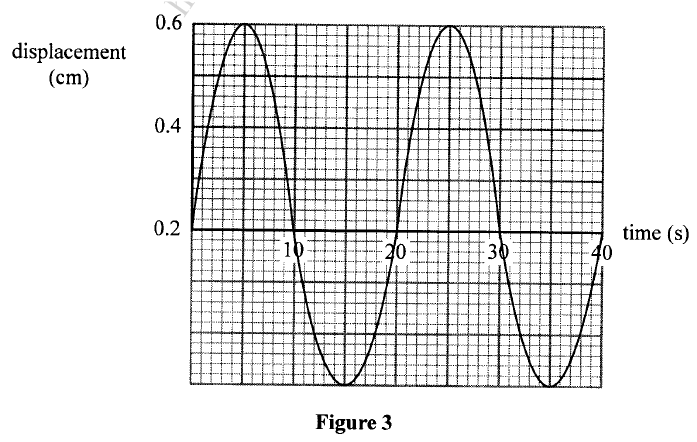
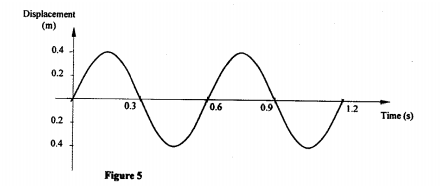
Figure 5, shows how the displacement of a point varies with time as a wave passes it.
On the same diagram, draw a wave which passes the point with half the amplitude and twice the frequency of the one shown.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN08
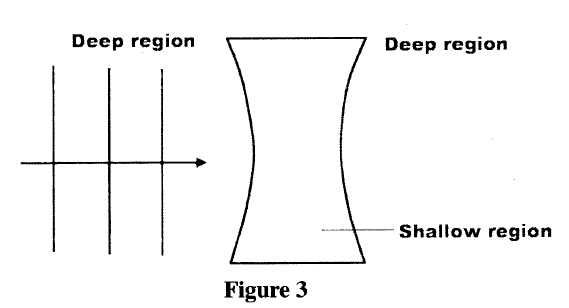
Figure 3 shows straight waves incident on a diverging lens placed in a ripple tank to reduce its depth.
Complete the diagram to show the waves in both the shallow region and beyond the lens.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN07
State two differences between electromagnetic waves and mechanical waves.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN04The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is 4.0 X 106 Hz. Determine its wavelength. (take speed of light as 3.0 X 108ms-1.K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN03
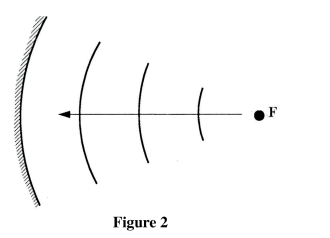
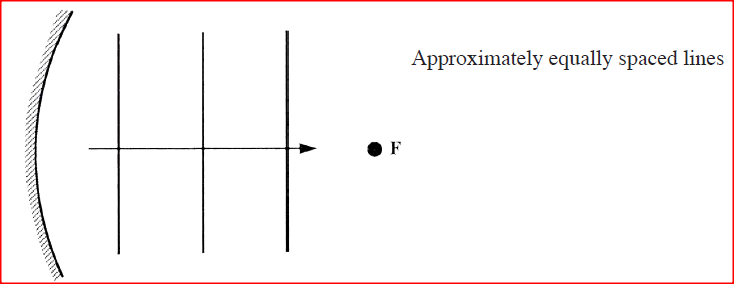
Figure 2 shows circular waves originating from the principal focus F of a concave mirror and moving towards the mirror.
Complete the diagram to show the reflected waves.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN018
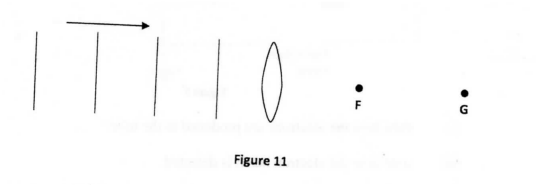
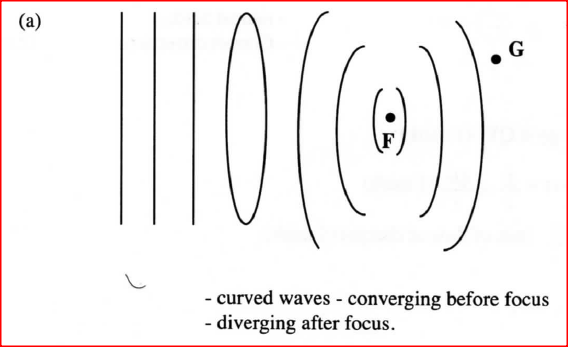
(a) Figure 11 shows plane light waves in air incident on a convex lens whose principal focus is F, the waves move past point G.
Complete the diagram to show the pattern of the emergent waves between the lens and point G.
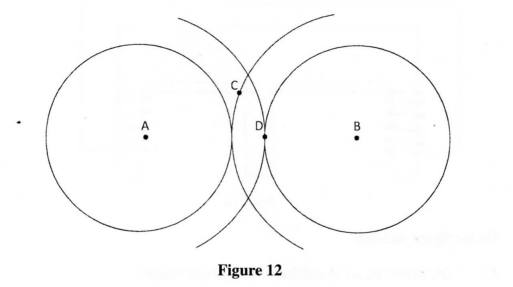
(b)Figure 12 shows crests of circular water waves spreading from two points A and B due to a vibrator. C and D are points on the surface of the water.
Given that the amplitude of each wave is 5 cm, state with a reason the amplitudes of the waves at point:
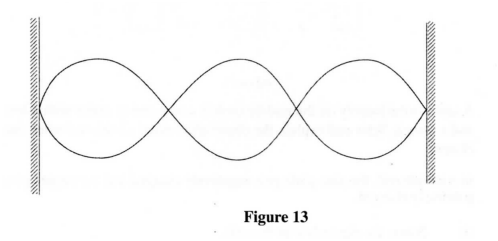
(i) C; (ii) D. (c) Figure 13 shows a standing wave formed when a string of length 1 .5 m stretched between two supports is plucked in the middle.
(î) Explain how the standing wave is formed.
(ii) Determine the wavelength of the standing wave. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2012PP2QN014
(a) Figure 12, shows a displacement - time graph for a progressive wave.
(i) state the amplitude of the wave.
(ii) determine the frequency of the wave. (iii) given that the velocity of the wave is 20m/s,determine its wavelength. (b) Figure 13 shows two identical dippers A and B vibrating in water in phase with each other. The dippers have the same constant frequency and amplitude, The wavesproduced are observed along line MN:
It is observed that the amplitudes are maximum at points Q and S, and minimum at points P and R.
(i) explain why the amplitude is maximum at Q. (ii) state why the amplitude is minimum at R. (iii) State what would happen if the two dippers had different frequencies. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN09
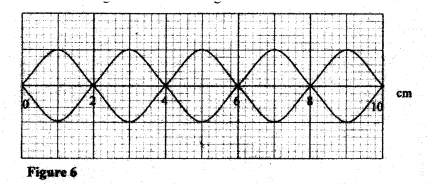
Figure 6, shows standing waves on a string. It is drawn to a scale of 1:5
(a) Indicate on the diagram the wavelength of the standing wave.
(b) Determine the wavelength of the wave. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2010PP2QN08
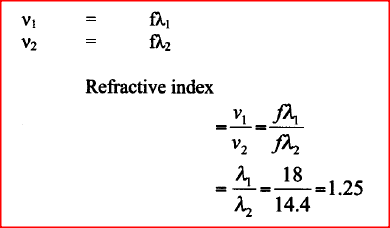
A water wave of wavelength 18 mm is incident on a boundary of shallow water at right angles. If the wavelength in the shallow end is 14.4 mm, determine the refractive index of water for a wave moving from the deep to the shallow end.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2010PP2QN07
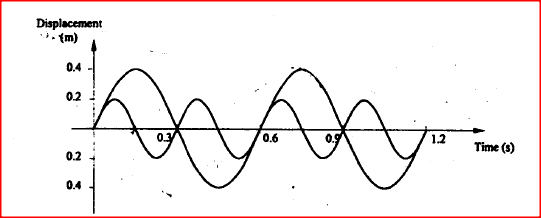
Figure 5, shows how the displacement of a point varies with time as a wave passes it.
On the same diagram, draw a wave which passes the point with half the amplitude and twice the frequency of the one shown.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2009PP2QN19
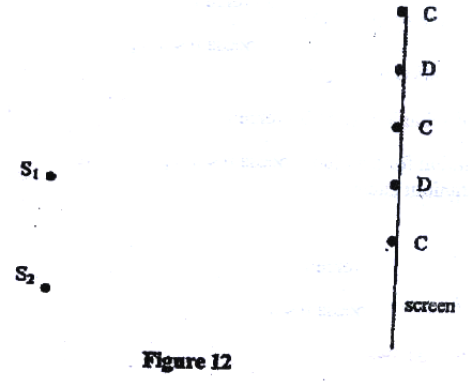
Figure 12 shows a set up for observing interference of waves from two sources S1 and S2. The points C and D represent positions of the constructive and destructive interference respectively as observed on the screen
(a) If the observation was made in a ripple tank, describe:
(i) How the constructive and destructive interferences are identified (b) Explain how the constructive interference C and the destructive interference D patterns are produced. Draw: (i) The line joining all points where waves from S1 and S2 have traveled equal distance. Label it A (ii) The line joining all points where waves from S2 have traveled one wavelength further than the waves from S1. Label it B. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2009PP2QN06
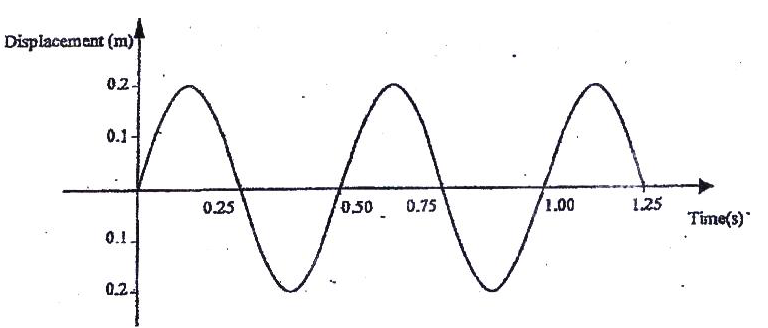
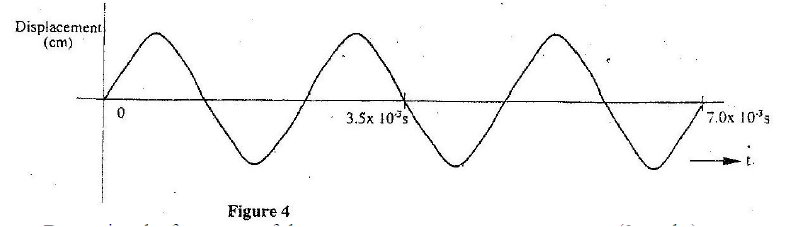
Figure 2 shows how the displacement varies with time for a certain wave
Determine the frequency of the wave
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2008PP2QN08
Figure 5 shows wavefronts approaching the boundary between two media.
The speed of the waves in medium (2) is higher than that in medium (1). On the same diagram complete the figure to show the wavefronts after crossing the boundary.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2007PP2QN06
Figure 5 (a) and (b), show wavefronts incident on barriers blocking part of the path.
On the same figures sketch the wavefronts to show the behavior of the waves as they pass each barrier and after passing the barrier.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2007PP2QN05
Figure 4. shows the displacement – time graph for a certain wave
Determine the frequency of the wave
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2006PP2QN05
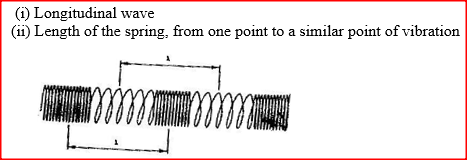
A long coil is attached to a vibrating blade as shown in figure 3
State the type of mechanical wave generated by the set - up and mark alongside the coil, the length corresponding to the wavelength of the wave.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN32
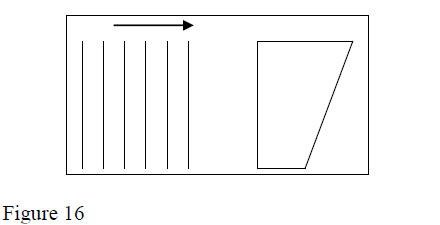
Fig 16 shows wave fronts in a ripple tank approaching a shallow region in the tank
Complete the diagram to show the wave front as they pass over the shallow region and after leaving the regions
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN28
Fig 15 shows an arrow which indicates the direction of travel of a wave in a medium. P is a particle of the medium that is in path of the wave.
In the space provided sketch diagram to show how the particles P moves when the wave is
(i) A transverse wave (ii) A longitudinal wave. |
CATEGORIES
Categories
All
Topics
FORM I - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM II - PHYSICS SYLLABUSTOPICS
FORM III - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM IV - PHYSICS SYLLABUSARCHIVES
RSS FEEDS
AUTHOR
M.A NyamotiMy passion is to see students pass using right methods and locally available resources. My emphasis is STEM courses
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|
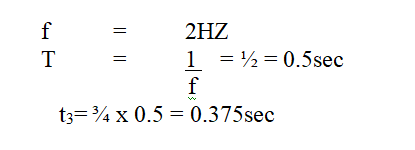


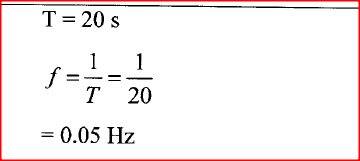



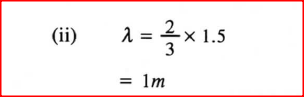





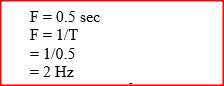





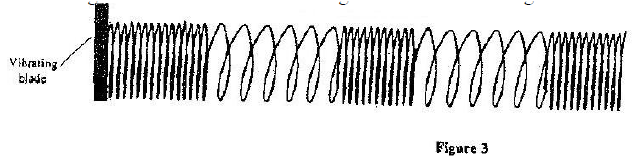


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed