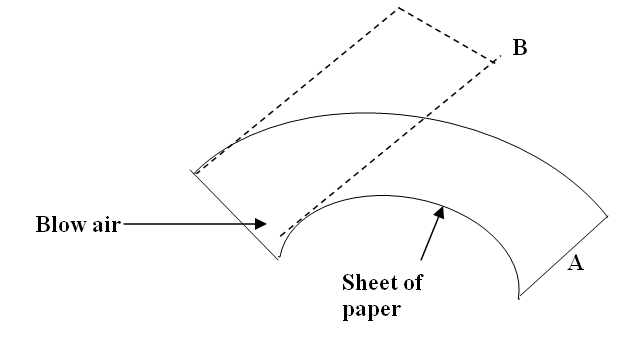
A student holds a sheet of paper at an end so that it hangs in the position A as shown below17/10/2021 Explain why the paper rises to the position B when the student blows air in the direction shown by the arrow (2mks)There is pressure difference created as a result of air blown above the paper i.e. high velocity , low pressure
0 Comments
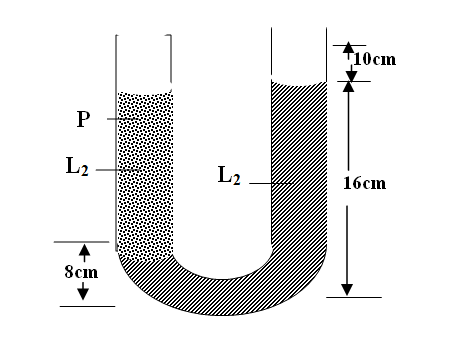
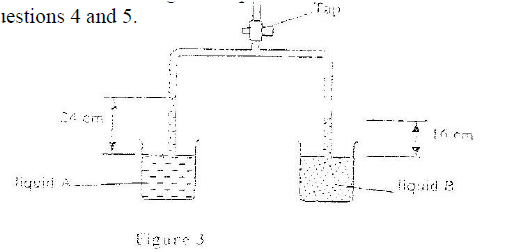
(a) Mark accurately the point in liquid L2 that is at the same pressure as point P (1mk)
AT the same level as O in the right limb
(b) Determine the number of times L1 is denser than L2 (2mks)
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN17
(a) State Pascal’s principle of transmission of pressure in liquids.
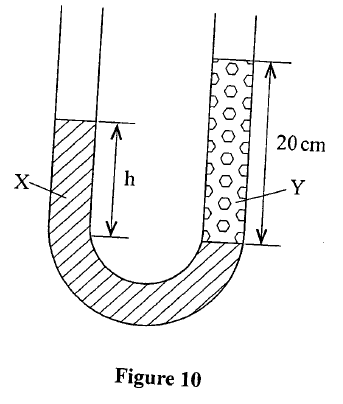
(b) Figure 10 shows heights of two immiscible liquids X and Y in a U-tube (drawn to scale).
(i) State with a reason which of the two liquids X and Y has a higher density.
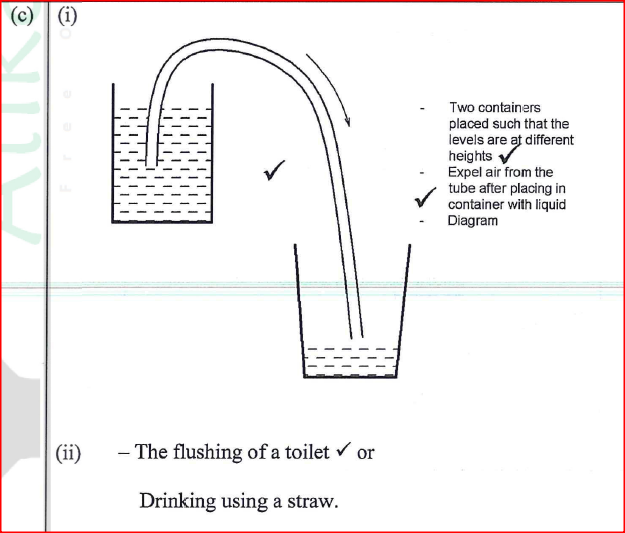
(ii) Determine the value of h. (iii) Given that the density of liquid Y is p, write down an expression for the density d of liquid X ¡n terms of p. (c) (i) With the aid of a diagram, describe how a liquid may be siphoned from one container to another using a flexible tube. (ii) State one application of the siphon. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN04
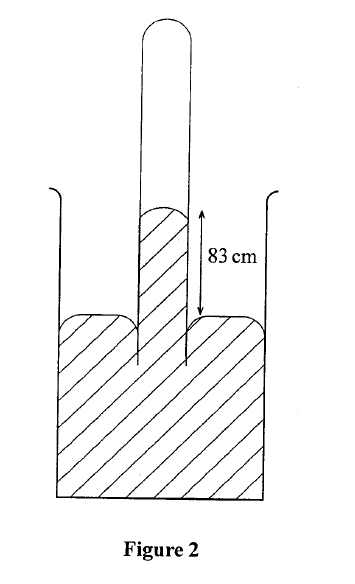
Figure 2 shows an instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure.
State with a reason the modification that would be required in a similar set up if mercury were to be replaced with water.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN18
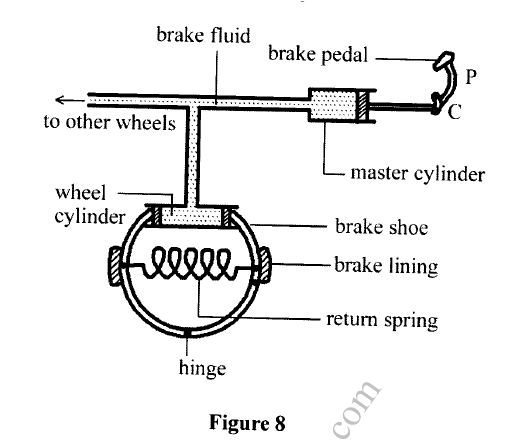
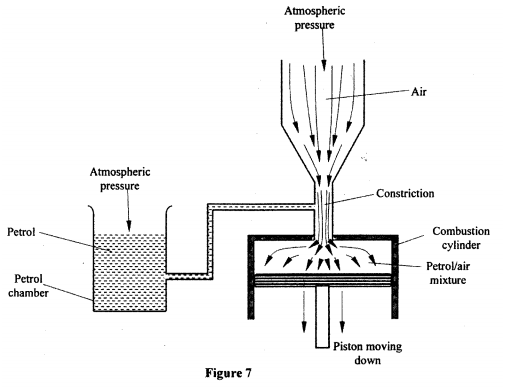
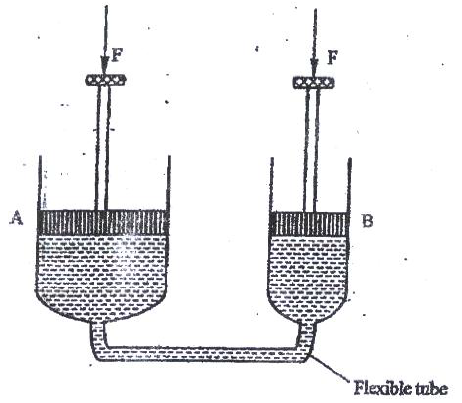
(a) Figure 8 shows part of a hydraulic brake system.
Describe how the systems works.
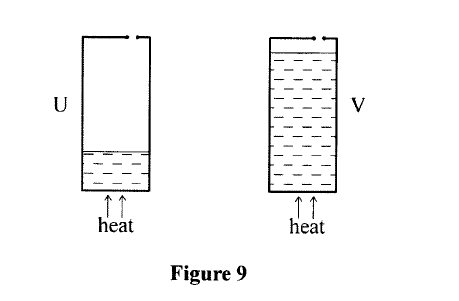
(b) State three conditions necessary for a driver to negotiate a bend on a flat level road at a relatively high speed. (c) Figure 9 shows two identical cans U and V each with a small opening at the top. Different amounts of water were put into the cans and heated until the water started to boil.
Explain what will be observed when both cans are then suddenly dipped into a cold water bath.
answers
(a) (i) The driver applies a force on the pedal.
This force transmits pressure the master cylinder fluid. Equal pressure is transmitted to the wheel cylinder causing the pistons of the wheel cylinder to push brake shoe hence Pressing the brake pads that in turn press the wheel reducing its rotation. When the applied force is removed, the return spring pulls back the shoe and pistons to the original position. (b) Higher friction (wider tyres, rougher road) Lower radius Higher mass (c) U is observed to crush. It has more steam which when cooled creates a greater vacuum hence pressure causes collapsing. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN10Figure 8 shows two cylinders of different cross-sectional areas connected with a tube. The cylinders contain an incompressible fluid and are fitted with pistons of cross-sectional areas 4 cm2 and 24 cm2.Opposing forces P and Q are applied to the pistons such that the pistons do not move. If the pressure on the smaller piston is 5 N cm2, Determine force Q.A student wearing sharp pointed heeled shoes is likely to damage a soft wooden floor. Explain.24/7/2020
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN05
A student wearing sharp pointed heeled shoes is likely to damage a soft wooden floor. Explain.
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN04
State two factors that determine the pressure at a point in a liquid.
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN07
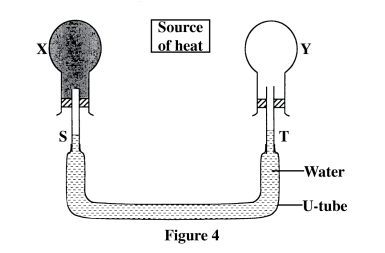
Figure 4 shows a source of heat placed at equal distances from two identical flasks X and Y containing air. The surface of X is painted black while Y is clear
X and Y are linked by a U-tube filled with water whose levels S and T are initially the same.
It is later observed that S falls while T rises. Explain this observation.
answer
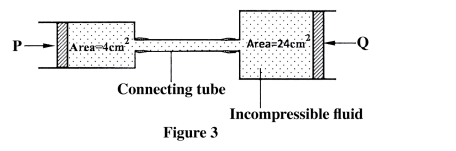
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN05Figure 3 shows two cylinders of different cross-sectional areas connected with a tube. The cylinders contain an incompressible fluid and are fitted with pistons of cross-sectional areas 4 cm2 and 24 cm2.Opposing forces P and Q are applied to the pistons such that the pistons do not move. If the pressure on the smaller piston is 5 N cm-2. Determine force Q.K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN11
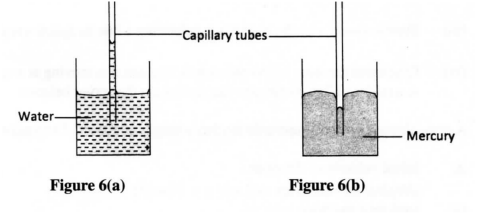
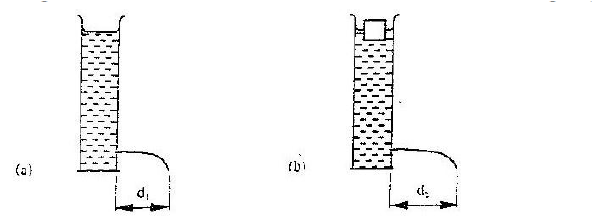
Figure 6 (a) and 6(b) show capillary tubes inserted in water and mercury respectively.
It is observed that in water the meniscus in the capillary tube is higher than the meniscus in the beaker, while in mercury the meniscus in the capillary tube is lower than the meniscus in the beaker. Explain these observations.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN10
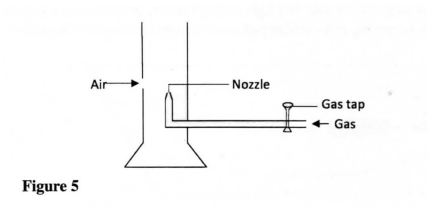
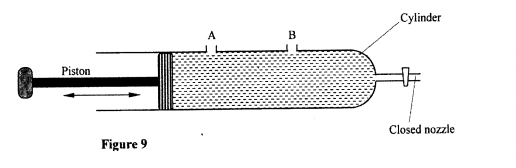
Figure 5 shows a Bunsen burner.
Explain how air is drawn into the burner when the gas tap is open.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN09
Explain why brakes fail in a hydraulic braking system when air gets into the system.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN03
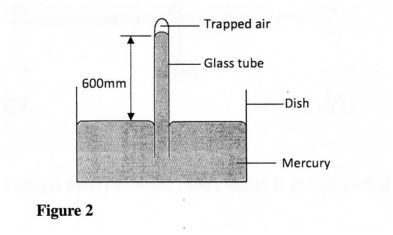
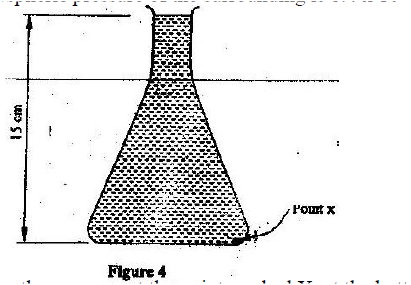
Figure 2 shows some air trapped by mercury in a glass tube. The tube is inverted in a dish containing mercury.
Given that the atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg and the height of mercury column in the tube is 600 mm, determine the pressure of the air trapped in the tube in mmHg.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN19
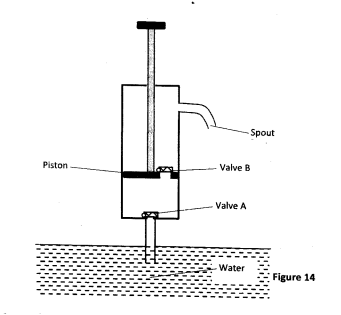
(a) Figure 14 shows a lift pump.
Explain why, when the piston is:
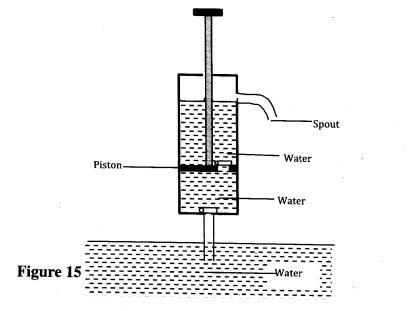
(i) pulled upwards, valve A opens while valve B closes. (ii) pushed downwards, valve A closes while valve B opens. (b) After several strokes, water rises above the piston as shown in Figure 15. State how water is removed from the cylinder through the spout.
|
CATEGORIES
Categories
All
Topics
FORM I - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM II - PHYSICS SYLLABUSTOPICS
FORM III - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM IV - PHYSICS SYLLABUSARCHIVES
RSS FEEDS
AUTHOR
M.A NyamotiMy passion is to see students pass using right methods and locally available resources. My emphasis is STEM courses
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|
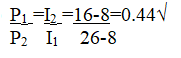




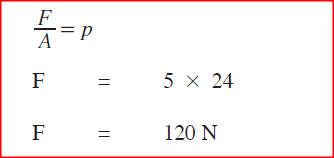

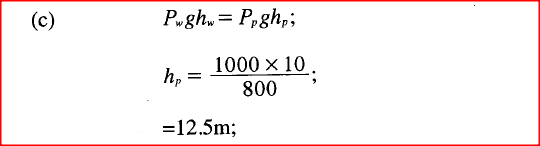
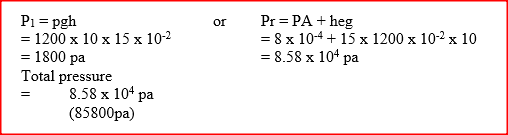

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed