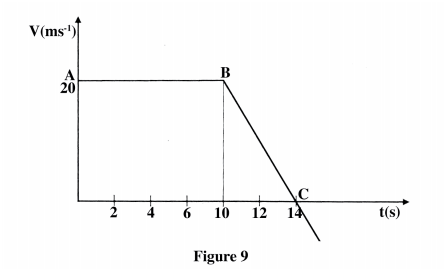
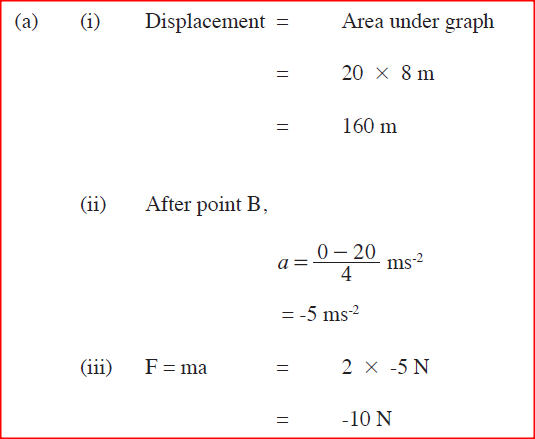
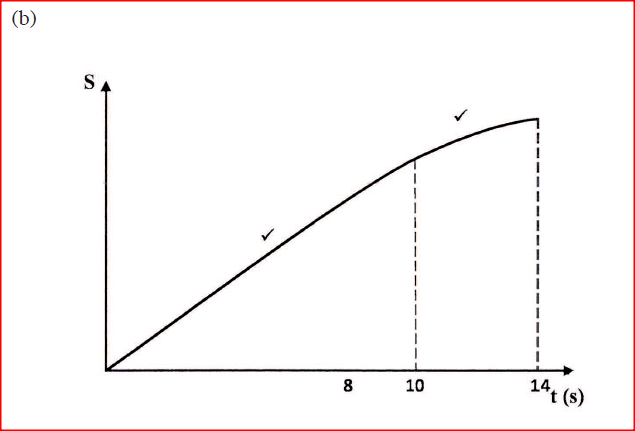
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN018
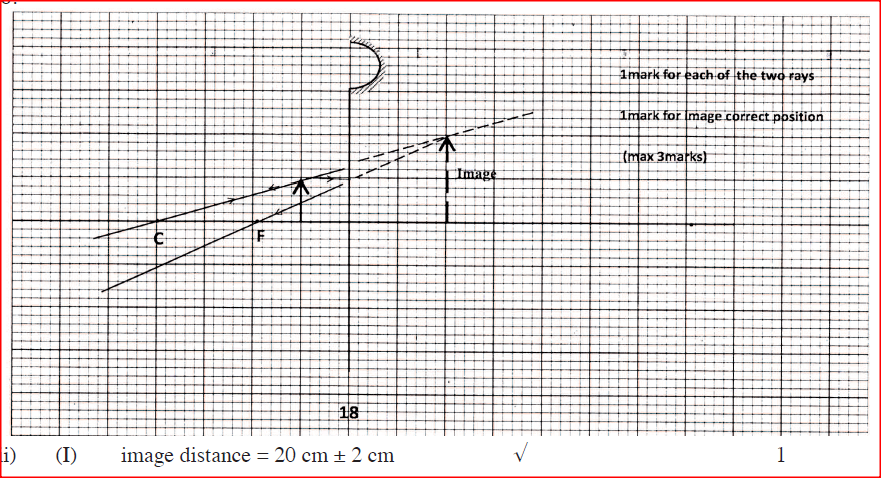
Figure 11 shows an object placed 10cm infront of a concave mirror whose radius of curvature is 40 cm.
(a) (i) On the same figure, draw a ray diagram to show the position of the image formed.
(ii) Use the ray diagram to determine: (I) the image distance. (II) the magnification. (iii) State where the position of the image would be if the object had been placed at the principal focus. (b) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a partially dark shadow and a totally dark shadow during the eclipse of the sun.
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN017
(a) Figure 9 shows two speakers and S2 which produce sound of the same frequency.
They are placed equidistant from a line AB and a line PQ. (PQ is perpendicular to line AB).
(i) A student walking from A to B hears alternating loud and soft sounds. Explain why at some point the sound heard is soft.
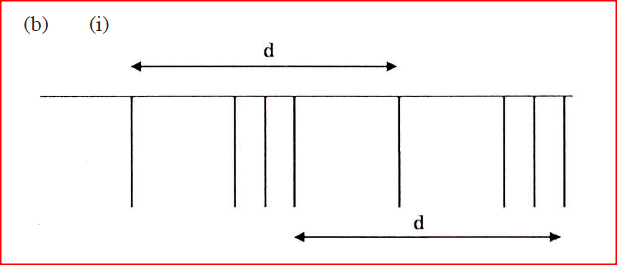
(ii) The student now walks along line PQ. State with reason the nature of the sound the student hears. (b) Figure 10 shows sound waves in air produced by a vibrating tuning fork. R is an air molecule on the path of the waves.
(i) Using a line, indicate on the diagram a distance d equal to one wavelength of the wave.
(ii) In the space provided, show with an arrow the direction of motion of the air molecule R as the waves pass. (iii) Explain the reason for the answer in (ii).
answers
(a) (i) (I) sound is soft when the waves arrive out of phase;such waves undergo destructive interference.
(ii) same sound — loud. Along PQ the waves undergo constructive interference as they arrive in phase.
(iii) As the longitudinal waves pass molecule R moves along to either side.
For a crest. R moves away from source. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN16
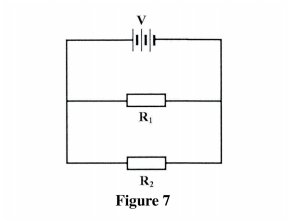
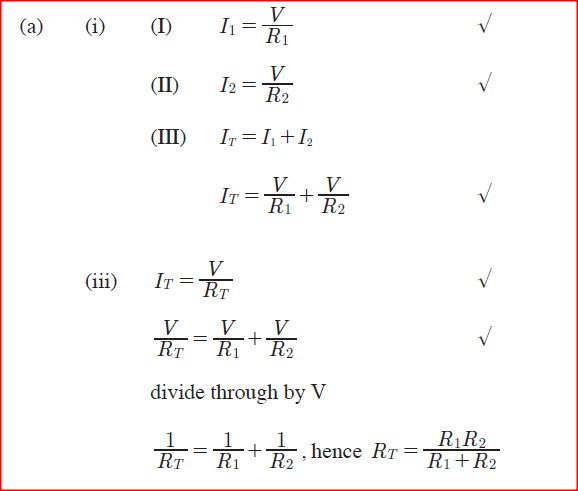
(a) Figure 7 shows resistors R1 and R2 connected in parallel. Their ends are connected to a battery of potential difference V volts.
(i) In terms of V1, R1 and R2, write an expression for:
(I) current I, through R,. (II) current I2 through R,; (III) total current I in the circuit.
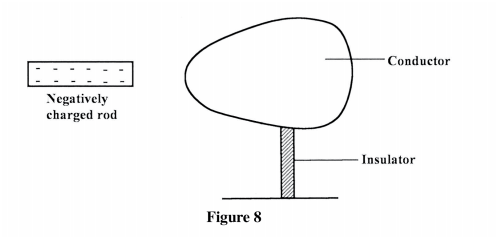
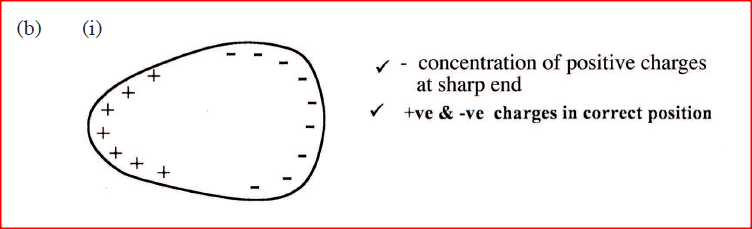
(b) Figure 8 shows a negatively charged rod placed near an uncharged conductor resting on an insulating support.
(i) Show the charge distribution on the conductor.
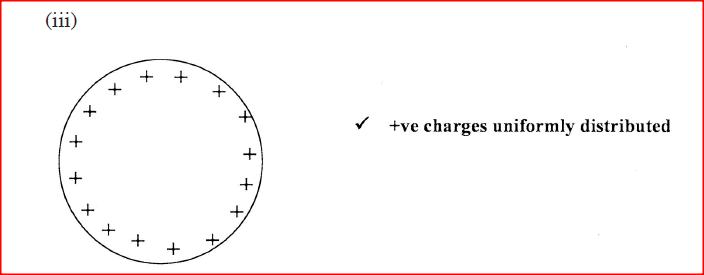
(ii) State the effect: (I) of momentarily touching the conductor with a finger while the charged rod is still near the conductor. (II) on the charge distribution of withdrawing the negatively charged rod after momentarily touching the conductor. (iii) In the space provided, sketch a diagram to show how the charge in ii (II) would have been distributed if the conductor was a sphere. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN15
(a) One of the causes of energy loss in a transformer is heating in the coils when current flows. State:
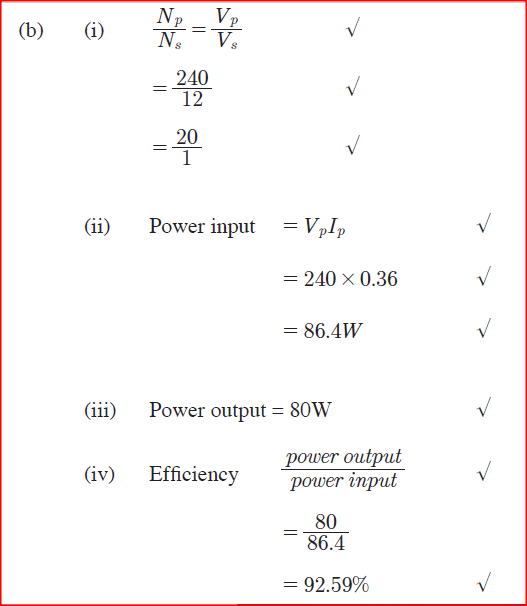
(i)the reason why the current causes heating. (ii) how the heating can he minimized. (b) The input voltage of a transformer is 240 V and its output is 12 V. When an 80 W bulb is connected across the secondary coil, the current in the primary coil is 0.36 A
Determine:
(I) the ratio Np/Nsof the transformer, (where Np is the number of turns in the primary coil and Ns is the number of turns in the secondary coil) (ii) the power input of the transformer. (iii) the power output of the transformer. (iv) the efficiency of the transformer. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN14
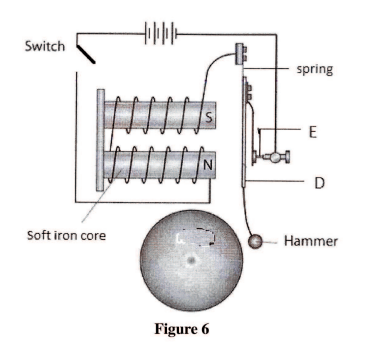
(a) Figure 6 shows a simple electric bell circuit
(i) Name the parts labelled:
(I) D (II) E (ii) When the switch is closed, the hammer hits the gong repeatedly. Explain why: (I) the hammer hits the gong. (II) the hammer hits the gong repeatedly. (b) An electric bulb is rated 60 W, 240 V. Determine: (i) the current that flows through it when it is connected to a 240 V supply. (ii) the resistance ol the bulb.
answers
(a) (i) I D - soft iron armature
II E contacts (ii) I. Soft iron core is magnetized and attracts the armature the hammer hits the gong. II. Contact is broken when armature is attracted by the core. The core then loses magnetism. The armature loses magnetism and springs back making contact again and the process is repeated. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN13The current of electrons hitting the screen of a cathode ray oscilloscope is 2.0 X 10-4A
|
CATEGORIES
Categories
All
Topics
FORM I - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM II - PHYSICS SYLLABUSTOPICS
FORM III - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM IV - PHYSICS SYLLABUSARCHIVES
RSS FEEDS
AUTHOR
M.A NyamotiMy passion is to see students pass using right methods and locally available resources. My emphasis is STEM courses
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|







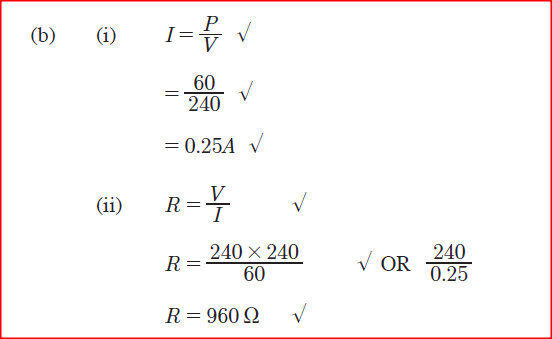















 RSS Feed
RSS Feed