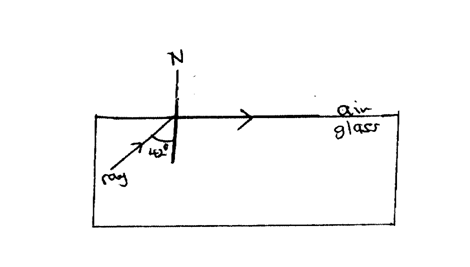
The figure below shows the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass block placed in airCalculate the refractive index of glass (2mks)
0 Comments
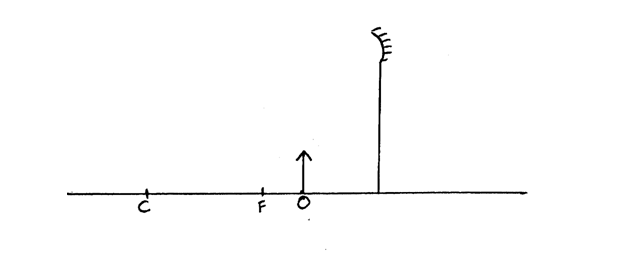
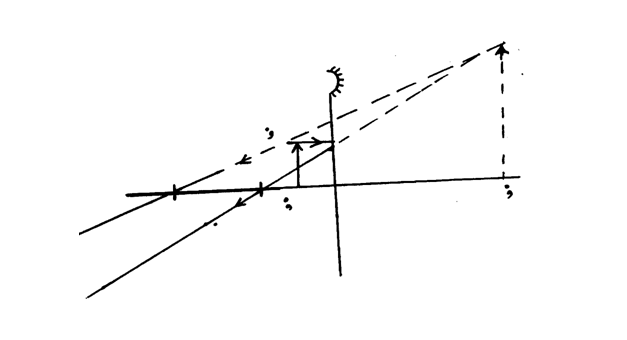
The figure below shows an object placed in front of a concave mirror. By use of correct ray diagram, locate the position of imageSolution
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2019PP2QN17
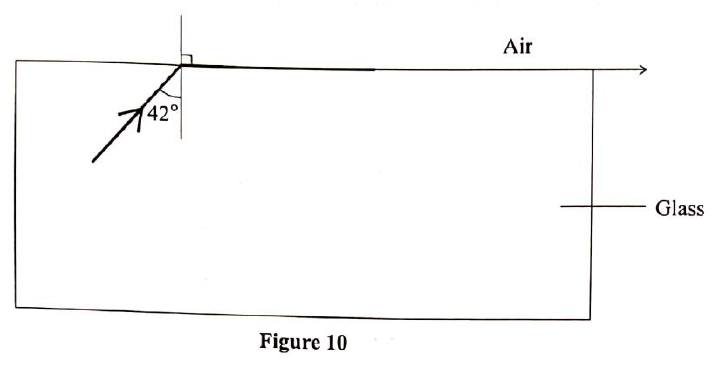
(a) Figure 10 shows a ray of light travelling from glass to air.
Determine the:
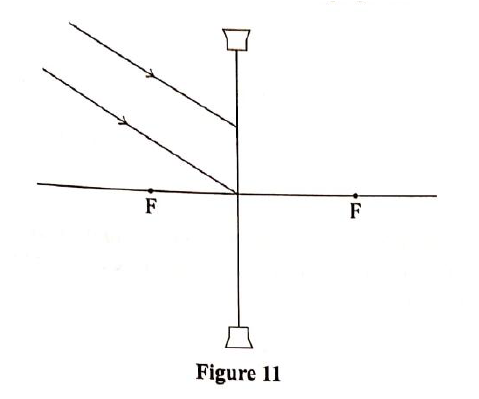
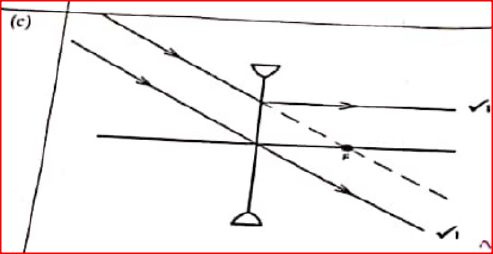
(i) critical angle of the glass — air interface (ii) refractive index of glass (b) Apiece of metal is embedded at the centre of an ice block 15cm from the surface of the ice. Given that the refractive index of ice is 1.32, determine how far from the surface of the ice block the metal appears to be. (c) Figure 11 shows, two rays of incident on a diverging lens.
Complete the ray diagram to show the path of the rays after passing through the lens.
(d) (i) State two differences between the human eye and a camera lens. (ii) State the name of the part of the eye that enable the lens to focus images of objects at different distances. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP2QN05
The angle of incident for a ray of light moving from air to a certain liquid is 30. Given that the refractive index of the Liquid is 1 .36, determine the angle of refraction.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN15
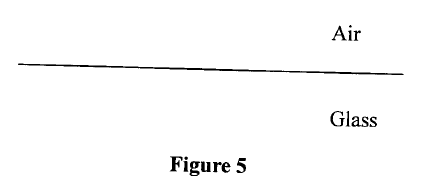
(a) Figure 5 shows the interface between glass and air.
Draw on the figure a ray diagram to illustrate the critical angle.
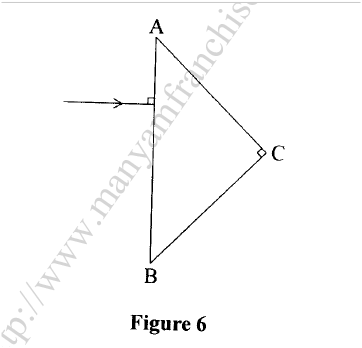
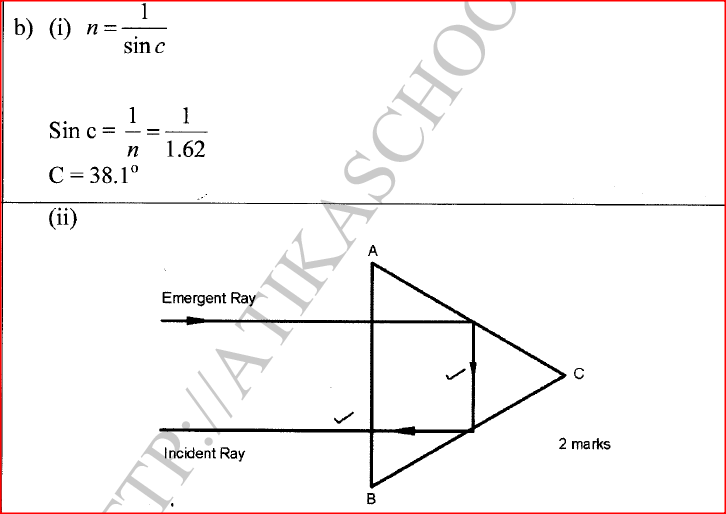
(b) Figure 6 shows a ray of light incident at right angles to face AB of a right angled glass prism of refractive index 1.62.
(i) Determine the critical angle of the material.
(ii) Complete the ray diagram to show the path of light until it leaves the prism. (c)State any two applications of prisms. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN09
Draw a ray diagram to show how a ray of light may be totally internally reflected two times in an isosceles right - angled glass prism.(Assume that the critical angle of glass is 42
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN01
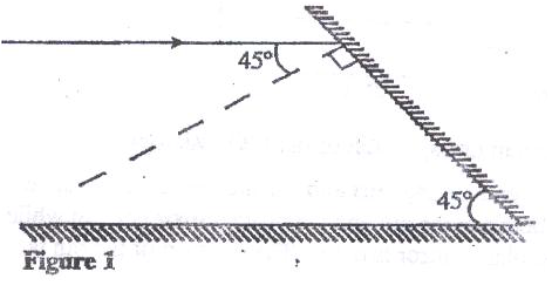
Figure 1 shows a ray of light incident on a mirror at an angle of 45°.Another mirror is placed at an angle of 45° to the first one as shown.
Sketch the path of the ray until it emerges.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN10
A nail at the bottom of a beaker containing glycerine appears to be 6.8 cm below the surface of glycerine. Determine the height of the column of glycerine in the beaker. (take the refractive index of glycerine as 1.47)
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN06
Figure 3 shows a ray of light passing into a glass prism ABC.
Sketch the path of the ray as it travels from face AC. (critical angle for glass is 42o)K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2012PP2QN05
Figure 5, shows an object O at the bottom of a beaker full of a liquid. An observer above the beaker sees its image at point X inside the liquid.
Determine the refractive index of the liquid.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2012PP2QN02K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN10
Figure 7, shows two rays of light incident normally on face PQ of a glass prism, whose critical angle is 42°.
Complete the diagram to show the paths of the two rays as they pass through the prism.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2009PP2QN16
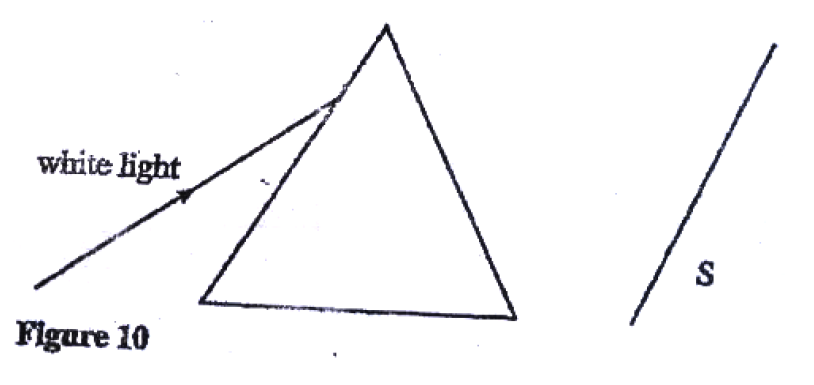
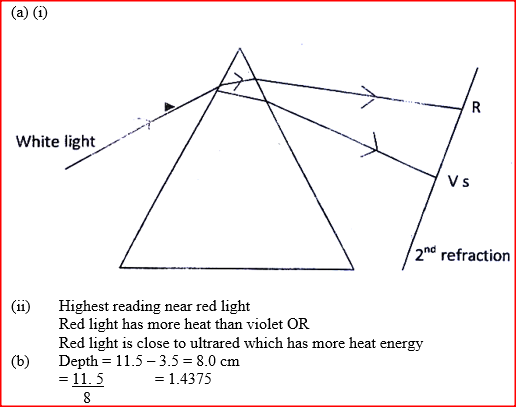
(a) Figure 10 shows a ray of light incident on a triangular glass prism and white screen S placed after the prism
(i) Complete the path of the ray through the prism to show how a spectrum is formed on the screen
(ii) A thermometer with a blackened bulb is placed at various parts of the spectrum. State with reason the region where the thermometer indicates the highest reading (b) A pin is placed at the bottom of a beaker of depth 11.5 cm. The beaker is then filled with kerosene. By using another on the side of the beaker and observing from the top, the distance of the image of the pin in the beaker is found to be 3.5 cm from the bottom. Determine the refractive index of kerosene. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2009PP2QN02Figure 1 shows a ray of light incident on a mirror at an angle of 450. Another mirror is placed at an angle of 450 to the first one as shown
Sketch the path of the ray until it emerges
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2008PP2QN16
(a) State two conditions necessary for total internal reflection to occur
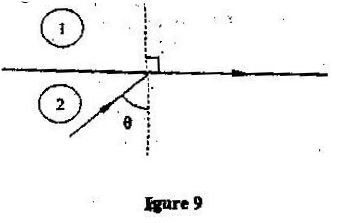
(b) Figure 9 shows a ray of light incident on the boundary between two media 1 and at an angle
Show that the refractive index for a ray of light traveling from medium 1 to medium 2 is given by:
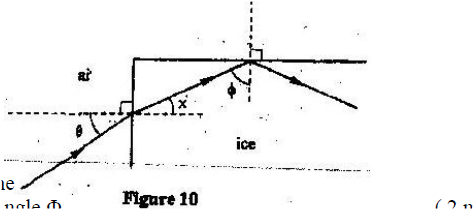
M2 = 1/Sin θ (c) Figure 10 shows a ray of light incident on one face of a block of ice of refractive index 1. 31 and totally reflected at the adjacent face
Determine
(i) Angle Φ (ii) Angle x (iii) Angle θ, the greatest angle for which the total internal reflection is possible K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2007PP2QN07
Figure 6 shows a ray of light incident on the face of a water prism
Sketch the path of the ray as it passes though the prism
Critical angle for water is 49 K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2006PP2QN19
(a) Define the refractive index of a substance
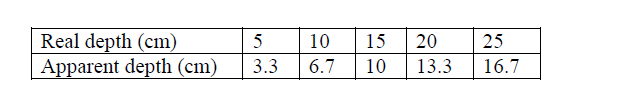
(b) In an experiment to determine the refractive index of a liquid, the liquid was poured into a measuring cylinder. A pin was placed at the bottom of the cylinder and another pin was used to locate the apparent position of the first pin. The real depth and apparent depth were measured. The experiment was repeated with other values of real depth. The table below shows the results obtained.
(i) Plot the graph of real depth against apparent depth
(ii) From the graph determine the refractive index of the liquid (c) Figure 9 shows a ray of light incident on a glass – air interfac
Given that the refractive index of the glass is 1.6. Determine angle θ
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN23&24
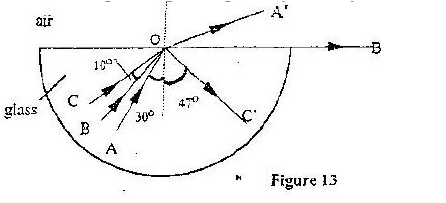
Fig 13 shows rays of light AO,BO, and CO incident on a glass-air interface. OA" OB" and OC" are the corresponding emergent rays. Study and answer questions 23 and 24.
Determine the critical angles of the glass material
Determine the refractive of index of the glass material. K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN24
Figure 13 shows a coin placed in a large empty container. And observer looking into the container from the position shown is unable to see the coin
Sketch two rays from a point on the coin to show how the observer is able to see the image of the coin after the container if filled with water.
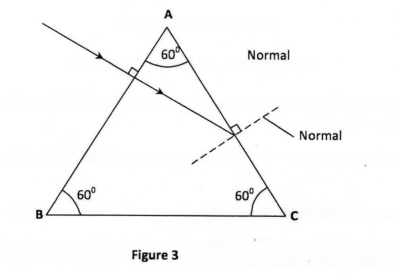
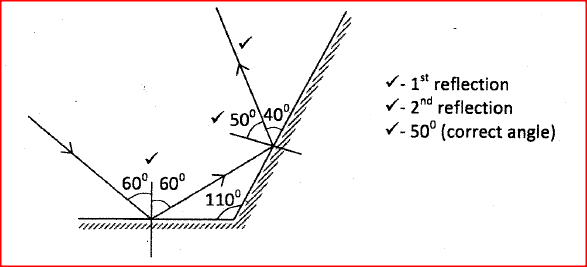
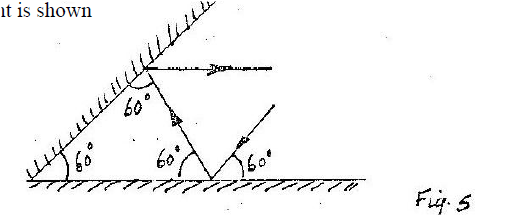
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN07Figure 5 shows two mirrors inclined at an angle of 600 to each other. A ray of light is shown
Sketch the same diagram, the path of the ray until it leaves the two mirrors. Indicate the angles at each reflection.
answer
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2002PP2QN01
Figure 1 shows the path of array of yellow light through a glass prism. The speed of yellow light in the prisms is 1.88 x 108m/s.
a) Determine the refractive index of the prism material for the light (speed of light in vacuum e = 3.0 x 108 ms-1)
b) Show on the figure the critical angle, c, and determine its value.
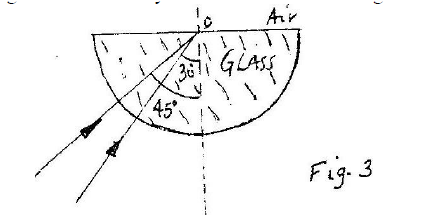
c) Given that r = 2 1 .2°, determine the angle O d) On the same figure, sketch the path of the light after striking the prism if the prism was replaced by another of similar shape but lower refractive index. (Use dotted line for your answer) K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN08Fig. 3 shows two rays of A and B entering a semi – circular glass block which has a critical angle of 42o. The rays are incident at an air – glass boundary at point O.
Complete the path of the two rays from point O. label A" and B" the corresponding rays.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2001PP1QN21
Fig. 15 14 shows a ray of light incident on a glass prism.
If the critical angle of the glass is 39 sketch on the same diagram the path of the ray until it emerges from the prism.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2000PP1QN24
Fig 13. Shows a semicircular glass block placed on a bench. A ray of light is incident at point O as shown. The angle of incidence, I , is just greater than the critical angle of glass.
A drop of water is now placed on the bench so as to make contact with the glass at point O. Sketch on the same figure the path followed by the ray after placing the drop of water.
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 1999PP1QN22
A microscope is focused on a mark on horizontal surface. A rectangular glass block 30mm thick is place on the mark. The microscope is then adjusted to 10mm upwards: to bring the mark back to focus. determine the refractive index of the glass
|
CATEGORIES
Categories
All
Topics
FORM I - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM II - PHYSICS SYLLABUSTOPICS
FORM III - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM IV - PHYSICS SYLLABUSARCHIVES
RSS FEEDS
AUTHOR
M.A NyamotiMy passion is to see students pass using right methods and locally available resources. My emphasis is STEM courses
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|
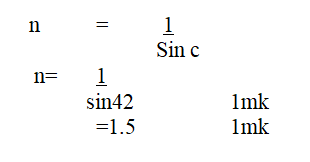


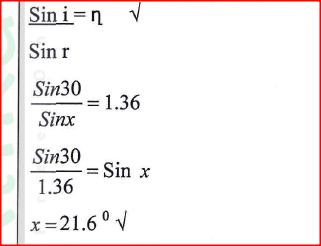













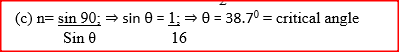




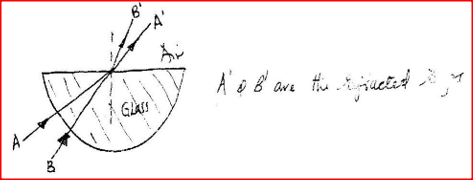



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed