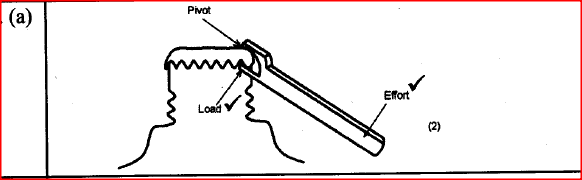
(a) Define Radio-activity (2mks)
Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of a nucleus releasing
alpha, beta and gamma radiations accompanied by the release of energy (b) When carrying out experiments with radioactive substances the source should never be held with bare hands but with forceps. Explain? (1mk)
Radioactive substances are harmful to body cells when ingested
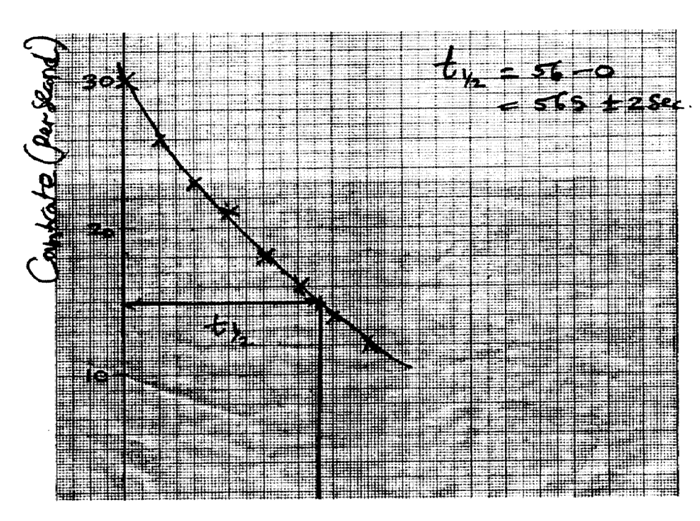
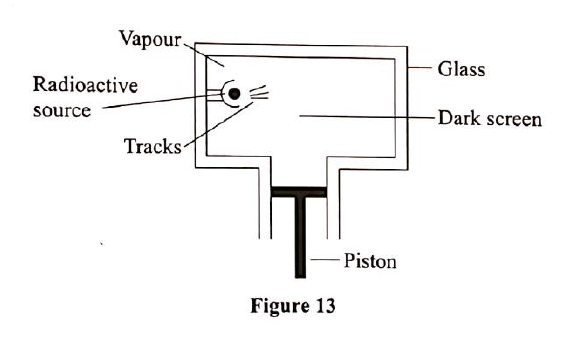
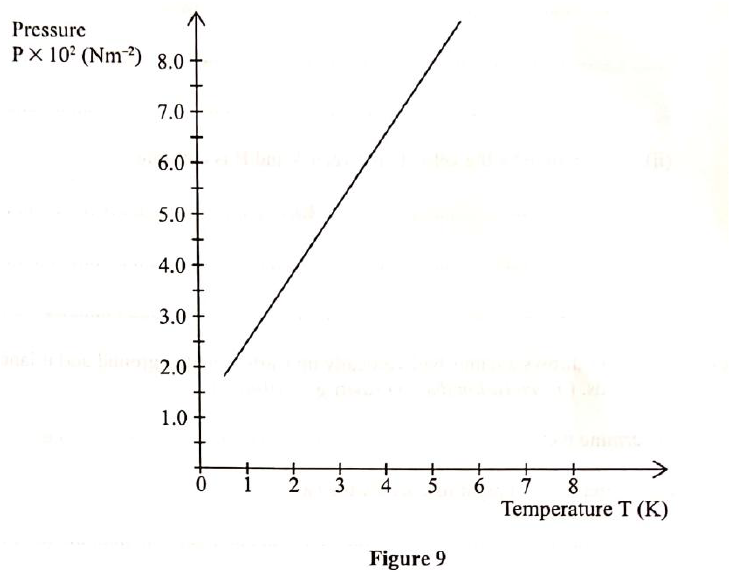
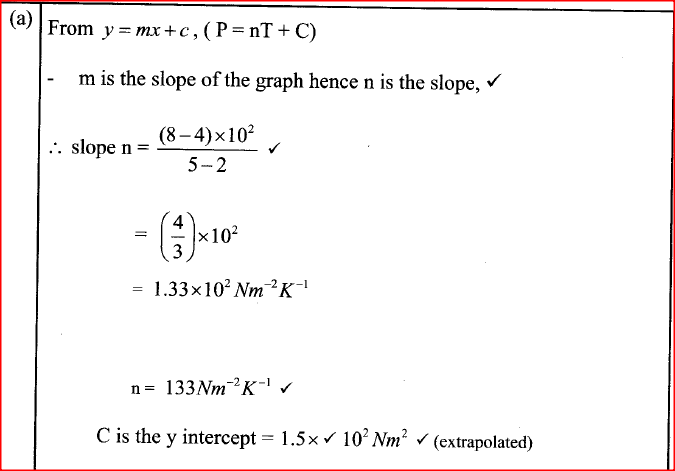
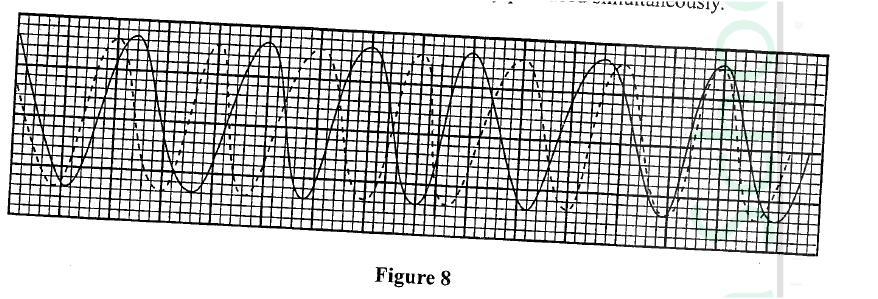
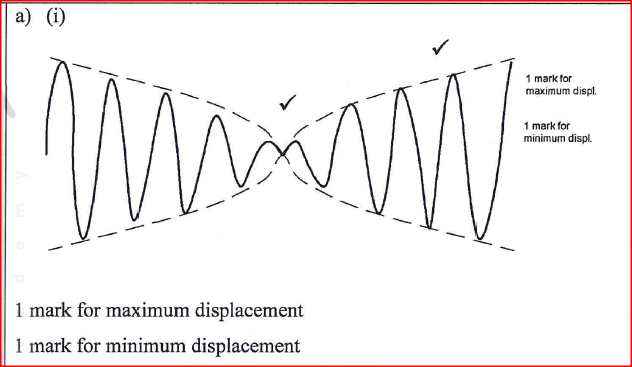
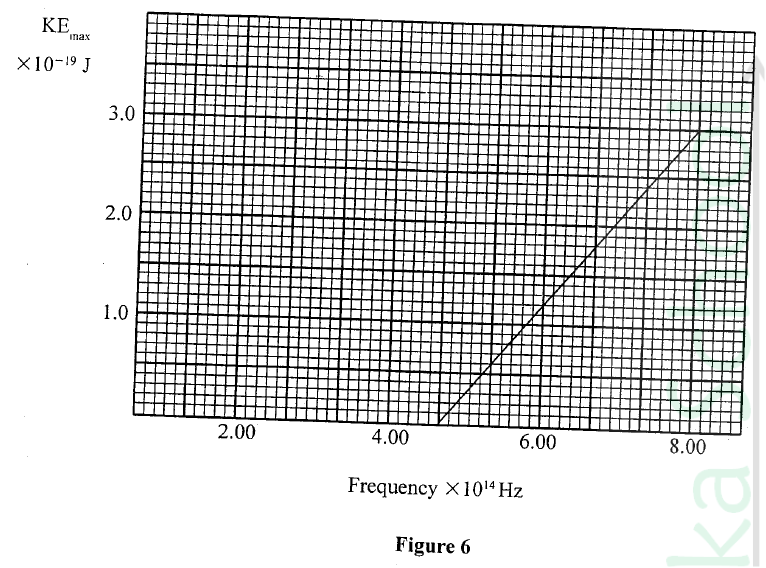
(i) Plot on the graph paper provided the graph of the count rate (y-axis) against time(ii) From the graph, determine the half-life of Radon-220 (1mk)
Half-life of radon 220=54 sec + 2 (showing on graph a must)
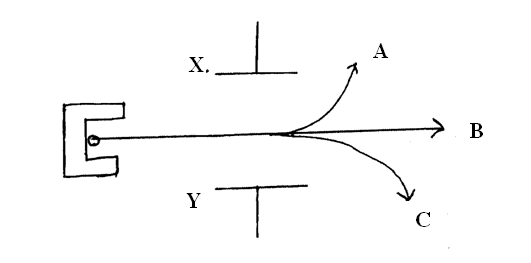
(e) The diagram in the figure below shows paths taken by three radiations A,B and C from a radioactive isotope through an electric field.(i) State the charge on plate Y (1mk)
(ii) Identify the radiations A and C (2mks)
(iii) Give a reason why C deviates more than A (1mk)
C more massive than A
0 Comments
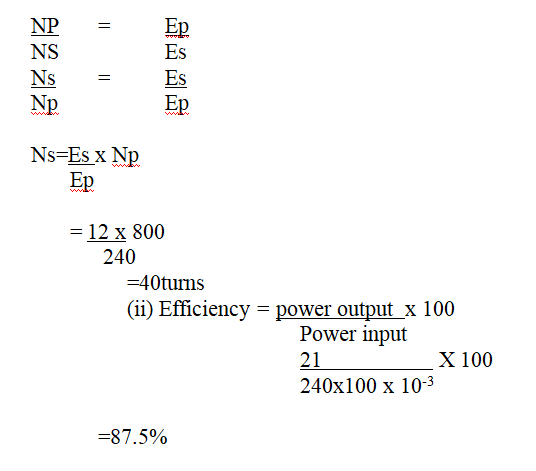
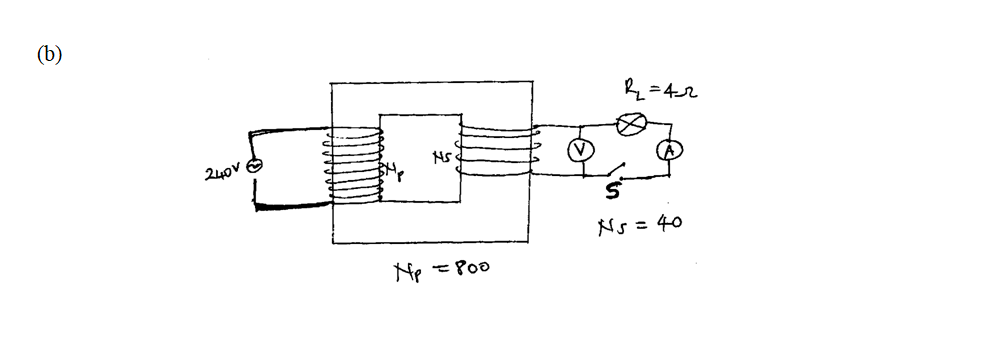
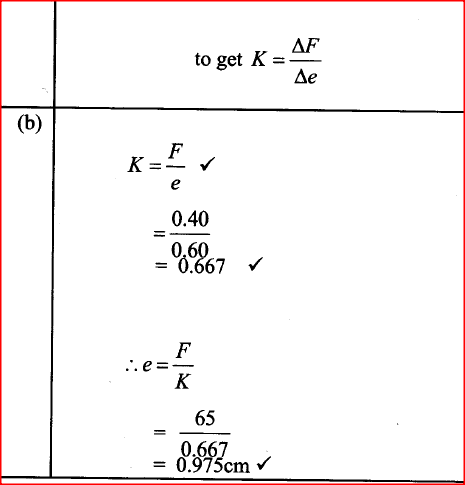
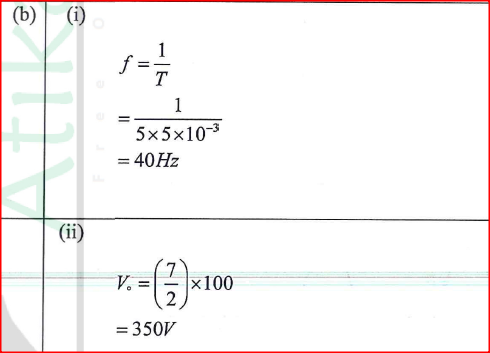
(a) A 240v mains transformer has 800 turns in the primary and N turns in the secondary. It is used to supply energy to a 12v/21w lamp. (i) Calculate the number of turns in the secondary (2mks)(ii) What is the efficiency of the transformer if the current drawn from the 240V mains is 100mA (2mks)
Calculate.(i) the reading of voltmeter, V, with, S, open (2mks)(ii) the reading of the ammeter A with S closed (neglect the effective resistance of the secondary winding) (2mks)(iii) the power dissipated in the lamp (2mks)(iv) the primary current if the transformer is 90% efficient (3mks)
(a) State two advantages of a C.R.O as a voltmeter
(b) A television tube is a cathode ray tube modified. State two modifications
(c) State the functions of the following parts of a C.R.O(i) Grid
(ii) X-plates
(iii) Fluorescent screen
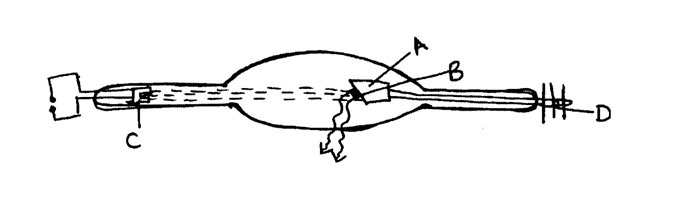
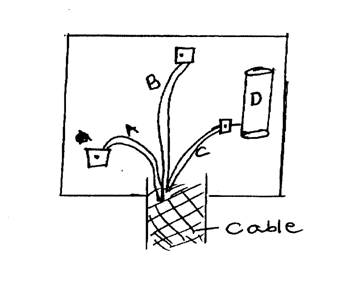
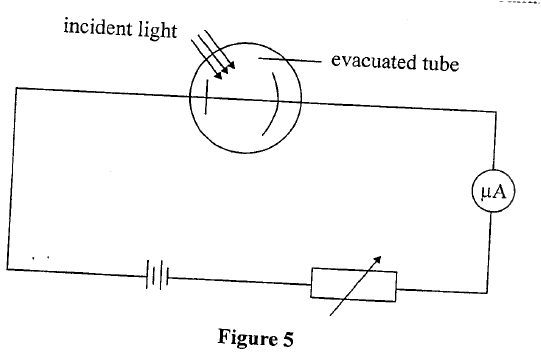
(d) A modern X-ray tube is shown below(i) Name the parts labeled A-D (2mks)A
Copper Anode
B
Tungsten Target
C
Filament
D
Cooling fins
(ii) Give the functions of:- (1mk)(i) Shielding with lead
Lead absorbs the radiation (1mk)
(ii) Evacuating the tube
Prevents collisions, avoid secondary electrons (1mk)
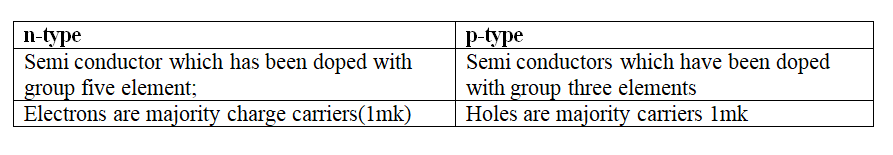
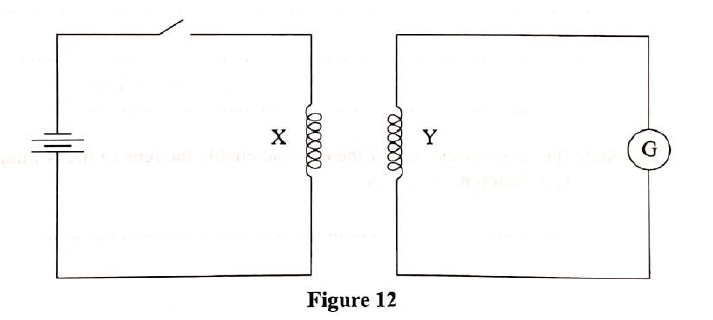
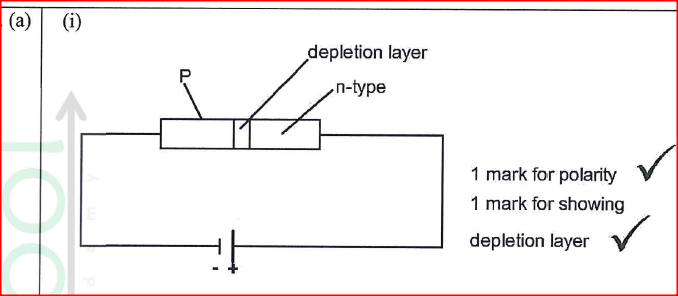
(a) Define doping (1mk)
Process of introducing foreign element (impurity) into a pure semi-conductor,
(b) Distinguish between a p-type and n-type semi conductors (2mks)
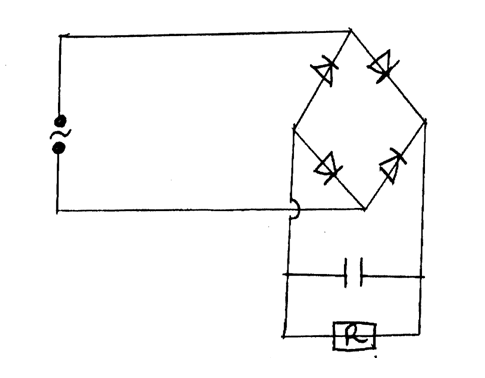
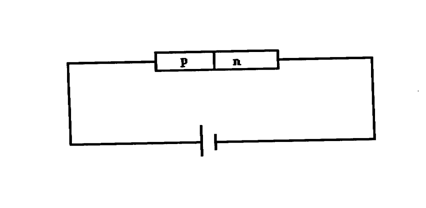
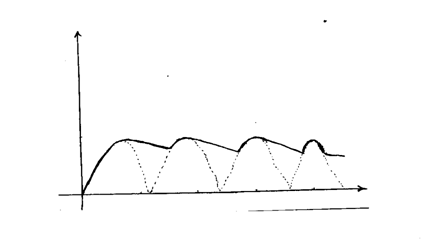
(c) Using a diagram illustrate a forward P-N junction (2mks)(d) The figure below shows a bridge circuit(i) Sketch of the figure below the wave form when a CRO is connected across the resistor, R(ii) On the same axes, sketch a wave form when C.R.O is connected across R when the capacitor has been removed (1mk)
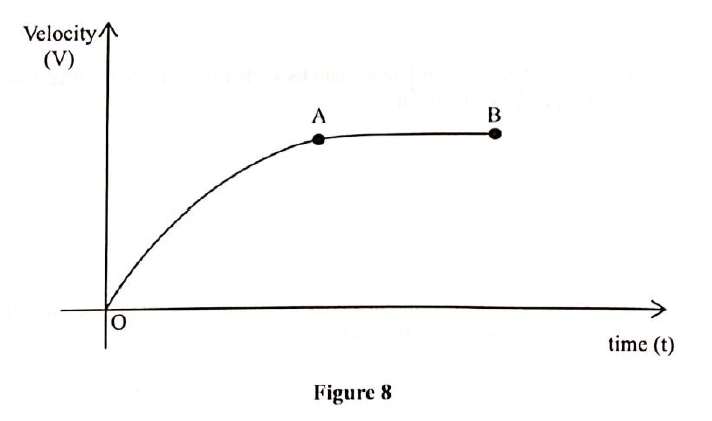
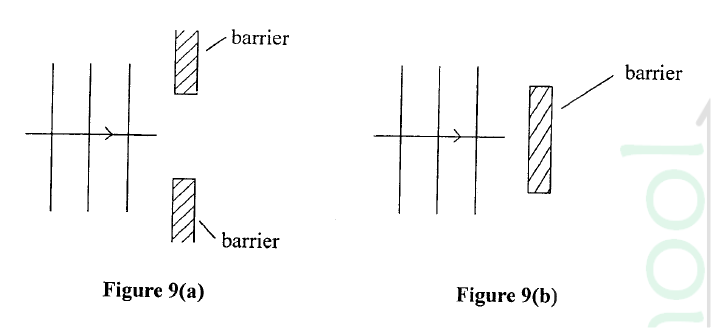
(a) Explain why bulbs in along corridor are not wired in series (2mks)
(b) An electric cooker has an oven rated 2500w, a grill rated 1500w and two plates each of 1000W. This cooker operates directly from 240v supply. What is the costs of operating all the parts at once for 30 minutes if electricity costs sh.10.00 per unit? (3mks)(c) Study the figure below(i) What name is given to the fitting in the diagram (1mk)
3 pin plug
(ii) Identify the parts labeled (2mks)A
Neutral wire
B
Earth wire
C
Live wire
D
Fuse
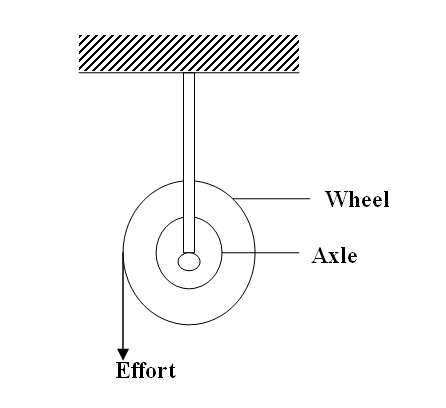
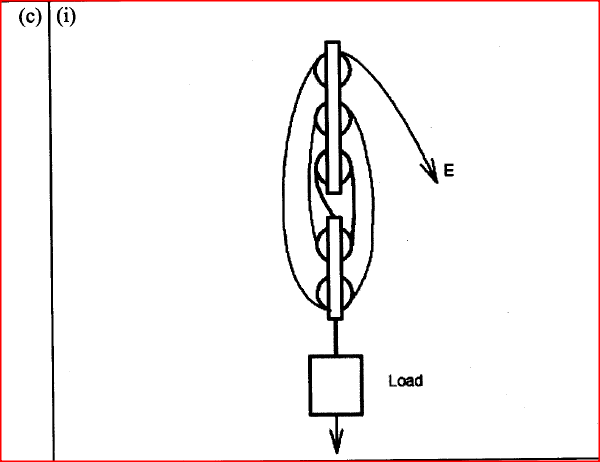
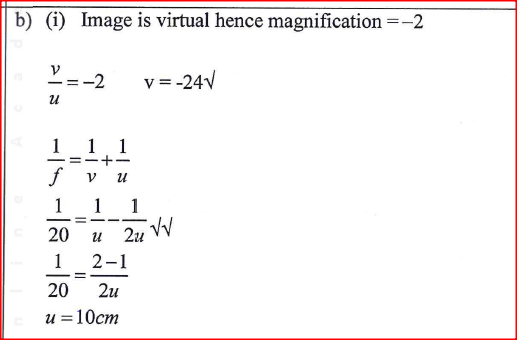
(a) The diagram in the figure below represents a wheel and axle used as a machine, whose efficiency is 80% to raise 400N of building materials. The wheel and axles have diameters of 75cm and 15cm respectively.
(i) Mark on the diagram the correct position and direction of the load to be lifted (1mk)(ii) Name the principle on which this machine works (1mk)
The principle of moments
(iii) Calculate the effort needed to raise the load (3mks)
(iv) The machine is operated manually and raises the load to a height of 5m in 20 seconds. Calculate the power developed by the operator (2mks)(b)
|
CATEGORIES
Categories
All
Topics
FORM I - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM II - PHYSICS SYLLABUSTOPICS
FORM III - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM IV - PHYSICS SYLLABUSARCHIVES
RSS FEEDS
AUTHOR
M.A NyamotiMy passion is to see students pass using right methods and locally available resources. My emphasis is STEM courses
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|
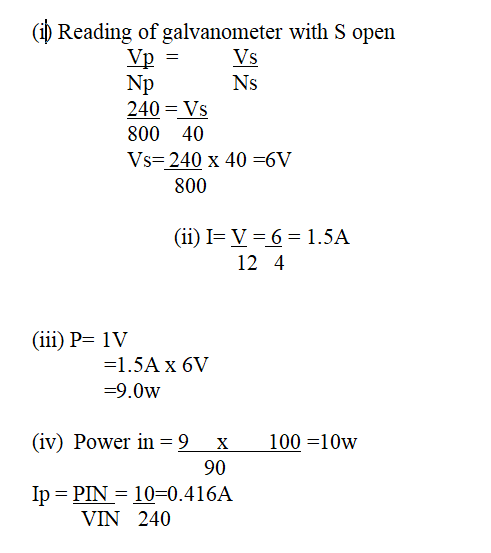
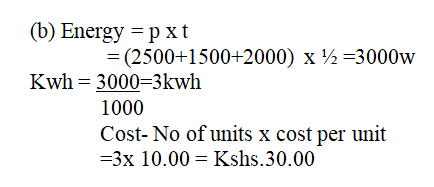
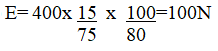
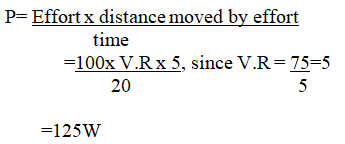
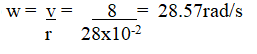
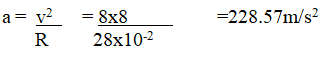
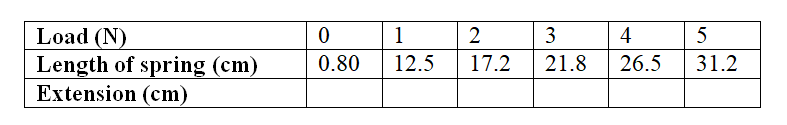

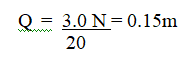
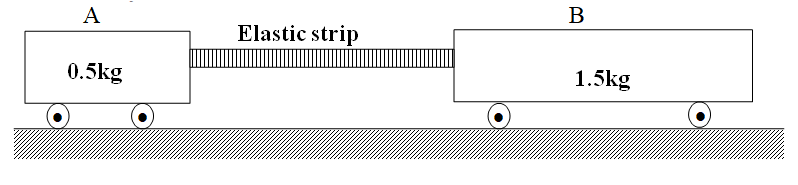
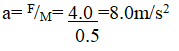
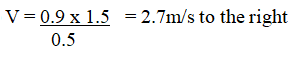

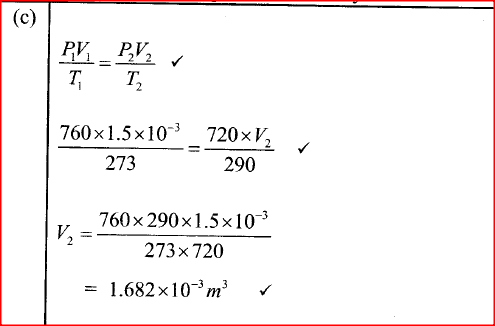




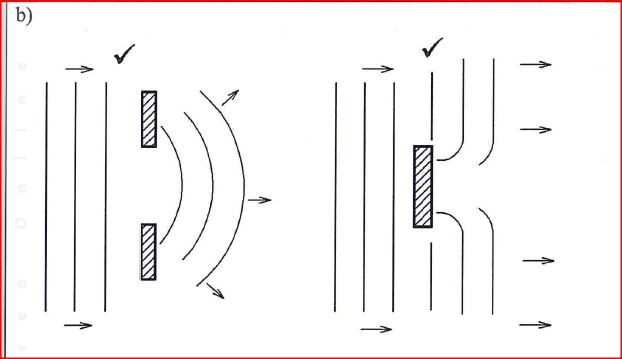
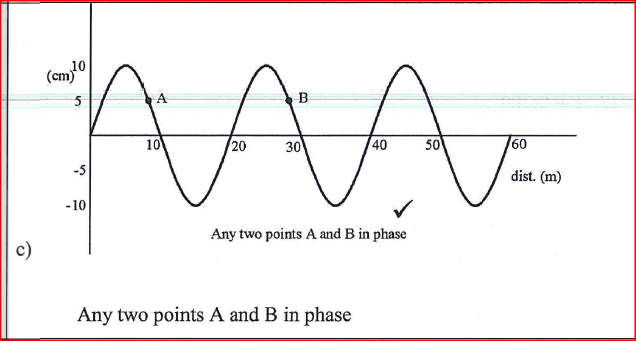
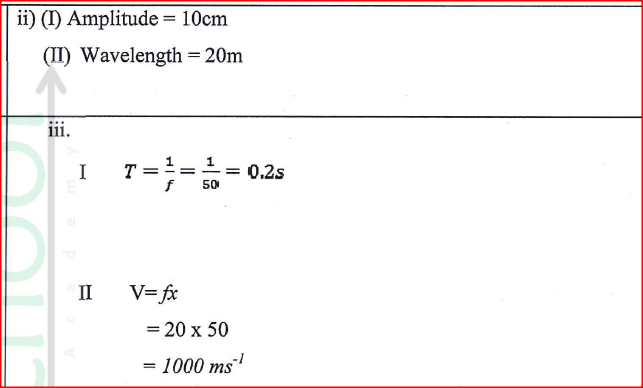
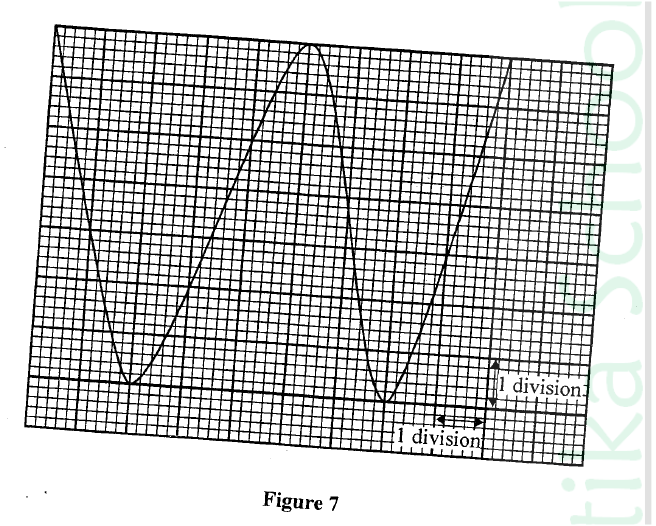

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed