K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN17
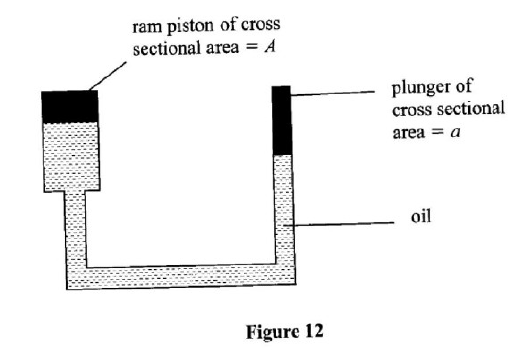
(a) State Pascal’s principle of transmission of pressure in liquids.
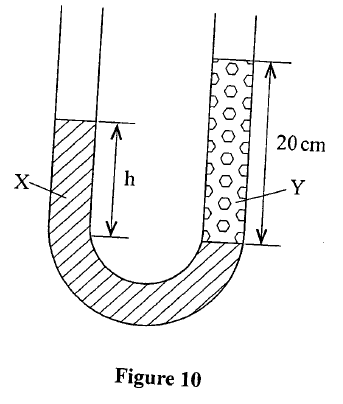
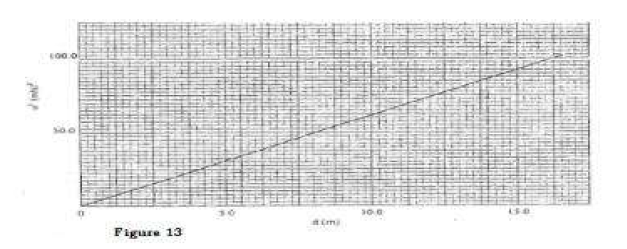
(b) Figure 10 shows heights of two immiscible liquids X and Y in a U-tube (drawn to scale).
(i) State with a reason which of the two liquids X and Y has a higher density.
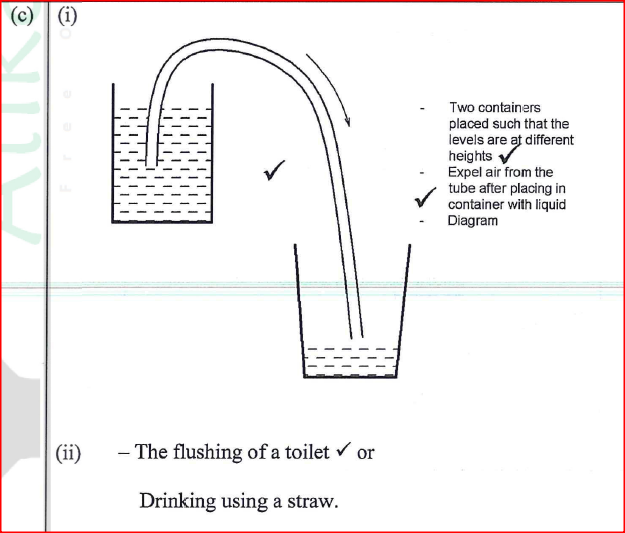
(ii) Determine the value of h. (iii) Given that the density of liquid Y is p, write down an expression for the density d of liquid X ¡n terms of p. (c) (i) With the aid of a diagram, describe how a liquid may be siphoned from one container to another using a flexible tube. (ii) State one application of the siphon.
2 Comments
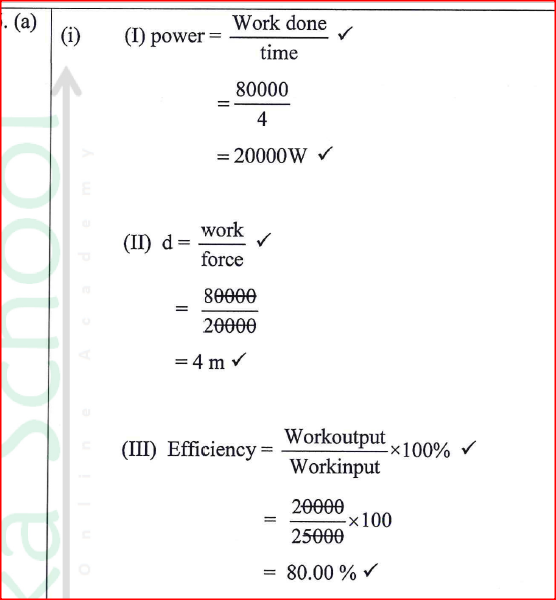
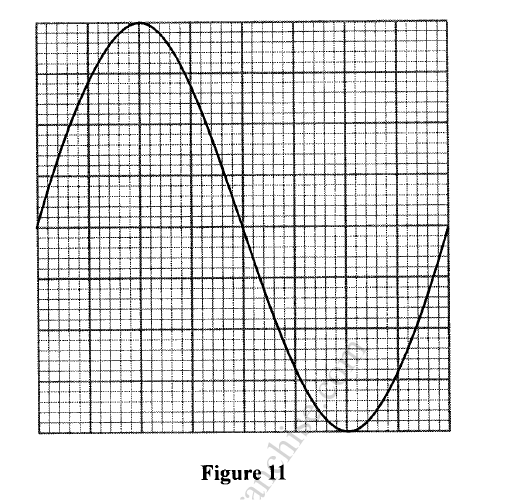
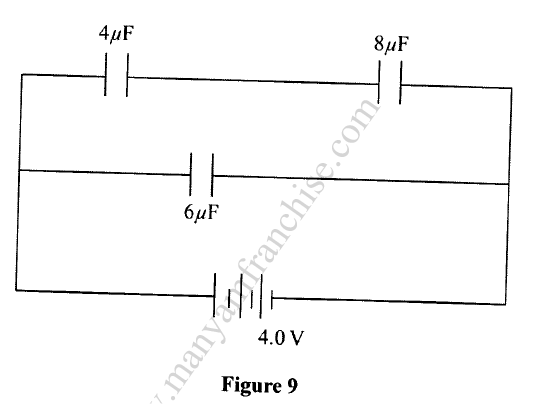
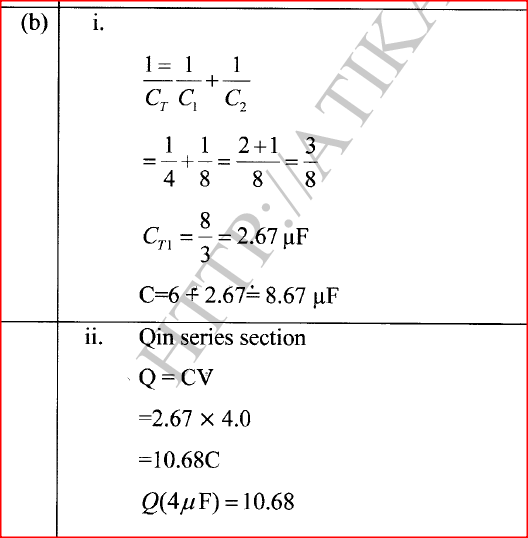
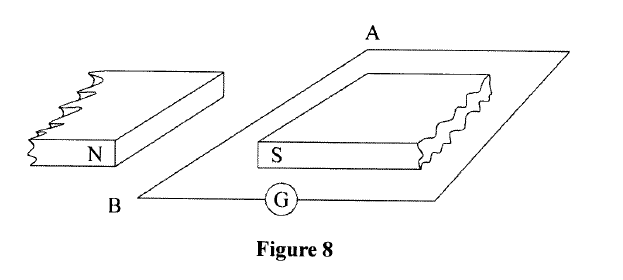
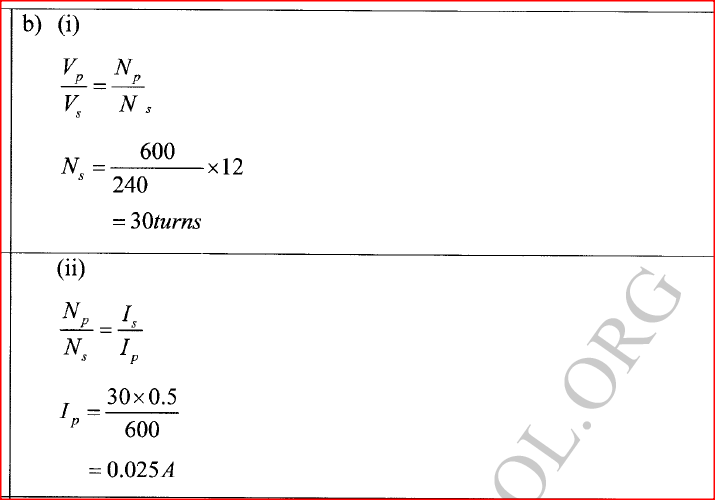
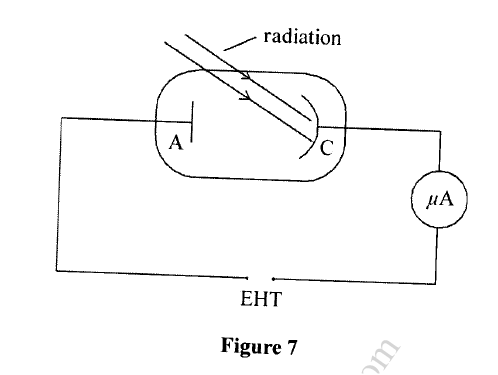
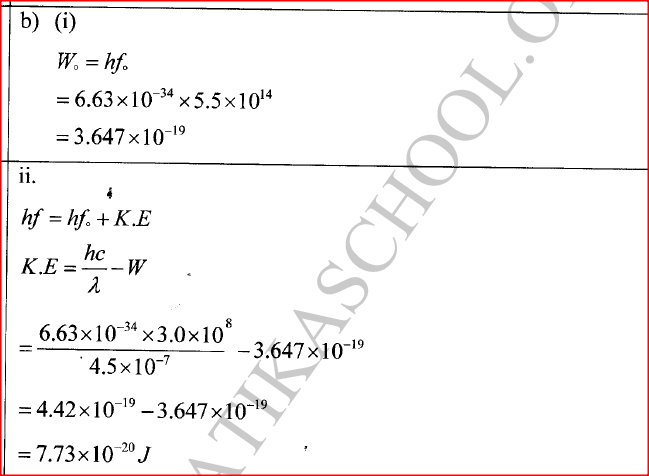
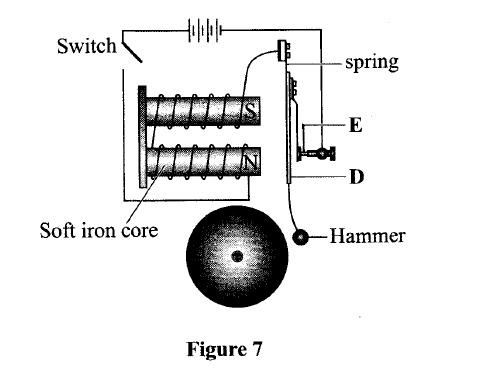
K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN16(a) An electric crane uses 8.0 x104 N of energy to lift a load of 2.0 X 104N in 4s.
|
CATEGORIES
Categories
All
Topics
FORM I - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM II - PHYSICS SYLLABUSTOPICS
FORM III - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM IV - PHYSICS SYLLABUSARCHIVES
RSS FEEDS
AUTHOR
M.A NyamotiMy passion is to see students pass using right methods and locally available resources. My emphasis is STEM courses
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |





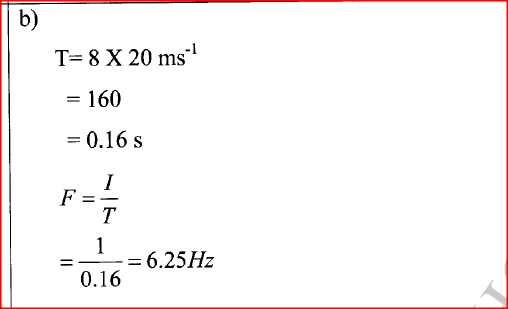











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

