K.C.S.E Physics Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN18
(a) State two differences between cathode rays and electromagnetic radiations.
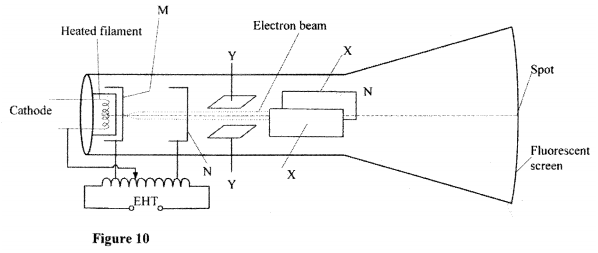
(b) Figure 10, shows the main features of a cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO)
(i) Name the parts labelled M and N.
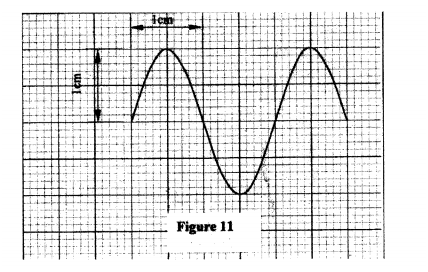
M N (ii) Explain how electrons are produced in the tube. (iii) When using the CRO to display waveforms of voltages, state where the following should be connected: (I) the voltage to be displayed on the screen; (II) the time base voltage. (iv) state why the tube is highly evacuated. (c) Figure 11, shows the waveform of a voltage displayed on the screen of a CRO. The Y-gain calibration was 5V per cm.
(i) Determine the peak-to-peak voltage of the Y-input.
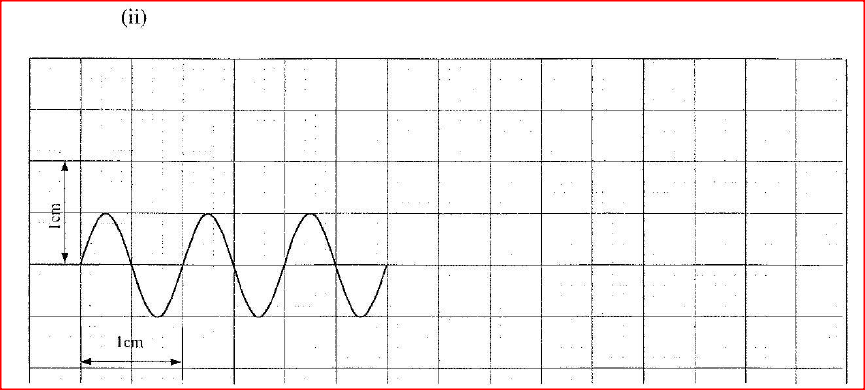
(ii) Sketch on the same figure the appearance of the waveform after the voltage of the input signal is halved and it’s frequency is doubled.
answers
(a) -Cathode rays have charge but e.m radiations don’t have charge;
-Cathode rays are particles and have a mass but e.m radiations are waves; -Cathode rays travel at a speed depending on the accelerating voltage but e.m radiations travel at the speed of light in vacuum; - Different in the mode of production. (b) (i) M - grid; N - accelerating anode/anode/vacuum; (ii) Cathode is heated by filament; electrons are released from cathode; by thermionic emission (iii) (I) across Y-Y plates. (Il) across X-X plates. (2 m (iv) to reduce collisions, (hence ionization) with air molecules in the tube. (c) (i) peak-to-peak voltage = 5 x 2 =10v
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
CATEGORIES
Categories
All
Topics
FORM I - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM II - PHYSICS SYLLABUSTOPICS
FORM III - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM IV - PHYSICS SYLLABUSARCHIVES
RSS FEEDS
AUTHOR
M.A NyamotiMy passion is to see students pass using right methods and locally available resources. My emphasis is STEM courses
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed