|
1. 1996 Q11 P1 Name two forces that determine the shape of liquid drop on the solid surface. (2 marks) 2. 1996 Q37 P1 In the Brownian motion experiment, smoke particles are observed to move randomly. Explain how this motion is caused (2 marks) 3. 1997 Q25 P1 Ice changes to water at 00C. Equal masses of the ice and water at 00C are each heated to 10C. Give a reason why more heat energy is required to heat ice. 4. 1998 Q23 P1 Cleavage in crystals is possible in certain directions only. Explain this observation. 5. 2000 Q6 P1 State the reason why gases are easily compressible while liquids are solids are not 6. 2001 Q5 P1 Fig. 4 (i) shows a beaker filled with water. Some potassium permanganate was gently introduced at the bottom of the beaker at the position shown. 7. 2003 Q5 P1 Explain the cause of random motion of smoke particles as observed in Brownian motion experiment using a smoke cell. 8. 2005 Q7 P1 Two identical tubes A and B held horizontally contain air and water respectively. A small quantity of coloured gas is introduced at one end of A while a small quantity of coloured water is introduced at one end of B. State with reason the tube in which the colour will reach the other end faster. 9. 2006 Q14a P1 (a) Distinguish between solid and liquid states of matter in terms of intermolecular forces 10. 2007 Q15 P1 Brown motion of smoke particles can be studied by using the apparatus shown in figure 9 to observe the motion, some smoke is enclosed in the smoke cell and then observed through the microscope. (a) Explain the role of the smoke particle, lens and microscope in the experiment (b) State and explain the nature of the observed motion of the smoke particles (3 marks) (c) State what will be observed about the motion of the smoke particles if the temperature surrounding the smoke cell is raised slightly. (1 mark) 11. 2008 Q9 P1 Explaining the difference between a liquid and a gas in terms of intermolecular distances and forces. (2 marks) 12. 2009 Q5 P1 Two identical beakers A and B containing equal volumes of water are placed on a bench. The water in A is cold while the water in B is warm. Identical pieces of potassium permanganate are placed gently at the bottom of each beaker inside the water. I t is observed that the spread of colour in B is faster than in A. Explain this observation. (2 marks). 13. 2011 Q8 P1 When the temperature of a gas in a closed container is raised, the pressure of the gas increases. Explain how the molecules of the gas cause the increase in pressure. (2 marks) 14. 2011 Q10 P1 State the reason why it is easier to separate water into drops than to separate a solid into smaller pieces. (1 mark) 15. 2012 Q4 P1 A bottle containing a smelling gas is opened at the front bench of a classroom. State the reason why the gas is detected throughout the room. (1 mark)
2 Comments
Brian
14/6/2020 10:49:47
State why it is easier to separate water into drops than to separate a solid into small pieces
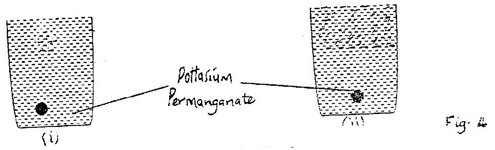
Reply
14/6/2020 11:54:36
The inter molecule forces between water molecules are weaker than in a solid.
Reply
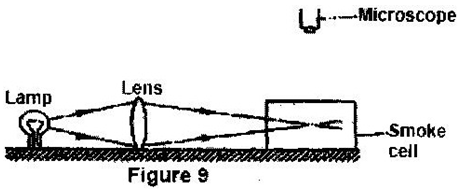
Leave a Reply. |
CATEGORIES
Categories
All
Topics
FORM I - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM II - PHYSICS SYLLABUSTOPICS
FORM III - PHYSICS SYLLABUSFORM IV - PHYSICS SYLLABUSARCHIVES
RSS FEEDS
AUTHOR
M.A NyamotiMy passion is to see students pass using right methods and locally available resources. My emphasis is STEM courses
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed