|
Featured categories include: paper 1 and paper 2, form 1, 2, 3, 4, year of examinations, topics and much more
0 Comments
The Essential Defense: How Blood Safeguards the BodyThe blood plays a crucial role in protecting the body through various mechanisms. Here are some ways in which the blood protects the body:
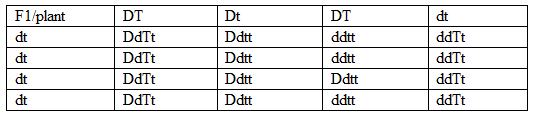
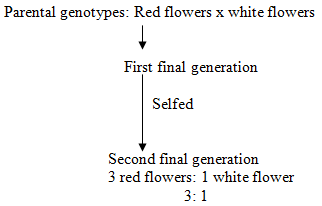
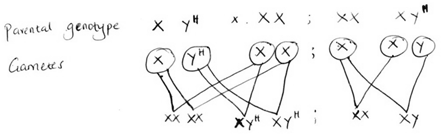
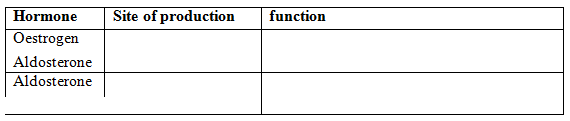
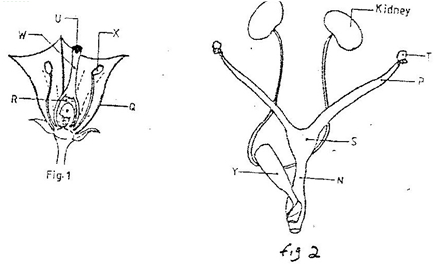
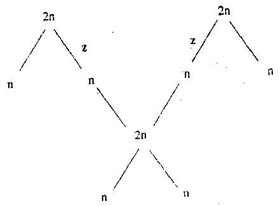
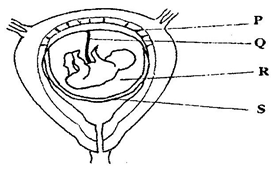
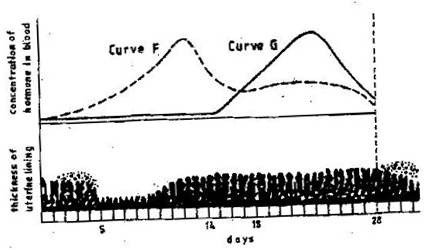
GENETICS: KCSE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ON TOPIC1. 1989 Q13 P1 In an experiment, a variety of garden peas having a smooth seed coat was crossed with a variety with a wrinkled seed coat. All the seeds obtained in the f generation had a smooth seed coat. The f generation was selfed. The total number of f2 generation was 7324. (a) Using appropriate letter symbols. Work out the genotype of the f1 generation (b) From the information above, work out the following for the f2 generation 2. 1990 Q2 P1 The figure below is a structural diagram of a portion from anucleic acid stand. -----S – P – S – P – S – P – S ----- C G U C (a) Giving a reason, name the nucleic acid to which the portion belongs (b) Write down the sequence of bases of a complementary strand to that show above 3. 1990 Q12 P1 A garden pea plant having green round seeds was crossed with another garden pea plant having yellow wrinkled seeds. The seeds produced in the f1 generation were all green and round (a) State the dominant traits in these plants (b) If D and d represents genes that determine seed colour, while T and T represents genes that determines seed texture; (i) Give the genotype of each parent plant (ii) Give a reason for your answer (b) (i) above (iii) Work out the genotypes of the F1 generation. (iv) In the table below, work out the progeny between the F1 generation and a plant having yellow wrinkled seeds (v) What was the phenotypic ratio of the progeny in (b) (iv) above? 4. 1991 Q13 P1 In a certain birds species, the spotted pattern of feathers is controlled by a dominant gene B, and the plain pattern by a recessive gene b. Red colour of the legs is controlled by a dominant gene R and brown colour by a recessive gene r If a homozygous spotted red legged bird was crossed with a plain feathered brown legged bird, what are:- (a) (i) The parental genotype? (ii) The gametes produced by these parents (iii) The genotypes and phenotypes of F1 generation. (b) Using a punnet square, work out the cross between two F1 individuals and show the phenotype ration of the F2 generation. 5. 1992 Q14 P1 (a)Write the base sequence of messenger RNA (mRNA) that would be coded from the DNA strands shown below. C – A – T – G – A – G – T (b) What is mutation? (c) Name two types of chromosomal mutation (d) State two factors that may cause mutation (e) What is the significance of chlasma formation during melotic cell division 6. 1993 Q12 P1 In a certain plant species, some individual plants may have only white, red or pink flowers. In an experiment a plant with white flowers was crossed with red flowers. The parent plants were pure lines. All the plants from F1 generation were pink. Using letter R to represent the gene for the red colour and letter W for white colour. (a) Work out the genotype of F1 generation. (b) If the plants from F1 generation were selfed, what would be the phenotypic ration of the F2 generation?. (c) What is the genetic explanation for the absence of plants with red and white in the flowers F1 generation? 7. 1994 Q11 P1 State two structural differences between ribonucleic acid (RNA) and Deoxyribonucleic (DNA). 8. 1995 Q9 P1 Name a disorder of human blood that is caused by mutation. 9. 1996 Q1 P1 State the function of Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecule (1 mark) 10. 1996 Q18 P1 In an experiment black mice were crossed and the offspring were back and brown. The gene for black colour is dominant over that of brown colour. Using letter B to represent the gene for black colour and b to represent the gene for brown colour (a) Work out the genotypes of the F1 generation (4 marks) (b) What is the phenotype ration of the spring (1 mark) 11. 1997 Q16 P1 In a breeding experiment, plants with red flowers were crossed. The produced 123 plants with red flowers and 41 with white flowers (a) Identify the recessive character Give a reason (b) What was the genotype of the parent plants that gave rise to the plants with a red and white flowers? 12. 1998 Q12 P1 In a family with four children, three were found to have normal skin pigmentation while one was an albino. Using letter A to represent gene for normal skin pigmentation and a to represent the gene for albinism, (a) What are the genotypes of the parents? (b) Work out the genotype of (i) Normal pigmentation (ii) The albino child Genotype of normal pigmented children (c )What is the probability that the fifth child will be an albino? 13. 1999 Q7 P1 An investigation plants with red flowers were crossed with plants with white flowers. All the plants in the F1 generation had pink flowers. a) Give a reason for the appearance of pink flowers in the F1 generation. b) If the plants the F1 generation were selfed, state the phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation. 14. 2000 Q12 P1 The chart below represents the result of successive crosses, staring with red- flowered plants and white flowed plants and in which both plants are pure breeding. (a) What were parental genotypes? Use letter R to represent the gene for red colour and r for white colour (b) (i) What was the colour of the flowers in the first filial generation? (ii) Give a reason for your answer in b (i) above (c) If 480 red flowered plants were obtained in the second filial generation, how many F2 plants and white flowers? Show your working. 15. 2001 Q9 P1 Name three types of chromosomal mutations 16. 2001 Q14 P1 Tallness in pea plants is due to a dominant gene.Two tall pea plants were crossed and their F1 generation were in the ratio of 3 tall: 1 short. Using letter T to represents the gene for tallness and t for shortness give the (a) (i) Genotype of the parents (ii) Gamete of the parents (iii) Genotype ratio of the F1 generation (b) What is meant by the term testcross in genetic studies? 17. 2002 Q5 P1 State two characters that researchers select in breeding programme. 18. 2002 Q11 P1 Give an example of a sex – linked trait in humans on: Y CHROMOSOME. X CHROMOSOME. a) What is meant by the term sex – linkage? b) Name two sex – linked traits in humans. c) In Drosophila Melanogaster, the inheritance of eye colour is sex – linked. The gene of red eye is dominant. A cross was made between a homozygous red – eyed female and a white – eyed male. Work out the phenotypic ration of F1 generation. (Use R to represent the gene for red eyes). 19. 2004 Q12 P1 Across between a red flowered plant and white flowered produced plants with pink flowers. Using letter R to represent the gene for red colour, and W for white colour a) What were the parental genotypes (1 mark) b) Workout a cross between F1 plants (4 marks) c) Give the i) Phenotypic ratio of F2 plants (1 mark) ii) Genotypic ratio of F2 plants (1 mark) d) Name a characteristic in humans, which is controlled through a mammalian heart? 20. 2005 Q12 P1 In a garden with plants of same species, 705 plants had red flowers while 224 had white flowers. a) Work out the ratio of red to white flowered plants (1 mark) b) (i) Using letter R to represent the dominant gene, work out a cross between F1 offspring and a white flowered plant. (4 marks) (ii) What is the genotypic ratio from the cross in b(i) above? (1 mark) c) What is meant by the term allele? (1 mark) 21. 2006 Q2 P2 a) Name two disorders in human caused by gene mutation. (2 marks) b) Describe the following chromosomal mutations. (2 marks) a. Inversion b. Translocation. c) In mice the allele for black fur is dominant to the allele for brown fur. What percentage offspring would have brown fur form across between heterozygous black mice? Show your working. Use letter B to represent the allele for black colour. (4marks) 22. 2007 Q20 P1 (a) What is meant by the term allele? (1 mark) (b) Explain how the following occur during gene mutation: (i) Deletion (1 mark) (ii) Inversion (1 mark) (c) What is a test- cross? (1 mark) 23. 2007 Q5 P2 In maize the gene for purple colour is dominant to the gene for white colour. A pure breeding maize plant with purple grains was crossed with a heterozygous plant. (a) (i) Using letter G to represent the gene for purple colour, work out the genotype ratio of the offspring (5 marks) (ii) State the phenotype of the offspring (1 mark) (b) What is genetic engineering? (1 mark) (c) What is meant by hybrid vigour? (1 mark) 24. 2008 Q6 P1 (a) What is meant by non- disjunction? (1 mark) (b) Give two examples of continuous variation in humans (2 marks) 25. 2008 Q2 P2 A pea plant with round seeds was crossed with a pea plant that had Wrinkled seeds the gene for round seeds is dominant over that for wrinkled seeds Using letter R to represent the dominant gene state: (a) The genotype of parents if plant with round seed was heterozygous (2 marks) (b) The gametes produced by the round and wrinkled seed parents Round seed parent Wrinkled seed parent (c) The genotype and phenotype of F1 generation. Show your working (3 marks) (d) What is a test – cross? (1 mark) 26. 2009 Q5 P1 (a) What is meant by the following terms? (i) Hybrid vigour (1 mark) (ii) Polyploidy? (1 mark) (b) State two causes of chromosomal mutations (2 marks) 27. 2010 Q10 P1 State two advantages of hybrid vigour. (2 marks) 28. 2010 Q27 P1 a) What is meant by the term non-disjunction? (1 mark) b) Give an example of a genetic disorder caused by: i) Non-disjuction; (1 mark) ii) Gene mutation ( 1 mark) 29. 2010 Q5 P2 When pure breeding black guinea pigs were crossed with pure breeding white guinea pigs, the offsring had a coat with black and white patches. a) Using letter G to represent the gene for black coat colour and letter H for white coat colour, work out the genotypic ratio of F2. b) State the phenotypic ratio of F2. (1 mark) c) i) Name the term used when two alleles in heterozygous state are fully expressed phenotyically in an organism. (1 mark) ii) Give an example of a trait in human beings where the condition whose term is named in (c) (i) above expresses itself. (1 mark) 30. 2011 Q24 P1 (a) Differentiate between the following terms: (i) dominant gene and recessive gene (1 mark) (ii) Continous variation and discontinuous variation (1 mark) (b) What would be the expected results from a test cross? (2 marks) 31. 2011 Q2abc P2 In humans, hairy ears is controlled by a gene on the Y chromosome. (a)Using letter YH to represent the chromosome carrying the gene for hairy ears, work out a cross between a hairy eared man and wife. (4 marks) (b) (i) What is the probability of the girls having hairy ears? (1 mark) (ii) Give a reason for your answer in b (i) above (1 mark) (c) Name two disorders in humans that are determined by sex-linked genes. (2 marks) 32. 2012 Q1 P2 In a certain plant species which is normally green, a recessive gene for colour (n) causes the plants to be white in colour. Such plants die at an early age. In the heterozygous state, the plants are pale green in colour but grow to maturity. (a) Give a reason for the early death of the plants with the homozygous recessive gene. (2 marks) (b) If a normal green plant was crossed with the pale green plant, what would be the genotype of the first filial generation (F1 generation)? Show your working. (4 marks) (c) If heterozygous plants were self-pollinated and the resulting seeds planted, work out the proportion of their offspring that would grow to maturity. (2 marks) 33. 2012 Q8 P1 What is the probability of a couple with blood group AB getting a child with blood group AB? Comprehensive KCSE Questions and Answers on Reproduction in Plants and Animals1. 1989 Q5 P1 The table below shows two mammalian hormones. For each hormone, state the site of production and its function in the body. 2. 1989 Q10 P1 At what stage of mitosis do chromosomes replicate to form daughter chromatids? 3. 1990 Q5 P1 Fill in the blank spaces in statement below. After fertilization of an ovule……………………develops in to a testa and…………………………..develops into endosperm. 4. 1990 Q8 P1 State the differences between the composition of maternal blood entering the placenta and maternal blood leaving the placenta. 5. 1991 Q3 P1 After four months of pregnancy, the ovaries of a woman can be removed without terminating pregnancy. However, during the first four months of pregnancy, the ovaries must remain intact if pregnancy is to be maintained. Explain these observations. 6. 1991 Q12 P1 (a) State the type of sexual reproduction in each of the following organisms. (i) Hydra ............ (ii) Moss (funari) ............... (b)State two advantages of sexual reproduction to the survival of a species. (c)State two ways in which man has utilized vegetative reproduction in plants for his own benefits. 7. 1992 Q8 P1 Name two mechanisms that prevent self-pollination in flowers that have both male and female parts 8. 1993 Q11 P1 The diagram below represents some stages in mitosis (a) Name the stages represented by the diagrams labeled A,B and C A……………………………………………………. B…………………………………………………… C…………………………………………………… (b) State the significance of mitosis to an organism. (c) Name two regions in higher plants where cells actively undergo mitosis 7. 1995 Q16 P1 (a) Describe how insect pollinated flowers are adapted to pollination (b)Describe the role or each of the following hormones in the human menstrual cycle (i) Oestrogen (ii) Progesterone (iii) Luteinising hormone (9 marks) 8. 1996 Q2 P1 State two ways by which acquired Immune deficiency syndrome (A.I.D.S) Virus is transmitted. (2 marks) 9. 1996 Q9 P1 State three characteristics that ensure cross – pollination takes place in flowering plants (3 marks) 10. 1996 Q12 P1 Give a reason why it is necessary for frogs to lay many eggs (1 mark) 11. 1996 Q22 P1 Describe how new plants arise by asexual reproduction (20 marks) 12. 1997 Q17 P1 Figures 1 and 2 below represent reproductive organ of plants and an animal respectively. (a)Which letters in figures 1 and 2 represents the organs that produce female gametes? Figure 1……… Figure 2……… (b) What is the function of the structure labeled S? (c) Name the structure labeled W (d) Which letters in figures 1 and 2 represents the structures where fertilization takes Place (e) Which letter in figure 1 represents the structure where male gametes are produced? 7. 1998 Q8 P1 A flower was found to have the following characteristics: Inconspicuous petals Long feathery stigma Small, light pollen grains (a)What is the likely agent of pollination of the flower (b)What is the significance of the long feathery stigma in the flower? 8. 1998 Q11 P1 State two ways by which the human immune-deficiency (H.I.V) is transmitted other than through sexual intercourse? 17. 1998 Q13 P1 (a) List four differences between meiosis and mitosis (b) Which sex chromosomes are found in human? (i) Sperm cell? (ii) Ova? 18. 1999 Q3 P1 Explain why sexual reproduction is important in organisms 19. 1999 Q8 P1 State two disadvantages of self-pollination. 20. 2000 Q9 P1 State two advantages of metamorphosis to the life of insects. 21. 2000 Q16 P1 (a) What is the significance of sexual reproduction? (b) State three advantages of asexual reproduction 22. 2000 Q18 P1 Describe the role of hormones in the human menstrual cycle 23. 2001 Q4 P1 Name the parts of the flower that are responsible the production of gametes 24. 2001 Q18 P1 (a) Describe the process of fertilization in a flowering plant (b) State the change that take place in a flower after fertilization 25. 2002 Q13 P1 The chart below shows the number of chromosomes before and after cell division and fertilization in a mammal. a) What type of cell division takes place at Z b) Where in the body of a female does process Z occur c) On the chart, indicate the position of parents and gametes d) Name the process that leads to addition or loss of one or more chromosomes. e) State three benefits of polyploidy in plants to a farmer 26. 2002 Q17 P1 a) What structures are produced by sisal for vegetative propagation? b) Give a reason for grafting in plants c) State four advantages of vegetation propagation. 27. 2003 Q3 P1 How do the male gamete nuclei reach the ovule after pollen grains land on the stigma? 28. 2003 Q19 P1 Describe how fruits and seeds are suited to their modes of dispersal. 29. 2004 Q5 P1 During which phase of meiosis does crossing over occur. (2marks) 30. 2004 Q11 P1 Fruit formation without fertilization is called (1mark) 31. 2004 Q15 P1 a) Give the differences between the following structures in wind and insect pollinated flowers. (3marks) i) Anther ii) Pollen grains iii) Stigma (1mark) b) What is the importance of cross pollination? (1mark) c) Explain how a seed is formed after an ovule is fertilized (4marks) 32. 2005 Q15 P1 a) What is meant by the terms (i) Epigymous flower (1mark) (ii) Staminate flower? (1mark) b) How are the male parts of wild pollinated flowers adapted to their function? (4marks) 33. 2006 Q2, 9 P1 2. Name the part of the flower that develops into a) Seed b) Fruit (1mark) 9. a) State two processes which occur during anaphase of mitosis. (2marks) b) What is significance of meiosis? (2marks) 34. 2006 Q19 P1 a) Explain how the following prevent self pollination. (1mark) (i) Protoadry (ii) Self – sterility. b) Give three advantages of cross pollination. (3marks) 35. 2006 Q5 P2 The diagram below represents human foetus in a uterus. a) Name the part labeled S. (1mark) b) i)Name the types of blood vessels found in the structure labeled Q. (2marks) ii) State the differences in composition of blood found in the vessels named in (b) (i) above. (2marks) c) Name two features that enable the structure labeled P carry out its function. (2marks) d) State the role of the part labeled R (1mark) 36. 2007 Q17 P1 The diagram below represents a stage during cell division (a) (i) Identify the stage of cell division (1 mark) (ii) Give three reasons for your answer in (a) (i) above (2 marks) (b) Name the structures labeled M (1 mark) 37. 2007 Q18 P1 State two disadvantages of sexual reproduction in animals (2 marks) 38. 2007 Q26 P1 State one way in which HIV / Aids is transmitted from mother to child (1mark) 39. 2007 Q3 P2 (a)What is meant by the following terms (i) Protandry (1 mark) (ii) Self sterility? (1 mark) (b)The diagram below shows a stage during fertilization in a plant (i) Name the parts labeled Q, R, and S (3 marks) (ii) State two functions of the pollen tube (2 marks) (c) On the diagram label the micropyle (1 mark) 40. 2008 Q8 P1 The diagram below shows a stage in mitosis in a plant cell (a) Name the stage of mitosis (1mark) (b) Give two reasons for your answer in (a) above (2 marks) (c) Name the part of the plant from which the cell used in preparation was Obtained (1 mark) 41. 2008 Q1 P2 The figure shows changes that take place during menstrual cycle in human (a) Name the hormone whose concentrations are represented by curves F and G ( 2 marks)
(b) State the effects of the hormones named in (a) above on the lining of the uterus ( 2 marks) (c) (i) Name the hormone which is released by the pituitary gland in high concentration on the 14th day of the menstrual cycle ( 1 mark) (ii) State two functions of the hormone named in (c) (I ) above (2 marks) (d) State the fertile period during the menstrual cycle (1 mark) 42. 2009 Q8 P1 (a) Pregnancies continues if the ovary of an expectant mother is removed after 4 months explain ( 2 marks) (b) What is the role of the testes in the mammalian reproductive systems? (2 marks) 43. 2009 Q7 P2 How are flowers adapted to wind and insect pollination? (20 marks) 44. 2010 Q22 P1 What is the function of the following structure in the human reproductive organ? a) Fallopian tubes. (1 mark) b) Epididymis. (1 mark) c) Scrotal sac (1 mark) 45. 2010 Q7 P2 Describe the process of fertilization in flowering plants. (20 marks) 46. 2011 Q26 P1 Name the gamete cells that are produced by the ovaries (1mark) 47. 2012 Q15 P1 What name is given to a group of hormones that controls the development of secondary sexual characteristics in a human male? (1mark) 48. 2012 Q16 P1 The diagram below represents an experimental set-up used by students to investigate a certain process. Flower Q produced seeds while P did not. Account for the results. (3marks) 49. 2012 Q17 P1 Name two substances that leave the foetal blood through the placenta. (2marks) 50. 2012 Q25 P1 State the role of the following hormones in the life cycle of insects: (2marks) Ecdsone hormone; …… Juvenile hormone…… The Inter-relationship between Living and Non-living Things
The Inter-relationship between Living and Non-living Things
In the intricate web of nature, there exists a profound inter-relationship between living and non-living things. These two components of the ecosystem are interconnected and rely on each other for survival and sustainability. Let's explore this relationship in more detail:
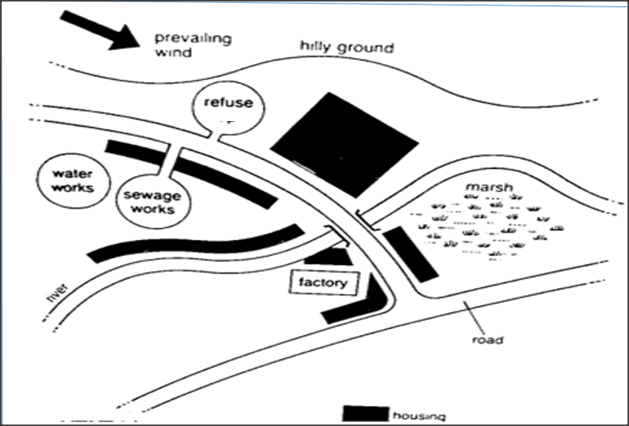
Below is a diagram of a poorly planned town showing some building and facilitiesa) Giving evidence from the diagram, state two likely sources of water pollution. (2mks)
b) State three ways that the positioning of the refuse pit and sewage works pose danger to the residence of the town. (3mks)
c) Residents living close to the marsh are likely to suffer from malaria. Explain. (1mk)
d) Suggest two control measures to overcome water pollution in the area. (2mks)
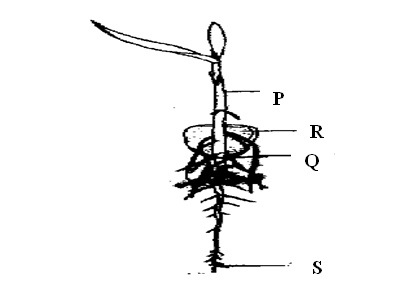
The diagram below represents a maize seedling.a) Name the structure labeled A and C (2mks)
b) State the functions of parts labeled A, B and C. (3mks)
c) Name the type of germination exhibited by maize (1mk)Hypogeal germination d) Name two conditions necessary for seed germination other than water and oxygen. (1mk)
e) What is the role of oxygen in seed germination? (1mk)It oxidizes the stored food in the seed to give energy for growth/synthesis of new materials;
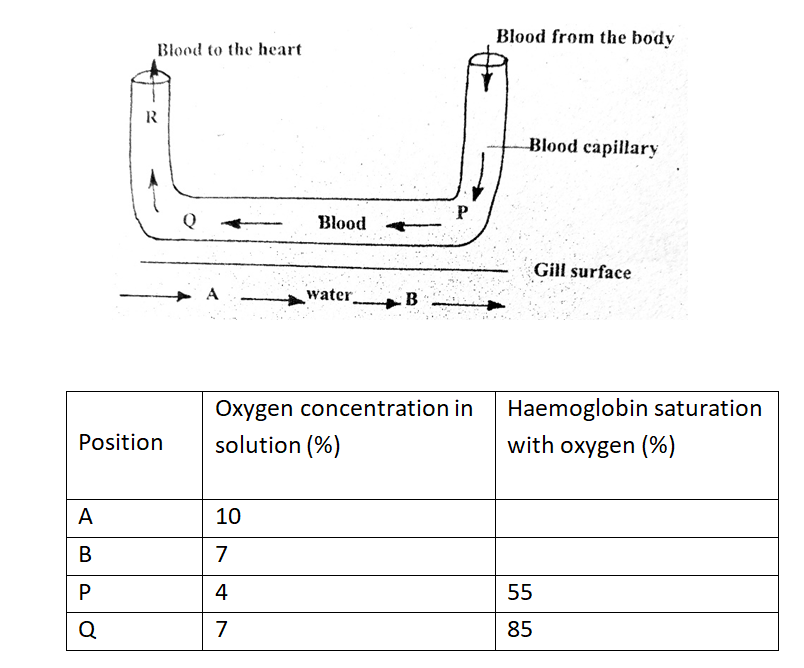
The diagram below represents the direction of flow of blood in a gill capillary. The percentage of oxygen in solution at position A, B, P, Q and R is given in the table below.a) Why is the oxygen percentage low at P? (1mk)
Blood coming from the body has supplied the tissue cells with oxygen/ oxygen has diffused out of capillary into the tissue fluid;
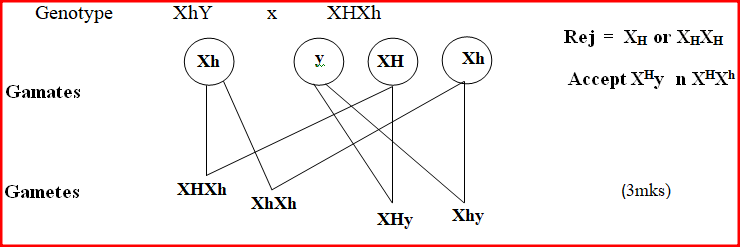
b) Using evidence from the data given, suggest what will happen to oxygen in the water at point B. (3mks)
Oxygen concentration at B reduces/will be at lowest; because blood at P has a lower oxygen concertation creating a diffusing gradient; From A to B there is a diffusion gradient hence at B much oxygen has diffused into the from water into the blood;
c) Name the organ into which blood coming from the capillary at Q flows. (1mk)
Heart
d) Suppose the flow of blood in the capillary illustrated above was in the opposite direction, explain the disadvantage it would have to the fish. (2mks)
Amount of exchange of respiratory gasses between blood and water would reduce; because of reduced diffusion gradient;
e) Name the principle where the blood flows in the opposite direction to another fluid. (1mk)
Counter flow system.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN02
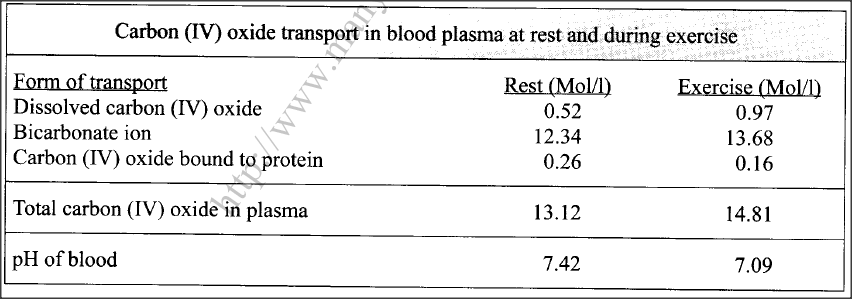
The table below shows variations in the form carbon (IV) oxide is transported in the blood at rest and during physical exercise.
(a) Explain why more carbon (IV) oxide ¡s transported in the form of bicarbonate ion.
(b)Account for the high total plasma content of carbon (IV) oxide during exercises. (c) State how one’s involvement in the exercises affects blood pH. (d) Name the protein responsible for the transport of carbon (IV) oxide in the blood.
ANSWERS
(a) Presence of carbonic anhydrase enzyme; which speeds up the conversion of carbon (IV) oxide to weak carbonic acid; which dissociates into hydrogen carbonate ion/(HCO3) (that diffuses out of the red blood cells into the blood plasma);
(b)The body needs high amount of energy; (for the exercise/muscle activity) hence high respiration rate (more oxygen intake); releasing more carbon (IV) oxide (in the blood plasma); (c)The high rate of respiration (during physical exercises coupled with normal cellular metabolism) results in the production of more carbon(IV) oxide/faster accumulation of lactic acid; lowering the blood plasma pH/making it more acidic (compared to when one is at rest); (d)Haemoglobin BIOLOGY REVISION KITS FORM 3 TERM 1 PAPER 2 MODEL26092022001
BIOLOGY REVISION KITS FORM 3 TERM 1 PAPER 3 MODEL26092022001
BIOLOGY REVISION KITS FORM 3 TERM 1 PAPER 1 MODEL26092022001
BIOLOGY PAPER 1 FORM 4 TERM 2 REVISION QUESTION PAPER WITH MARKING SCHEME MODEL20220108T064525Z-00121/8/2022 Explain how the kidney is adapted to its functionAdaptations for ultra-filtration
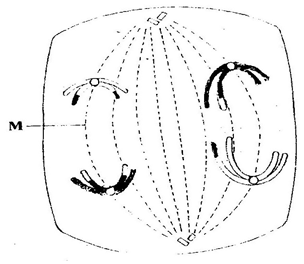
Adaptations for reabsorption
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN08
State three ways in which blood capillaries are structurally adapted to their functions.
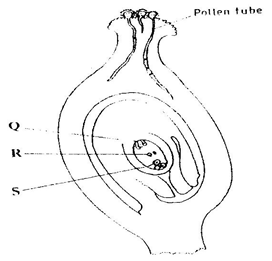
Explain structure and functions of the human eye. (20mks)
(a) Describe the mechanism of inhalation in man. (10mks)
External intercostals muscles contract; internal intercostals muscle relax, Rib cage move outwards; and upwards; Diaphragm muscles contract, Diaphragm flatten; volume in thoraci cavity increases; pressure reduces.
Atmospheric air enters the lungs; inflate (correct sequence to be followed) (b) Using photosynthesis theory explain the mechanics of opening of stomata. (10mks)
Guard cells have chloroplast which photosynthesis in the presence of light, to form sugar, the osmotic pressure of guard cell increases; water move from neighbouring cells into guard cells being thicker than outer walls. Causes the outer wall to stretch more resulting guard cells budging outwards.
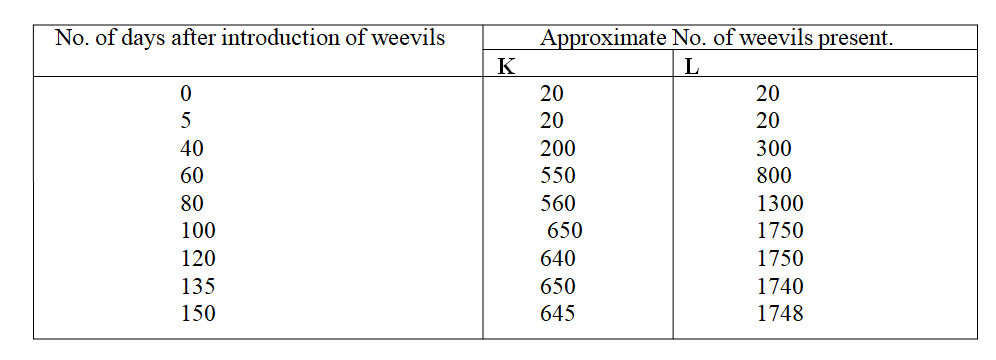
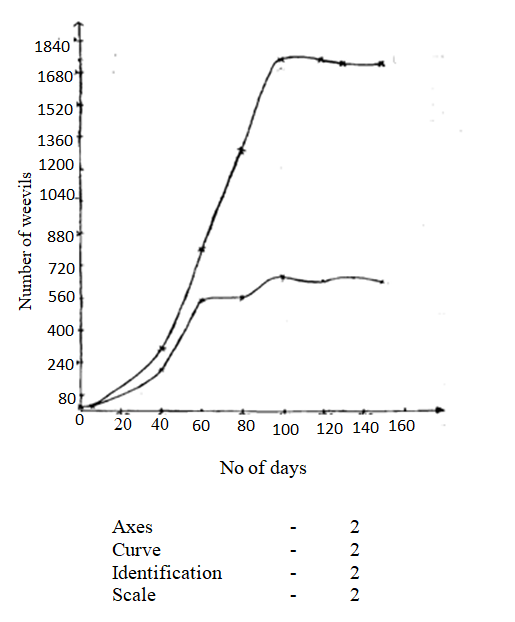
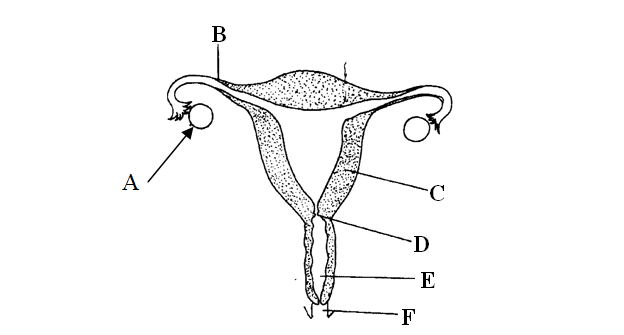
A group of students carried out a study of the population growth of flour weevils. They put 16 grams of maize flour into two equal boxes K and L respective . They then introduced equal numbers of weevils into the boxes. The boxes were kept under similar environmental conditions. The weevils were counted at intervals and the results recorded in the table below.
(a) Using a suitable scale ,draw two graphs on the same axes from the results in the table.
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |




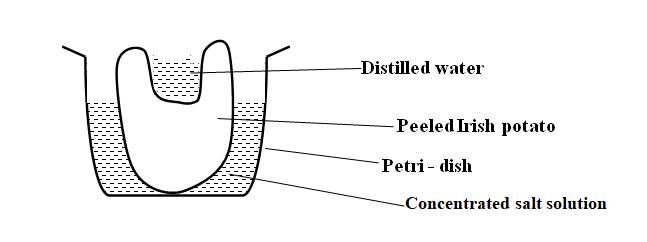
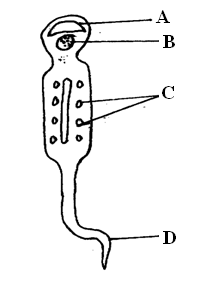








 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

