|
These are chemistry questions and answers categorized according to topics, papers i.e. Paper 1 and 2, Levels i.e. form 1 to form 4, kcse year the examination was done and section A or B
Select topic/category to open topical questions from that particular option provided. Chemistry Topics
0 Comments
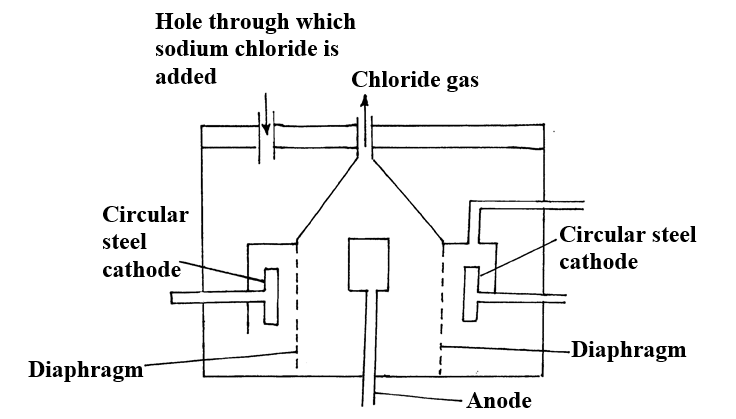
a) Name the substance the anode is made of (1mk)
Graphite
b) Explain your answer in (a) above (1mk)
Reject carbon
Graphite does not react with chlorine liberated at the anode
c) What is the role of the diaphragm in Down’s cell (1mk)
To prevent metal and chlorine gas from recombining
d) In Down’s cell for the manufacture of Sodium metal, Calcium chloride salt is added to lower the melting point from 8000C to 6000C. Explain why it is necessary to lower the melting point (1mk)
To reduce the cost of energy used to melt the sodium metal
e) Calculate the mass of sodium metal produced if a current of 50 amperes is passed through the molten Sodium chloride for two (2) hours (Na = 23, F = 96500C) (2mks)f) Below is a list of potential differences obtained when metal P, Q, R, S and T are used in the following electrochemical cell
|
| Molten M | Conduct electric current and is not decomposed |
| Molten N | Conduct electric current and a gas is formed at one of the electrodes |
Suggest the type of bonding present in;
a) Substance M (1mk)
Metallic bond
b) Substance N (1mk)
Ionic bond
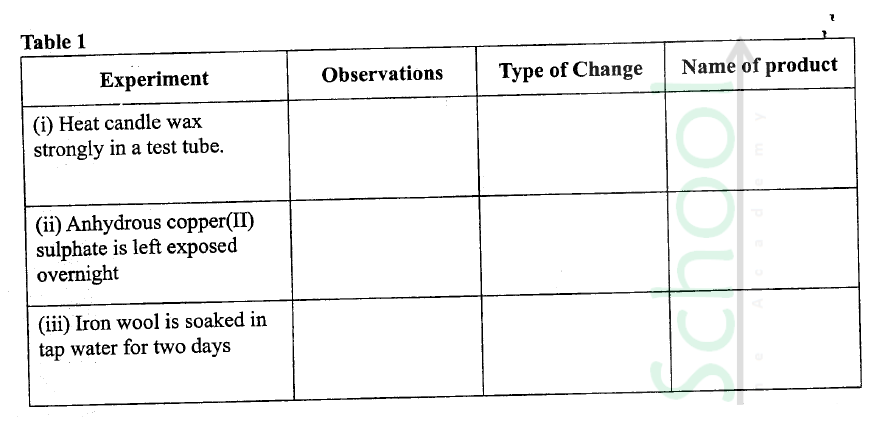
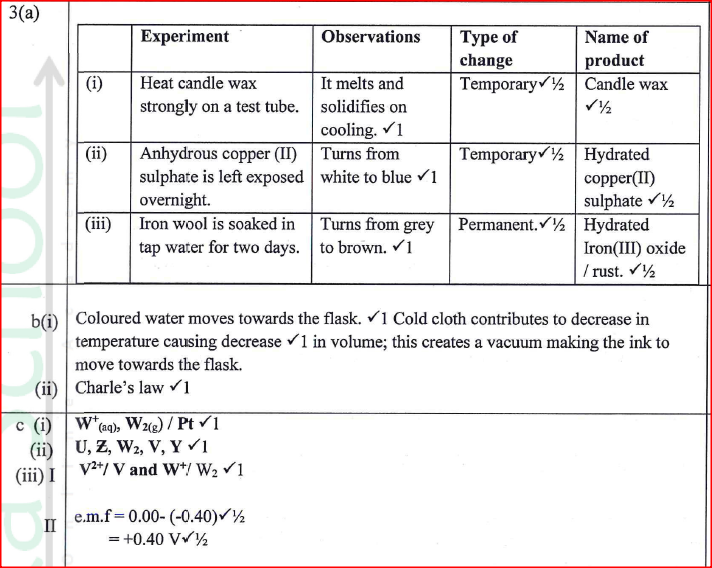
(a) Complete Table I by indicating the observations, type of permanent or temporary change and name of new compound formed.
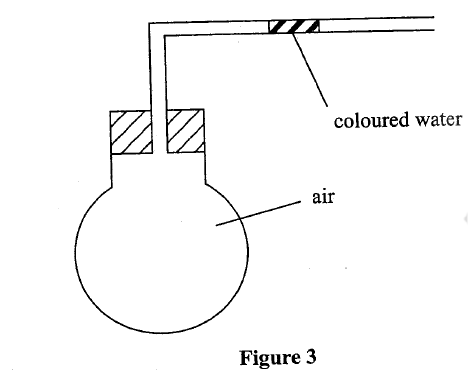
(b) Use the set-up in Figure 3 to answer the questions that follow. The flask was covered with a cloth that had been soaked in ice-cold water.
(i)State the observation made on the coloured water. Explain.
(ii) Name the gas law illustrated in Figure 3.
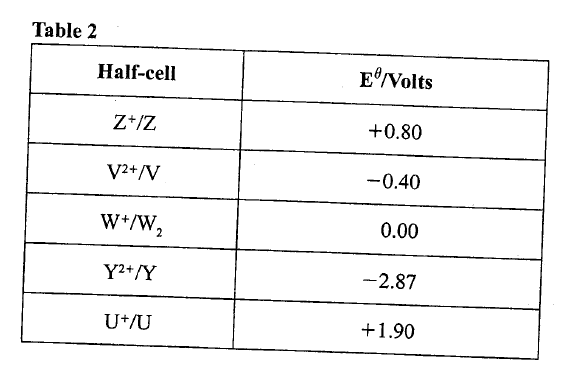
(c)Use the standard electrode potentials in Table 2 to answer the questions that follow.
(ii) Name the gas law illustrated in Figure 3.
(c)Use the standard electrode potentials in Table 2 to answer the questions that follow.
(i)Write the half-cell representation for the element whose electrode potential is for hydrogen.
(ii) Arrange the elements in order of reducing power, starting with the weakest reducing agent.
(iii) I Select two half cells which combine to give a cell with the least e.m.f.
II Calculate the e.m.f of the half cells identified in (iii) I.
(ii) Arrange the elements in order of reducing power, starting with the weakest reducing agent.
(iii) I Select two half cells which combine to give a cell with the least e.m.f.
II Calculate the e.m.f of the half cells identified in (iii) I.
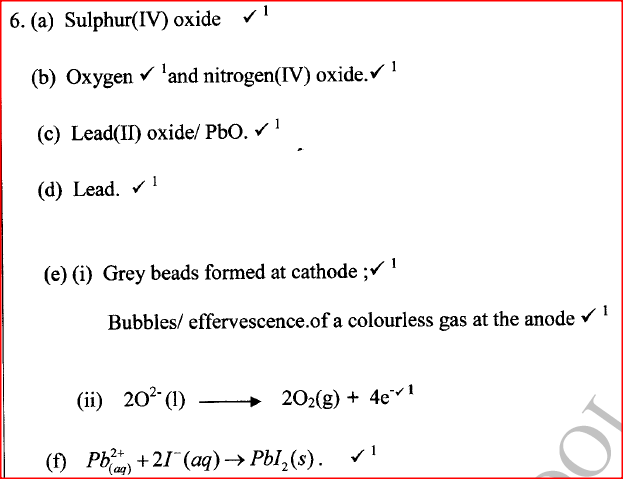
The following steps were used to analyse a metal ore.
(i) An ore of a metal was roasted in a stream of oxygen. A gas with a pungent smell was formed which turned acidified potassium dichromate(VI) green.
(ii) The residue left after roasting was dissolved in hot dilute nitric(V) acid. Crystals were obtained from the solution.
(iii) Some crystals were dried and heated. A brown acidic gas and a colourless gas were evolved and a yellow solid remained. (iv) The solid was yellow when cold.
(v) The yellow solid was heated with powered charcoal. Shiny beads were formed.
Name the:
(a) gas formed when the ore was roasted in air.
(b) gases evolved when crystals in step (iii) were heated.
(c) yellow solid formed in step (iii).
(d) shiny beads in step (iv).
(e) The yellow solid from procedure (iii) was separated, dried, melted and the melt electrolysed using graphite electrodes.
I. Describe the observations made at each electrode.
II. Write the equation for the reaction that took place at the anode.
(f) Some crystals formed in step (ii) were dissolved in water, and a portion of it reacted with potassium iodide solution. A yellow precipitate was formed. Write an ionic equation for this reaction.
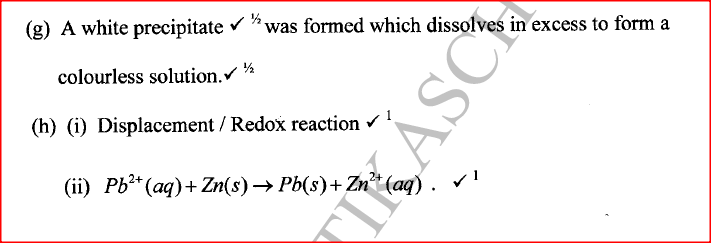
(g) To another portion of the solution from (f), sodium hydroxide solution was added drop by drop until there was no further change. Describe the observation made.
(h) To a further portion of the solution from (f), a piece of zinc foil was added.
I. Name the type of reaction taking place.
II. Write an ionic equation for the above reaction.
(i) An ore of a metal was roasted in a stream of oxygen. A gas with a pungent smell was formed which turned acidified potassium dichromate(VI) green.
(ii) The residue left after roasting was dissolved in hot dilute nitric(V) acid. Crystals were obtained from the solution.
(iii) Some crystals were dried and heated. A brown acidic gas and a colourless gas were evolved and a yellow solid remained. (iv) The solid was yellow when cold.
(v) The yellow solid was heated with powered charcoal. Shiny beads were formed.
Name the:
(a) gas formed when the ore was roasted in air.
(b) gases evolved when crystals in step (iii) were heated.
(c) yellow solid formed in step (iii).
(d) shiny beads in step (iv).
(e) The yellow solid from procedure (iii) was separated, dried, melted and the melt electrolysed using graphite electrodes.
I. Describe the observations made at each electrode.
II. Write the equation for the reaction that took place at the anode.
(f) Some crystals formed in step (ii) were dissolved in water, and a portion of it reacted with potassium iodide solution. A yellow precipitate was formed. Write an ionic equation for this reaction.
(g) To another portion of the solution from (f), sodium hydroxide solution was added drop by drop until there was no further change. Describe the observation made.
(h) To a further portion of the solution from (f), a piece of zinc foil was added.
I. Name the type of reaction taking place.
II. Write an ionic equation for the above reaction.
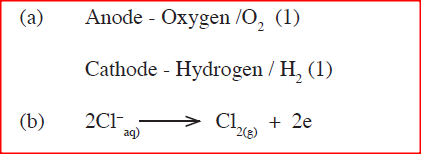
(a) What is an inert electrode?
(b) State the products formed when brine is electrolysed using inert electrodes.
Anode:
Cathode:
(b) State the products formed when brine is electrolysed using inert electrodes.
Anode:
Cathode:
ANSWERS
(a)Inert electrode is one which does not participate in the reaction / does not affect the products of electrolysis / does not react;
(b)Anode - chlorine;
Cathode - Hydrogen;
(b)Anode - chlorine;
Cathode - Hydrogen;
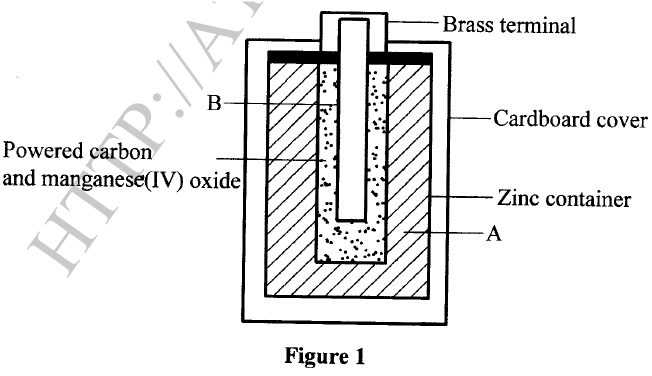
The diagram in Figure 1 shows a section of a dry cell. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Name the part labelled B.
(b) The part labelled A is a paste. Give a reason why it is not used in dry form.
(c) What is the purpose of the zinc container?
(b) The part labelled A is a paste. Give a reason why it is not used in dry form.
(c) What is the purpose of the zinc container?
ANSWERS
(a)Carbon electrode (Anode) /Graphite electrode.
(b)To allow movement of ions / to have it as an electrolyte. When dry, the ions are immobile.
(c)It is the cathode / negative electrode.
(b)To allow movement of ions / to have it as an electrolyte. When dry, the ions are immobile.
(c)It is the cathode / negative electrode.
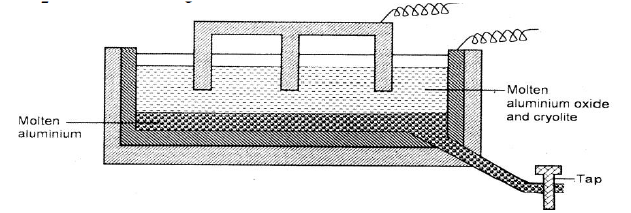
The diagram below represents a set up of an electrolytic cell that can be used in the production of aluminium.
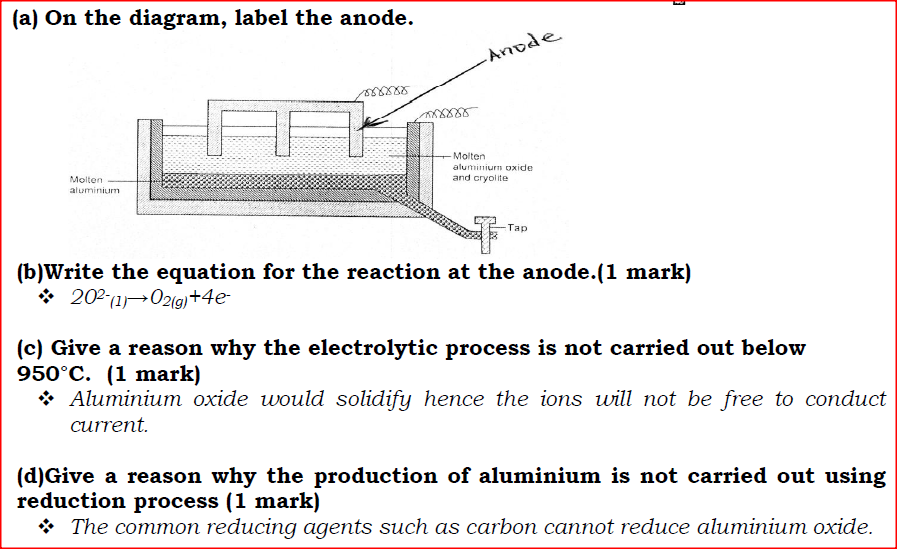
(a) On the diagram, label the anode.
(b)Write the equation for the reaction at the anode.
(c) Give a reason why the electrolytic process is not carried out below 950°C.
(d)Give a reason why the production of aluminium is not carried out using reduction process
(e)Give two reasons why only the aluminium ions are discharged
(f)State two properties of duralumin that makes it suitable for use in aircraft industry.
(g)Name two environmental effects caused by extraction of aluminium.
(b)Write the equation for the reaction at the anode.
(c) Give a reason why the electrolytic process is not carried out below 950°C.
(d)Give a reason why the production of aluminium is not carried out using reduction process
(e)Give two reasons why only the aluminium ions are discharged
(f)State two properties of duralumin that makes it suitable for use in aircraft industry.
(g)Name two environmental effects caused by extraction of aluminium.
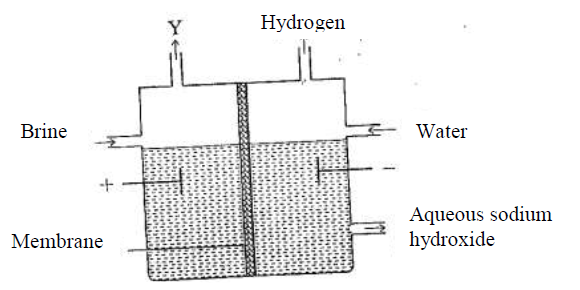
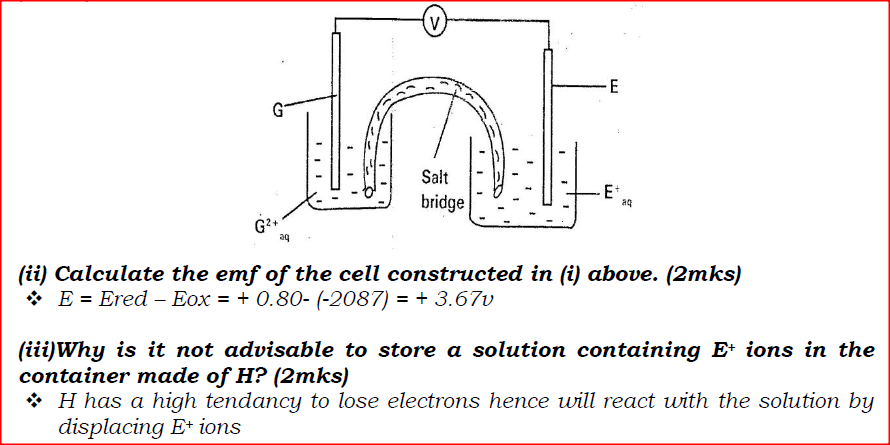
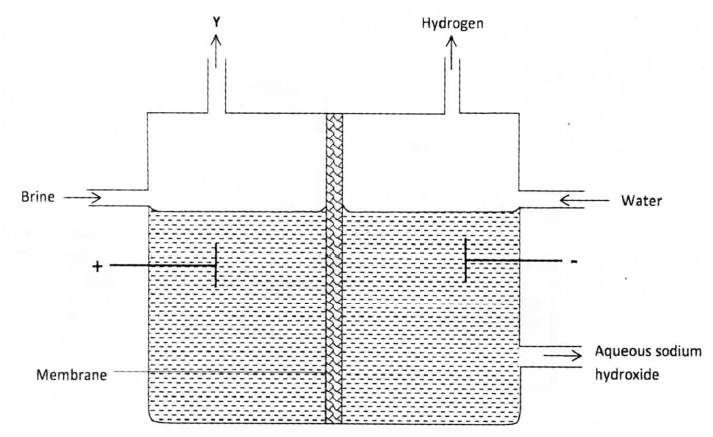
The set up below can be used to produce sodium hydroxide by electolysing brine.
(i) Identify gas Y.
(ii)Describe how aqueous sodium hydroxide is formed in setup above.
(iii)One of the uses of sodium hydroxide is in manufacture of soaps. State one other use of sodium hydroxide.
(b) Study the information given in the table below and answer the questions that follow.
(ii)Describe how aqueous sodium hydroxide is formed in setup above.
(iii)One of the uses of sodium hydroxide is in manufacture of soaps. State one other use of sodium hydroxide.
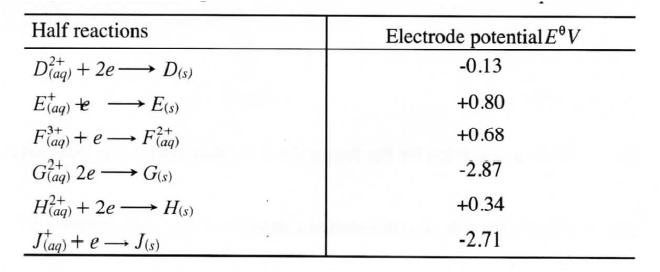
(b) Study the information given in the table below and answer the questions that follow.
(i) Construct an electrochemical cell that will produce the highest
(ii) Calculate the emf of the cell constructed in (i) above.
(iii)Why is it not advisable to store a solution containing E+ ions in the container made of H?
(ii) Calculate the emf of the cell constructed in (i) above.
(iii)Why is it not advisable to store a solution containing E+ ions in the container made of H?
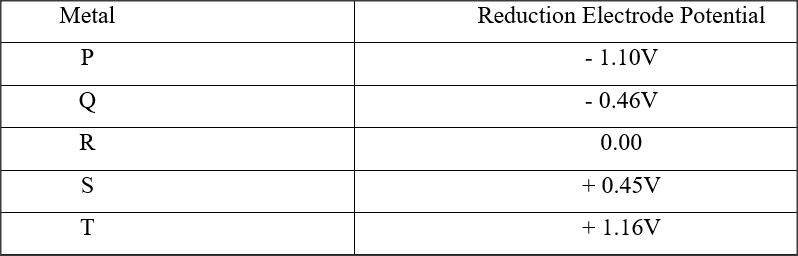
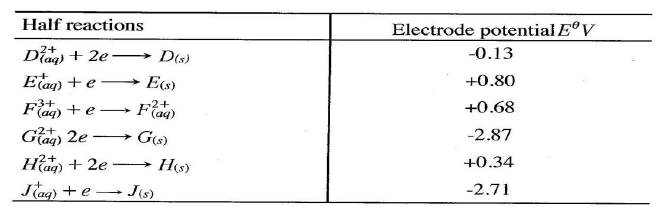
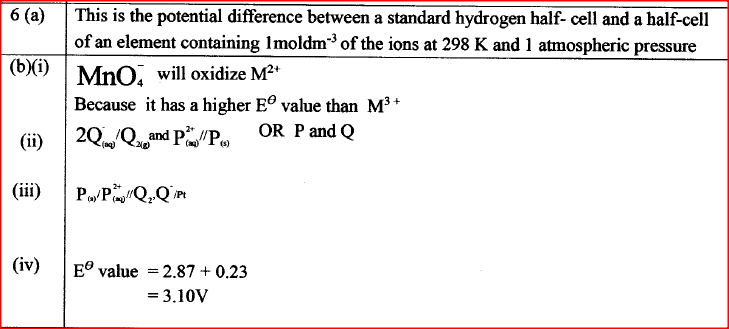
(a) What is meant by standard electrode potential of a an element? (1 mark)
(b) use the standard electrode potentials given below to answer the questions that follow.
(i) State whether acidified MnO4- can oxidise M2+. Give a reason. (2 marks)
(ii) Select two half-cells which when combined will give the highest e.m.f. (1 mark)
(iii) Write the cell representation for the cell formed in b (ii). (I mark)
(iv) Calculate the E0 value for the cell formed in b (iii). (2 marks)
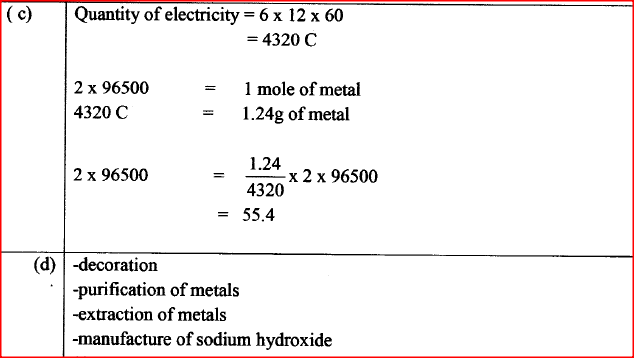
(c) A mass of 1.24g of a divalent metal was deposited when a current of 6A was passed through a solution of the metal sulphate for 12 minutes. Determine the relative atomic mass of the metal.
(1 Faraday = 96,500 C mol-1 (3 marks)
(d) State two applications of electrolysis. (I mark)
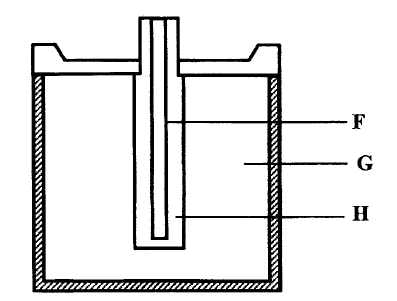
a) The diagram below represents a dry cell. Use it to answer the quest ions that follows.
i) Which of the letters represent
i) Carbon electrode?
ii) The electrolyte?
ii) One of the substances used in a dry cell is manganese (IV) oxide. State two roles of manganese (IV) oxide in the dry cells
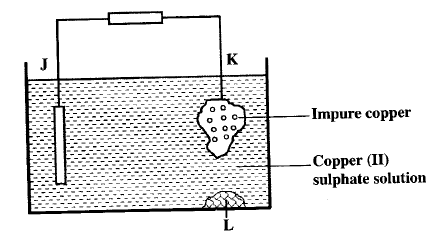
b) Below is simplified electrolytic cell used for purification of copper. Study it and answer the questions that follows.
i) Carbon electrode?
ii) The electrolyte?
ii) One of the substances used in a dry cell is manganese (IV) oxide. State two roles of manganese (IV) oxide in the dry cells
b) Below is simplified electrolytic cell used for purification of copper. Study it and answer the questions that follows.
i) Identify the cathode
ii) Write the equation for the reaction at the anode
iii) What name is given to L?
iv) A current of 0.6 A was passed Through the electrolyte for 2 hours.
Determine the amount of copper deposited (Cu=63.5; 1 Faraday = 96,500 coulombs)
v) St ate two uses of copper metal
ii) Write the equation for the reaction at the anode
iii) What name is given to L?
iv) A current of 0.6 A was passed Through the electrolyte for 2 hours.
Determine the amount of copper deposited (Cu=63.5; 1 Faraday = 96,500 coulombs)
v) St ate two uses of copper metal
ANSWERS
(a) (i) I F
II G
(ii) - Manganese (IV) oxide oxidises hydrogen to water /depolariser .
- It increases the surface area of the electrolyte
(b) (i) Cathode J.
II G
(ii) - Manganese (IV) oxide oxidises hydrogen to water /depolariser .
- It increases the surface area of the electrolyte
(b) (i) Cathode J.
(v)Uses of copper metal - soldering bits / wires
- Electrical cables and alloys - coins, ornaments/lightening arrestors/ diodes/
- calorimeters.
- Electrical cables and alloys - coins, ornaments/lightening arrestors/ diodes/
- calorimeters.
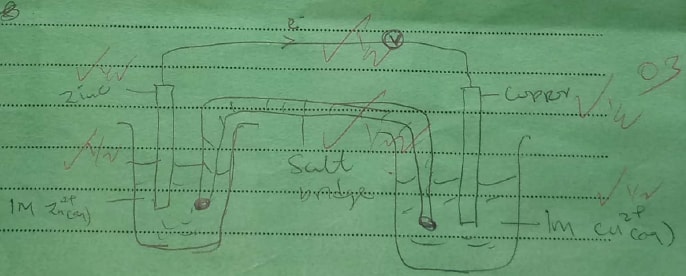
Given that the E° of Cu(s) /Cu2+(aq) is +0.34 V and that of Zn (s)/Zn2+(aq) is —0.76 V, draw a labelled diagram of zinc and copper electrochemical cell. (3 marks)
Study the standard electrode potentials in the table below and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Which of the metals is the strongest reducing agent?
(b) What observations will be made if a silver coin was dropped into an aqueous solution of copper (II) sulphate? Explain.
(b) What observations will be made if a silver coin was dropped into an aqueous solution of copper (II) sulphate? Explain.
ANSWERS
(a) Calcium
(b) No observable change silver is below copper in the reactivity series so it cannot displace it.
(b) No observable change silver is below copper in the reactivity series so it cannot displace it.
Dilute sulphuric (VI) acid was electrolysed using platinum electrodes.
Name the product formed at the anode and give a reason for your answer.
Name the product formed at the anode and give a reason for your answer.
(a) A student electrolyzed dilute sodium chloride solution using inert carbon electrodes. Name the products at:
i)Anode :
ii)Cathode:
(b) If the experiment was repeated using concentrated sodium chloride instead of dilute sodium chloride solution, write the half equation at the anode.
i)Anode :
ii)Cathode:
(b) If the experiment was repeated using concentrated sodium chloride instead of dilute sodium chloride solution, write the half equation at the anode.
a) Study the standard electrode potentials do the half – cells given below and
answer the questions that follow. (The letters do nor represent the actual symbols of the elements.)
answer the questions that follow. (The letters do nor represent the actual symbols of the elements.)
i) Identify the strongest oxidizing agent. Give a reason for your answer.
ii) Which two half – cells would produce the highest potential difference when
combined?
iii) Explain whether the reaction represented below can take place.
ii) Which two half – cells would produce the highest potential difference when
combined?
iii) Explain whether the reaction represented below can take place.
b) 100cm3 of 2M sulphuric acid was electrolysed using the set – up represented by the diagram below.
i) Write an equation for the reaction that produces gas L.
ii) Describe how gas K can be identified
iii) Explain the difference in :
I The volume of the gases produced at the electrodes.
II Brightness of the bulb if 100cm3 of 2M ethanoic acid was used in place of sulphuric acid.
ii) Describe how gas K can be identified
iii) Explain the difference in :
I The volume of the gases produced at the electrodes.
II Brightness of the bulb if 100cm3 of 2M ethanoic acid was used in place of sulphuric acid.
(a) the set below can be used to produce sodium hydroxide by electrolyzing brine
(i) Identify gas Y
(ii) Describe how aqueous sodium hydroxide is formed in the above set-up
(iii)One of the uses of sodium hydroxide is in the manufacturing of soaps state one other use of sodium hydroxide
(b).study the information given in the table below and answer the question that follows
(ii) Describe how aqueous sodium hydroxide is formed in the above set-up
(iii)One of the uses of sodium hydroxide is in the manufacturing of soaps state one other use of sodium hydroxide
(b).study the information given in the table below and answer the question that follows
(i) Construct an electrochemical cell that will produce the largest emf
(ii) Calculate the emf of the cell constructed in(i) above
(iii) Why is it not advisable to store a solution containing E+ ions in a container made of H?
(ii) Calculate the emf of the cell constructed in(i) above
(iii) Why is it not advisable to store a solution containing E+ ions in a container made of H?
ANSWERS
(a)(i)Gas Y is chlorine
(ii)
sodium and hydrogen ions migrate to the cathode .
The hydrogen ions are preferentially discharged, liberating hydrogen gas.
chlorine and hydroxide ions migrate to the anode .
The chloride ions are preferentially discharged liberating chlorine gas.
the sodium ions migrate to the cathode through the membrane .
the sodium ions combine with the hydroxide ions to form sodium hydroxide .
(iii) Glass making/paper manufacture (1), unclogging of drains, etching NaClo3,
Purification of bauxite.
(ii)
sodium and hydrogen ions migrate to the cathode .
The hydrogen ions are preferentially discharged, liberating hydrogen gas.
chlorine and hydroxide ions migrate to the anode .
The chloride ions are preferentially discharged liberating chlorine gas.
the sodium ions migrate to the cathode through the membrane .
the sodium ions combine with the hydroxide ions to form sodium hydroxide .
(iii) Glass making/paper manufacture (1), unclogging of drains, etching NaClo3,
Purification of bauxite.
An element P has a relative atomic mass of 88. When a current of 0.5 amperes was passed through the fused chloride of P for 32 minutes and 10 seconds, 0.44g of P were deposited at the cathode. Determine the charge on an ion of P. (1 faraday = 96500 Coulombs).
Expected Response
(a) A student electroplated a spoon with copper metal .Write an equation for the process that took place at the cathode.
(b) Calculate the time in minutes required to deposit 1.184g of copper if a current of 2 amperes was used. (1 Faraday = 96500 coulombs, Cu=63.5).
(b) Calculate the time in minutes required to deposit 1.184g of copper if a current of 2 amperes was used. (1 Faraday = 96500 coulombs, Cu=63.5).
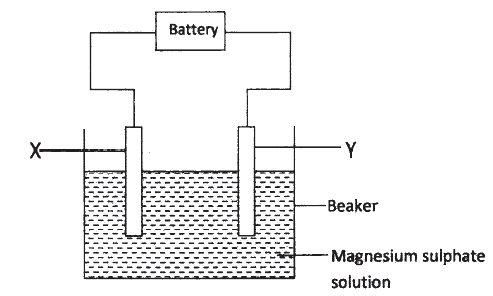
a) The set up below was used to investigate the products formed at electrodes during electrolysis of aqueous magnesium sulphate using inert electrodes. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
i) During the electrolysis, hydrogen gas was formed at electrode Y. identify the anode. Give a reason for your answer.
ii) Write the equation for the reaction with takes place at electrode X.
iii) Why is the concentration of magnesium sulphate expected to increase during electrolysis?
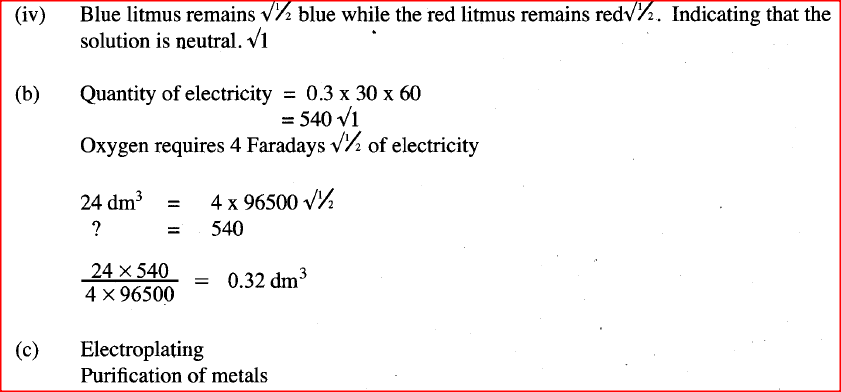
iv) What will be observed if red and blue litmus papers were dipped into the solution after electrolysis?
b) During electrolysis of magnesium sulphate, a current of 0.3A was passed for 30 minutes. Calculate the volume of gas produced at the anode.(Molar gas volume = 24dm3; 1 Faraday = 96,500C.).
c) State two applications of electrolysis.
ii) Write the equation for the reaction with takes place at electrode X.
iii) Why is the concentration of magnesium sulphate expected to increase during electrolysis?
iv) What will be observed if red and blue litmus papers were dipped into the solution after electrolysis?
b) During electrolysis of magnesium sulphate, a current of 0.3A was passed for 30 minutes. Calculate the volume of gas produced at the anode.(Molar gas volume = 24dm3; 1 Faraday = 96,500C.).
c) State two applications of electrolysis.
The apparatus shown in the diagram below were used to investigate the products formed when concentrated sodium chloride was electrolysed using inert electrodes.
(a) Write the equation for the reaction that takes place at electrode A.
(b) If the concentrated sodium chloride was replaced with dilute sodium chloride, what product would be formed at electrode A? Explain.
(b) If the concentrated sodium chloride was replaced with dilute sodium chloride, what product would be formed at electrode A? Explain.
Below is a representation of an electrochemical cell.
Calculate the E.M.F of the electrochemical cell.
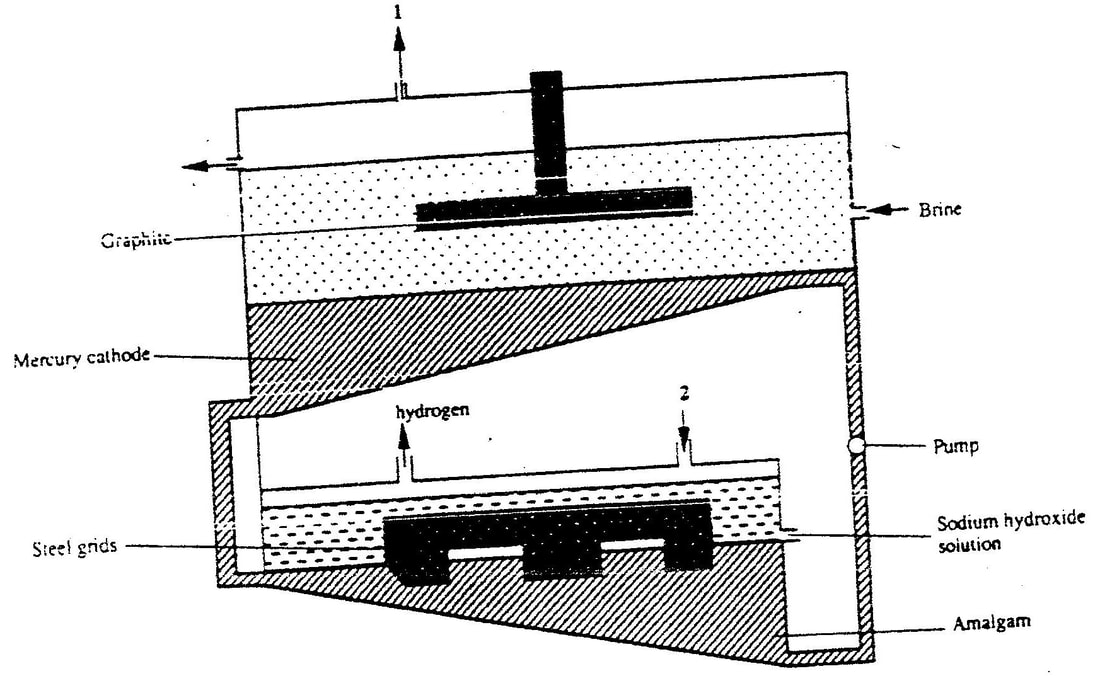
1 (a) The diagram below represents a mercury cell that can be used in the industrial manufacture of sodium hydroxide. Study it and answer the question that follow
- (i) Name
I. the raw material introduced at 2
II. Another substance that can be used in the cell instead of graphite - (ii) Identify the by – product that comes out at I
- (iii) Give
I. One use of sodium hydroxide
II. Two reasons why mercury is recycled
- (i) Write the equation for: The reaction that occurred at the mercury cathode
- (ii) Calculate the mass of sodium hydroxide that was produced
(Na = 23.0, O = 16.0, H = 1.0, 1 Faraday = 96500 Coulombs)
When a current of 1.5 amperes was passed though a cell containing m3+ ions of a metal M for 15 minutes, the mass of the cathode increased by 0.26g.
(1 Faraday = 96500 coulombs)
(a) Calculate the quantity of electricity used
(b) Determine the relative atomic mass of metal M
(1 Faraday = 96500 coulombs)
(a) Calculate the quantity of electricity used
(b) Determine the relative atomic mass of metal M
Chemistry Topics
All
Acetylene Gas
Acid Bases And Indicators
Acids Bases And Salts
Air And Combustion
Alkaline
Ammonia
Calcium Carbonate
Carbon And Its Compounds
Charles's Law
Chemical Families
Chemical Reactions
Chemistry Practical Assignments
Chlorine And Its Compounds
Cleansing Agent
DashBoard
Definition Of Chemistry Terms
Differences In Chemistry
Diffusion
Down's Cell
Electric Current On Substance
Electrochemistry I And II
Empirical Formula
Energy Changes In Chemical And Physical Processes
Ethanol
Ethene Gas
Form 1 Level
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
Gas Laws
General Chemistry
Haber Process
Hard Water
Hydrochloric Acid
Introduction To Chemistry
Kcse-1995
Kcse-1996
Kcse-1997
Kcse-1998
Kcse 1999
Kcse-2000
Kcse-2001
Kcse-2002
Kcse-2003
Kcse-2004
Kcse2005
Kcse-2005
Kcse-2006
Kcse2007
Kcse-2007
Kcse-2008
Kcse-2009
Kcse-2010
Kcse-2011
Kcse-2012
Kcse-2013
Kcse-2014
KCSE 2015
KCSE 2016
KCSE 2017
KCSE 2018
Kcse 2019
Metals
Molecular Formula
Nitrogen And Its Compounds
Notes And Tutorials
Nuclear Reactions
Organic Chemistry I
Organic Chemistry II
Oxidation
Oxygen
Paper 1
Paper 2
Paraffin
Periodic Table
Phenolphthalein Indicator
Phosphorous
Potassium
Propane
Properties-and-trends-across-the-period
Radioactivity
Reaction Rates And Reversible Reactions
Salts
Simple Classification Of Substances
Sodium
Structure Of The Atom And The Periodic Table
Structures And Bonding
Sulphur And Its Compounds
Sulphuric Acid
The Mole
Water And Hydrogen
Zinc
Archives
December 2024
January 2024
December 2023
November 2023
October 2021
November 2020
October 2020
September 2020
July 2020
May 2020
August 2019
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |
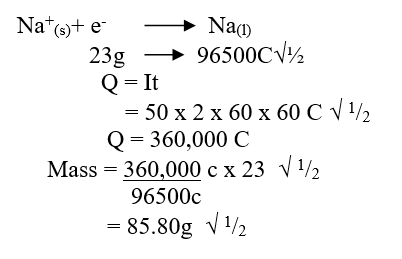
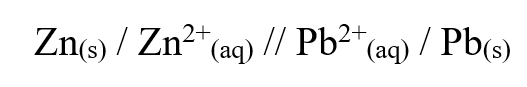


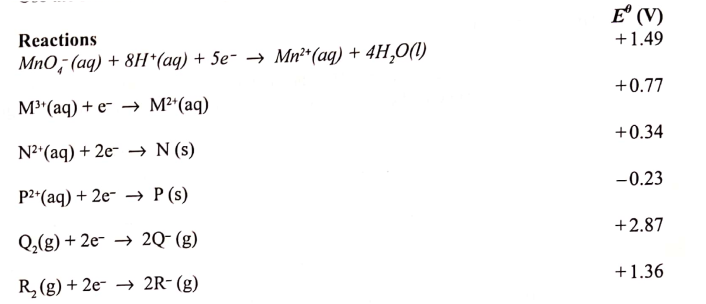

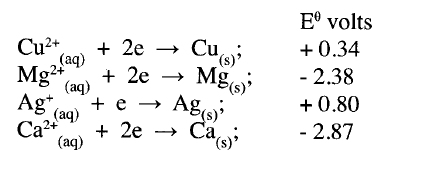














 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

